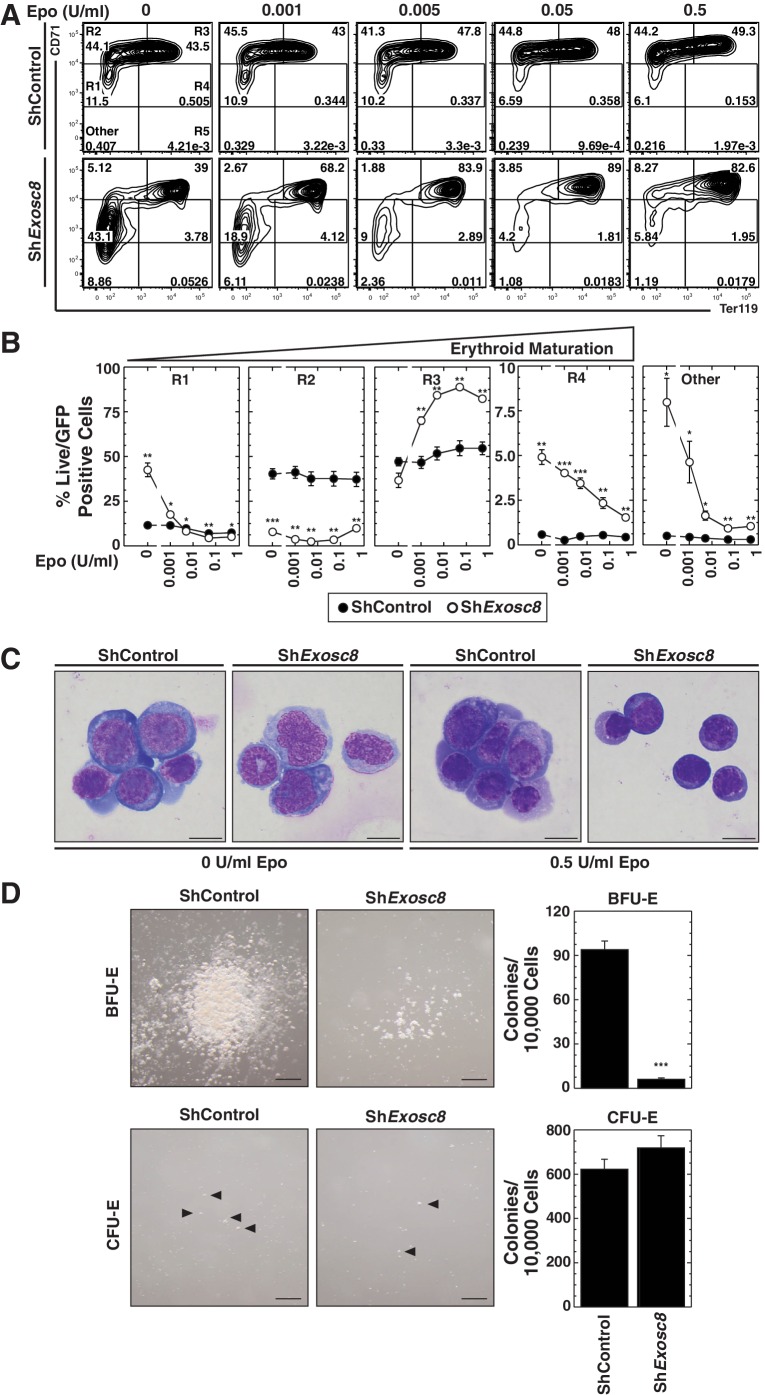
Figure 3. Erythropoietin is required for erythroid differentiation induced by disrupting the exosome complex.
(A) Flow cytometric quantification of erythroid markers CD71 and Ter119 in live control and Exosc8-knockdown erythroid precursor cells cultured for 48 hr in Epo-limiting media. Representative plots with R1-R5 gates denoted. (B) Quantitation of the percentage of live cells in control and Exosc8-knockdown conditions from the R1-R4 and non erythroid gates (mean ± SE, 4 biological replicates). (C) Representative images of Wright-Giemsa-stained, DRAQ7-negative erythroid precursor cells, infected with control or ShExosc8 retrovirus. Cells were cultured with or without Epo for 48 hr (Scale bar, 10 μm). (D) Representative images (left) and quantitation (right) of erythroid colony forming unit activity with FACS-sorted R1 cells 24 hr after Exosc8 knockdown (mean ± SE, 6 biological replicates) (Scale bar 200 μm). Statistical analysis of control and treatment conditions was conducted with the Student’s T-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Source data is available in Figure 3—source data 1.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17877.008