Abstract
Regenerative medicine and bone tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) hold great promise as an effective approach to bone and skeletal reconstruction. While adipose tissue harbors MSC-like progenitors, or multipotent adipose-derived cells (MADs), it is important to identify and characterize potential biological factors that can effectively induce osteogenic differentiation of MADs. To overcome the time-consuming and technically challenging process of isolating and culturing primary MADs, here we establish and characterize the reversibly immortalized mouse multipotent adipose-derived cells (iMADs). The isolated mouse primary inguinal MAD cells are reversibly immortalized via the retrovirus-mediated expression of SV40 T antigen flanked with FRT sites. The iMADs are shown to express most common MSC markers. FLP-mediated removal of SV40 T antigen effectively reduces the proliferative activity and cell survival of iMADs, indicating the immortalization is reversible. Using the highly osteogenic BMP9, we find that the iMADs are highly responsive to BMP9 stimulation, express multiple lineage regulators, and undergo osteogenic differentiation in vitro upon BMP9 stimulation. Furthermore, we demonstrate that BMP9-stimulated iMADs form robust ectopic bone with a thermoresponsive biodegradable scaffold material. Collectively, our results demonstrate that the reversibly immortalized iMADs exhibit the characteristics of multipotent MSCs and are highly responsive to BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation. Thus, the iMADs should provide a valuable resource for the study of MAD biology, which would ultimately enable us to develop novel and efficacious strategies for MAD-based bone tissue engineering.
Keywords: BMP9, adipose-derived stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells, bone formation, tissue engineering, immortalized progenitor cells
Introduction
Bone tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) holds great promise as an effective approach to bone and skeletal reconstruction [1-8]. MSCs are multipotent progenitors that can undergo self-renewal and differentiate into multiple lineages, such as osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic lineages [1,2,9-13]. MSCs have been isolated from numerous tissues, and one of the major sources in adults is the bone marrow stromal cells [5,10-12]. Osteogenic differentiation from MSCs recapitulates most of the molecular events occurring during skeletal development [14,15].
While many signaling pathways, such as Wnt, IGFs, FGFs, and Notch, play important roles in regulating osteogenic differentiation [9,16-24]. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are considered as a group of the most potent osteoinductive factors [9,25-27]. We have demonstrated that BMP9 (also known as growth differentiation factor 2, or GDF2) is one of the most potent BMPs among the 14 types of BMPs in inducing osteogenic differentiation [4,5,28,29], which may be attributable, at least in part, to the fact that BMP9 is more resistant to noggin inhibition [30]. Mechanistically, BMP9 has been shown to effectively induce osteoblast differentiation by regulating several important downstream targets [31,35], as well as through cross-talk with other important signaling pathways [36,41]. Thus, it is conceivable that using BMP9-expressing progenitor cells may be able to promote bone regeneration in large bony defects and/or fracture nonunion in clinical settings [3-5].
Once thought to merely function as a protective cushion for the internal organs, nerves and vessels, adipose tissue has more recently emerged as a premiere source of cells for evolving tissue engineering and regenerative therapies over the past few decades [42,47]. Adipose tissue is a complex, dynamic, and bioactive organ, which is involved in a diverse array of physiologic and disease processes [42,44-47]. Adipose tissue comprises various discrete depots, such as inguinal, interscapular, perigonadal, retroperitoneal and mesenteric depots [43,44]. Adipose tissue forms in utero, in the peripartum period and throughout life [42-44]. In adult humans, new adipocytes are generated continually and at substantial rates [44].
Since the early 2000’s, it has been reported that adipose tissue may harbor progenitor cells, so-called adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSCs), that have osteogenic potential [46,48-50]. In order to effectively utilize adipose tissue progenitors as a staple source of cells for bone tissue engineering, it is important to identify and characterize possible biological factors that can effectively induce osteogenic differentiation of AD-MSCs. While adipose tissue is abundant and easy to harvest, AD-MSCs only account for a small fraction of the total cell populations in adipose tissue. Thus, isolation and culture of AD-MSC cells remain a time-consuming process. In this study, we established reversibly immortalized mouse multipotent adipose-derived mesenchymal cells (iMADs) that were shown to exhibit the characteristics of multipotent MSCs and to be highly responsive to BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation. Therefore, the established iMADs should serve as a valuable resource to study AD-MSC biology, as well as to develop novel and efficacious strategies to utilize AD-MSCs for bone tissue engineering.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and chemicals
HEK-293 (from ATCC, Manassas, VA) and its derivative line 293pTP cells were maintained in the completed Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), as described [51,55]. Unless indicated otherwise, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) or Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA).
Synthesis of PPCN (polyethylene glycol citrate-co-N-isopropylacrylamide)
The polymer PPCN (polyethylene glycol citrate-co-N-isopropylacrylamide) was synthesized by sequential polycondensation and radical polymerization of citric acid, glycerol 1,3-diglycerolate diacrylate, poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG), and poly-N-isopropylacrylamide as described [56]. The chemical, biodegradable and thermoresponsive features were evaluated for each newly synthesized batch as reported [56]. Prior to mixing with cells, PPCN powder was dissolved in PBS (100 mg/ml stock solution), sterilized by syringe filtration using 0.22 µm filters, and kept at either room temperature or 4°C.
Generation and amplification of recombinant adenoviruses expressing BMP9, FLP recombinase, and GFP
Recombinant adenoviruses were generated using the AdEasy technology as described [57-59]. The coding regions of human BMP9 and flippase (FLP) recombinase were PCR amplified and cloned into an adenoviral shuttle vector, and subsequently used to generate recombinant adenoviruses in HEK-293 or 293pTP cells [51]. The resulting adenoviruses were designated as Ad-BMP9 and Ad-FLP, both of which also express GFP as the marker for monitoring infection efficiency [40,41,60,61]. Analogous adenovirus expressing only GFP (Ad-GFP) was used as a vector control [36,52,62].
Isolation and immortalization of multipotent adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MADs)
All animal studies were conducted by following the NIH guidelines approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Experimentally, skeletally mature CD1 mice (male, 4-week old, provided by The University of Chicago Transgenic Core Facility) were euthanized immediately prior to tissue harvest as described [37,63-66]. The adipose tissues were carefully dissected out from the inguinal region, rinsed in sterile PBS, and kept in sterile 100 mm cell culture dishes. The retrieved tissues were minced into small tissue bits, followed by 0.1% collagenase I digestion at 37°C for 20 min to 60 min. The dissociated mouse adipose-derived (MAD) mesenchymal stem cells were washed in complete DMEM and plated into 25 cm2 flasks at 37°C.
To establish the immortalized mouse multipotent adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMADs), early passages of primary MAD cells (< 3 passages) were seeded in 25 cm2 flasks and infected with retroviral vector SSR41, which expresses SV40 T antigen flanked with the FRT sites [67]. Stably immortalized MADs (or iMADs) were obtained by selecting the infected cells with hygromycin B (at 4 mg/mL) for one week as previously described [63-65,68-70].
Crystal violet assay
Subconfluent cells were seeded in 35 mm cell culture dishes and infected with the Ad-FLP or Ad-GFP adenovirus. At the indicated time points, the infected cells were subjected to crystal violet staining. The staining results were recorded under a bright field microscope. For quantitative measurement, the stained cells were dissolved in 10% acetic acid at room temperature for 20 min with agitation. Absorbance was measured at 570~590 nm as previously described [39,55,71-73].
WST-1 cell proliferation assay
The WST-1 assay was carried out as previously described [53,74-76]. Exponentially growing cells were plated into 96-well culture plates at 20% confluence. Unseeded wells were used as background controls. At the indicated time points, the premixed WST-1 (BD Clontech, Mountain View, CA) was added to each well and incubated at the 37°C CO2 incubator for 2 h. The plates were subjected to a microtiter plate reader to obtain absorbance reading at 450 nm. The obtained A450nm values were subjected to background reading subtractions. Each assay condition was done in triplicate.
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis
Subconfluent cells were harvested, fixed and stained with Hoechst 33342. Cell cycles were analyzed using the BD LSR II Flow Cytometer and the FlowJo software as previously described [52,53]. Each assay condition was done in triplicate.
RNA isolation and TqPCR analysis
Total RNA was isolated using TRIZOL Reagents (Invitrogen) and subjected to reverse transcription reaction with hexamer and M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA). The cDNA products were diluted 10 to 50-fold and used as PCR templates. The PCR primers (usually 18-20 mers, product size ranged 120 bp to 200 bp; Supplemental Table 1) were designed by using the online program Primer3Plus [77]. The TqPCR analysis was carried out as described [78]. TqPCR reactions were carried out using the following conditions, 95°C × 3″ for one cycle; 95°C × 20″, 66°C × 10″, for 4 cycles by decreasing 3°C per cycle; 95°C × 20″, 55°C × 10″, 70°C × 1″, followed by plate read, for 40 cycles. Gapdh was used as a reference gene. All reactions were done in triplicate.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity assay
ALP activity was assessed quantitatively with a modified assay using the Great Escape SEAP Chemiluminescence assay kit (BD Clontech) and qualitatively with histochemical staining assay (using a mixture of 0.1 mg/ml napthol AS-MX phosphate and 0.6 mg/ml Fast Blue BB salt) as described [30,32,79-82]. Each assay condition was performed in triplicate.
Matrix mineralization assay (Alizarin Red S staining)
Cells were seeded in 24-well culture plates, infected with AdBMP9 or AdGFP, and maintained in the presence of ascorbic acid (50 mg/mL) and β-glycerophosphate (10 mM) [28]. At 10 days post infection, mineralized matrix nodules were stained for calcium precipitation using Alizarin Red S staining as described [28,34,39,83]. Briefly, cells were fixed with 0.05% (v/v) glutaraldehyde at room temperature for 10 min and washed with distilled water, fixed cells were incubated with 0.4% Alizarin Red S for 5 min, followed by being extensively washed with distilled water. The staining of calcium mineral deposits was recorded under a bright field microscope. Each assay condition was done in triplicate.
Oil Red O staining assay
The iMADs were seeded in 12-well cell culture plates and infected with AdBMP9 or AdGFP for 10 days. Oil Red O staining was performed as described [30,40,79]. Briefly, cells were fixed with 10% formalin at room temperature for 10 min, and washed with PBS. The fixed cells were stained with freshly prepared Oil Red O solution (six parts saturated Oil Red O dye in isopropanol plus four parts water) at 37°C for 30-60 min, followed by washing with 70% ethanol and distilled water. The staining of lipid droplets was recorded under a bright field microscope. Each assay condition was done in triplicate.
Immunofluorescence staining
Immunofluorescence staining was performed as described [53,63,84-86]. Briefly, cells were fixed with methanol or 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 1% NP-40, and blocked with 10% donkey serum (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA), followed by an incubation with CD29, CD73, CD113, CD40, CD90, CD117/c-kit, CD166/ALCAM, CD105/endoglin, or BMPR-II antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 1 h at room temperature. After being washed, cells were incubated with FITC labeled secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories) for 30 min. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Stains were examined under a fluorescence microscope. Stains without primary antibodies were used as negative controls.
Subcutaneous implantation of BMP9-stimulated iMADs for ectopic bone formation
All animal studies were conducted by following the guidelines approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Stem cell-based ectopic bone formation was performed as previously described [29,37,63,87]. Briefly, iMADs were infected with AdBMP9 or AdGFP for 24 h, collected, and resuspended in 80 µl of PBS, or 80 µl of the thermoresponsive PPCN scaffold (100 mg/ml) [56], mixed with 0.2% gelatin (1:1=v:v) for subcutaneous injection (5 × 106/injection, n=5) into the flanks of athymic nude (nu/nu) mice (male, 4-6 wk old; Harlan Research Laboratories/ENVIGO, Indianapolis, IN). At 4 weeks after implantation, animals were sacrificed, and the implantation sites were retrieved for microcomputed tomography (µCT) imaging, histologic evaluation, and special stains (see below).
micro-CT analysis
All retrieved specimens were fixed and imaged using the µCT component of the GE triumph (GE Healthcare) trimodality preclinical imaging system. All image data analyses were performed using Amira 5.3 (Visage Imaging, Inc.), and 3D volumetric data were determined as described [37,63,64,83].
H&E staining and trichrome staining
Retrieved tissues were fixed, decalcified in 10% buffered formalin, and embedded in paraffin. Serial sections of the embedded specimens were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Trichrome stains were carried out as previously described [29,41,88].
Statistical analysis
All quantitative assays were performed in triplicate and/or carried out in three independent batches. Statistical analysis was carried out using Microsoft Excel program. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical significances were determined by one-way analysis of variance and the student’s t test. A value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Primary mouse adipose-derived (MAD) mesenchymal stem cells can be effectively immortalized by SV40 T antigen
Although there have been numerous reports about the use of adipose-derived MSCs (AD-MSCs), the biological features of these progenitor cells remain to be fully understood [42,44]. Though readily available, it is rather technically challenging and time-consuming to isolate and culture primary AD-MSCs, which may in turn hamper effective in-depth investigations into biological characteristics of AD-MSCs. Here, we sought to establish reversibly immortalized mouse adipose-derived (iMAD) mesenchymal stem cells and to characterize their responsiveness to osteogenic differentiation signals.
We first isolated primary MAD cells from the adipose tissue retrieved from the inguinal region of young CD1 mice (Figure 1Aa, 1Ab). Once reaching subconfluence, the primary MAD cells were replated and infected with retroviral vector SSR#41, which co-expresses SV40 T antigen and hygromycin flanked with FRT sites (Figure 1Ba) [64,65,67-70,84]. The infected MAD cells were subjected to hygromycin selection. The surviving cells formed colonies at as early as at 3 days after selection (Figure 1Bb) and the colonies became more apparent at 10 days after selection (Figure 1Bc). When passaged, the surviving cells grew robustly under conventional culture conditions at passage 2 and passage 20 (Figure 1Bd & 1Be). Thus, these results indicate that the obtained cells are stably immortalized and can maintain long-term proliferation, so have been designated as immortalized MADs or iMADs.
Figure 1.
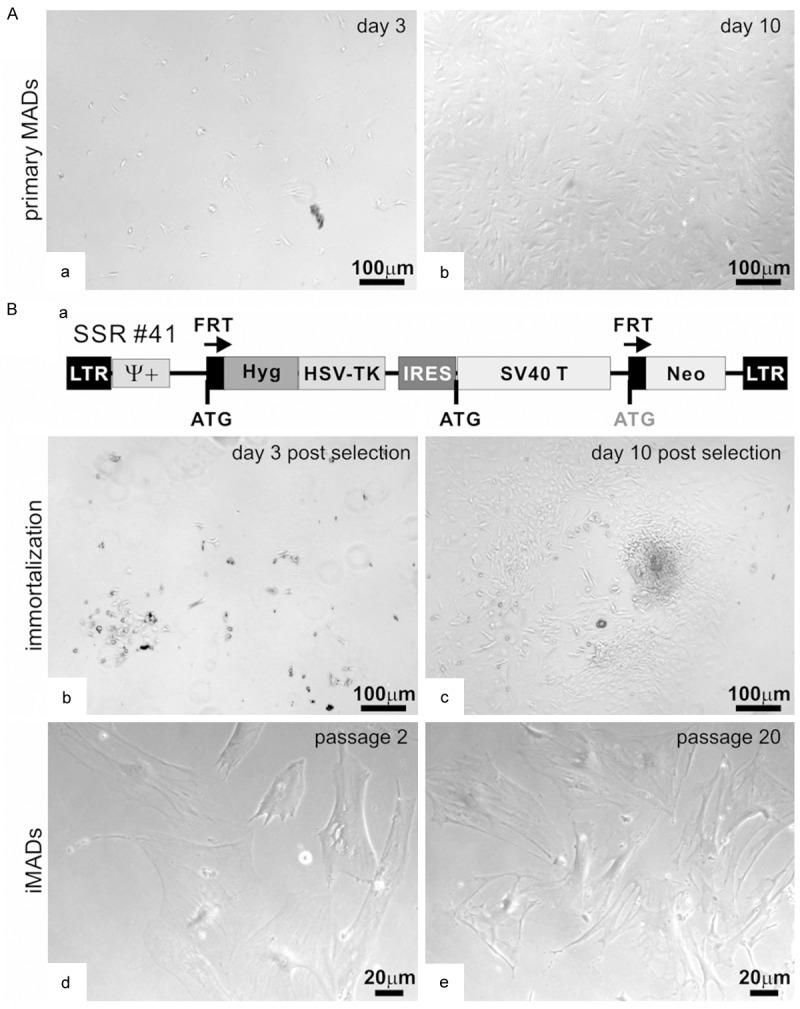
Isolation and immortalization of mouse adipose-derived (MAD) mesenchymal stem cells. (A) Primary MADs were isolated from the inguinal adipose tissue of 4-week old CD1 mice, and maintained in complete DMEM medium. Cell morphology was recorded at day 3 (a) and day 10 (b) after plating. (B) The primary MADs (under passage 3) were infected with retroviral immortalization vector SSR #41 (a). The infected cells were selected in hygromycin-containing medium. Surviving clonal growth was observed at 3 days (b) and 10 days (c) after selection. The immortalized iMAD cells were stable and retained long-term proliferation at passage 2 (d) or passage 20 (e). Representative images are shown.
The iMAD cells express most common mesenchymal stem cell markers
We next tested whether the iMADs express common mesenchymal stem cell markers [63,64,89]. Using immunofluorescence staining we found that vast majority of the iMAD cells exhibited positive staining with antibodies against CD29/integrin β1, CD31/PECAM1, CD73, CD99/Thy-1, CD105/Endoglin, CD117/c-Kit, CD133/Prom1, or BMPRII (Figure 2A-H). These results demonstrate that the iMADs express most of the consensus markers defining multipotent mesenchymal stem cells [89].
Figure 2.
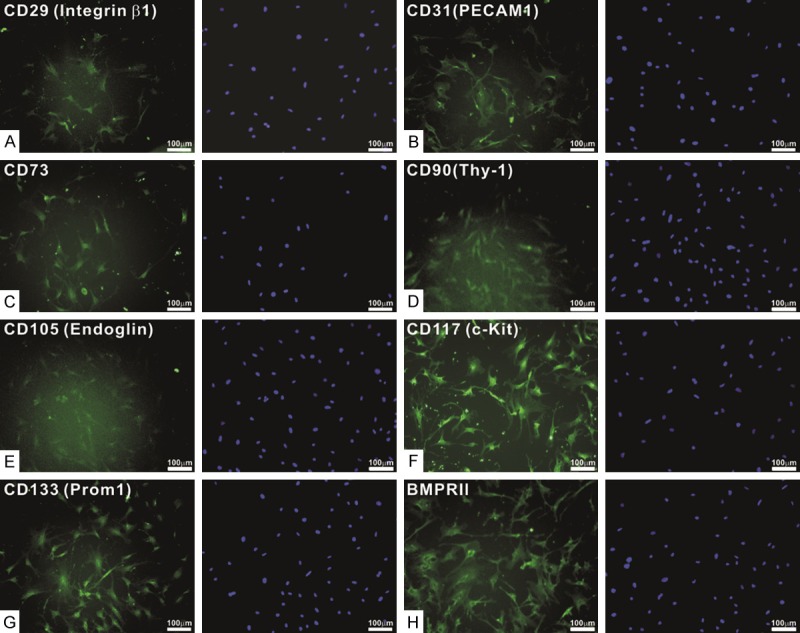
The iMADs express most mesenchymal stem cell markers. Subconfluent iMADs were fixed and stained with antibodies against CD29/integrin β1 (A), CD31/PECAM1 (B), CD73 (C), CD99/Thy-1 (D), CD105/Endoglin (E), CD117/c-Kit (F), CD133/Prom1 (G), or BMPRII (H). All antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Minus primary antibodies and isotype IgG were used as negative controls (data not shown). Cell nuclei were counter-stained with DAPI. Representative images are shown.
The FLP-mediated removal of SV40 T antigen effectively reduces proliferative activity and survival of iMAD cells
We next conducted a series of experiments to test whether the SV40 T antigen-mediated immortalization can be effectively reversed in iMADs. When the iMADs were infected with Ad-FLP, which expresses a high level of FLP recombinase [54,63], the cell proliferation of the infected iMADs was lower than that of the control Ad-GFP infected cells (Figure 3Aa). The decrease in cell growth was significantly lower at day 5 and day 7 in the Ad-FLP infected iMADs than that of the control cells (Figure 3Ab). Quantitatively, there was approximately 72% reduction of SV40 T antigen expression in the Ad-FLP-infected cells, compared with that of the Ad-GFP infected cells (Figure 3B), indicating that FLP recombinase can effectively remove most of SV40 T antigen from the immortalized cells although the FLP-mediated excision is not 100% efficient, consistent with previous reports [90,92].
Figure 3.
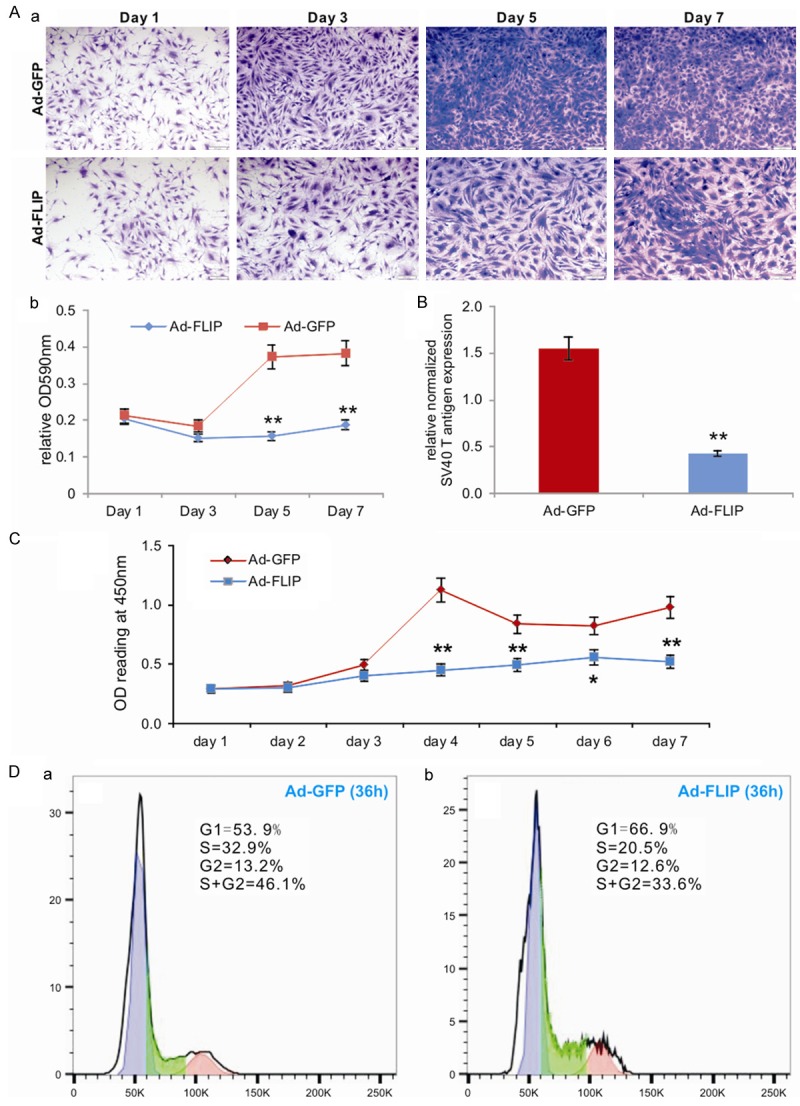
The immortalization phenotype of the iMADs can be reversed by FLP recombinase. (A) Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-FLP or Ad-GFP and fixed for Crystal violet staining at different time points (a). The stained cells were dissolved and quantitatively determined at A590nm (b). “**”, p<0.01 when compared between Ad-FLP and Ad-GFP infected groups. (B) Quantitative analysis of the FLP-mediated removal of SV40 T antigen in the iMADs. Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-FLP or Ad-GFP. At 3 days after infection, total RNA was isolated and subjected to RT-PCR and subsequently TqPCR analysis of SV40 T antigen expression. Gapdh was used as a reference gene. “**”, p<0.01 when compared between Ad-FLP and Ad-GFP infected groups. (C) WST-1 proliferation assay. Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-FLP or Ad-GFP. WST-1 substrate was added to the cell culture and assessed for A450nm readings at the indicated time points. Assays were done in triplicate. “**”, p<0.01. (D) Cell cycle analysis. Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-GFP (a) or Ad-FLP (b). At 36 h after infection, cells were collected, fixed, stained with Hoechst 33342, and subjected to FACS analysis. Assays were done in triplicate, and representative results are shown.
We carried out additional quantitative analyses on effect of FLP-mediated T antigen removal on the cell proliferation of the iMADs. The sensitive WST-1 assay indicates that Ad-FLP infected iMADs consistently grew more slowly, at as early as day 2 after infection, than of the control Ad-GFP infected cells (Figure 3C). Cell cycle analysis further revealed that Ad-FLP infected iMAD cells exhibited significantly increased G1 phase, decreased S phase and S/G2 phases, compared with that of the Ad-GFP infected cells (Figure 3Da vs. 3Db). Collectively, these results strongly indicate that the SV40 T antigen-mediated immortalization phenotype can be effectively reversed by FLP recombinase even though the SV40 T antigen may not be removed completely.
The iMADs are responsive to BMP9 stimulation, express multiple lineage regulators, and undergo osteogenic differentiation upon BMP9 stimulation
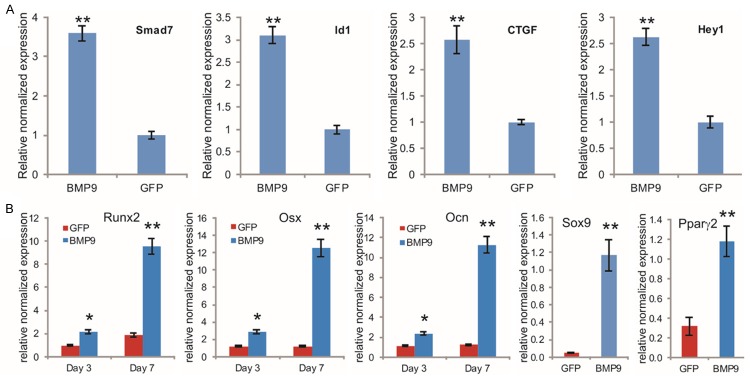
We previously demonstrated that BMP9 is one of the most osteogenic BMPs among the 14 types of human BMPs [4,5,26-29], and identified a panel of important downstream mediators of BMP9 signaling in mesenchymal stem cells [5,31-35,93]. We examined whether the iMADs were responsive to BMP9 stimulation. When the iMADs were transduced with Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP for 36 h, qPCR analysis revealed that several well-characterized immediate-early genes, such as Smad7, Id1, CTGF and Hey1 [5,31-34], were significantly upregulated in BMP9-transduced iMADs, compared with that of the control group (p<0.001) (Figure 4A), indicating that the iMADs are responsive to BMP9 stimulation.
Figure 4.
BMP9 induces the expression of early downstream genes and multiple lineage regulators in iMADs. A. Upregulation of early target genes in iMADs by BMP9. Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP. Total RNA was isolated at 36 h and subjected to TqPCR analysis using gene-specific primers for mouse Smad7, Id1, Ctgf and Hey1. B. BMP9 induces the expression of multiple lineage regulators/markers. Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP. Total RNA was isolated at the indicated time points and subjected to TqPCR analysis using gene-specific primers for Runx2, Osx, Ocn, Sox9 (day 7), or Pparγ2 (day 7). Gapdh was used as a reference gene. Reactions were done in triplicate. “*”, p<0.05, “**”, p<0.01.
We previously demonstrated that BMP9 can induce osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic lineage-specific differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells [5,79,94]. When the iMAD cells were stimulated with BMP9, osteogenic lineage regulators Runx2 and Osterix (Osx), as well as the late osteogenic marker osteocalcin (Ocn), were up-regulated at as early as day 3, and significantly increased at day 7 (Figure 4B). Similarly, the chondrogenic regulator Sox9 and the adipogenic regulator Pparγ2 were also significantly up-regulated in the iMADs by BMP9 at day 7 (Figure 4B).
We further analyzed the in vitro osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation capabilities of the iMADs. When iMAD cells were infected with Ad-BMP9, the activity of early osteogenic marker alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was readily detectable at day 5, while some basal ALP activity was also observed (Figure 5Aa). Quantitative ALP assay indicates that the ALP activity was significantly up-regulated in BMP9-treated iMADs at as early as day 3 (p<0.001) and the overall ALP activity kept increasing up to day 7 (Figure 5Ab). Furthermore, when the BMP9-treated iMADs were cultured in mineralization medium for 10 days, significant amounts of mineralized extracellular matrix nodules were observed as demonstrated by Alizarin Red S staining (Figure 5B). These results strongly suggest that the iMADs may have osteogenic potential upon BMP9 stimulation.
Figure 5.
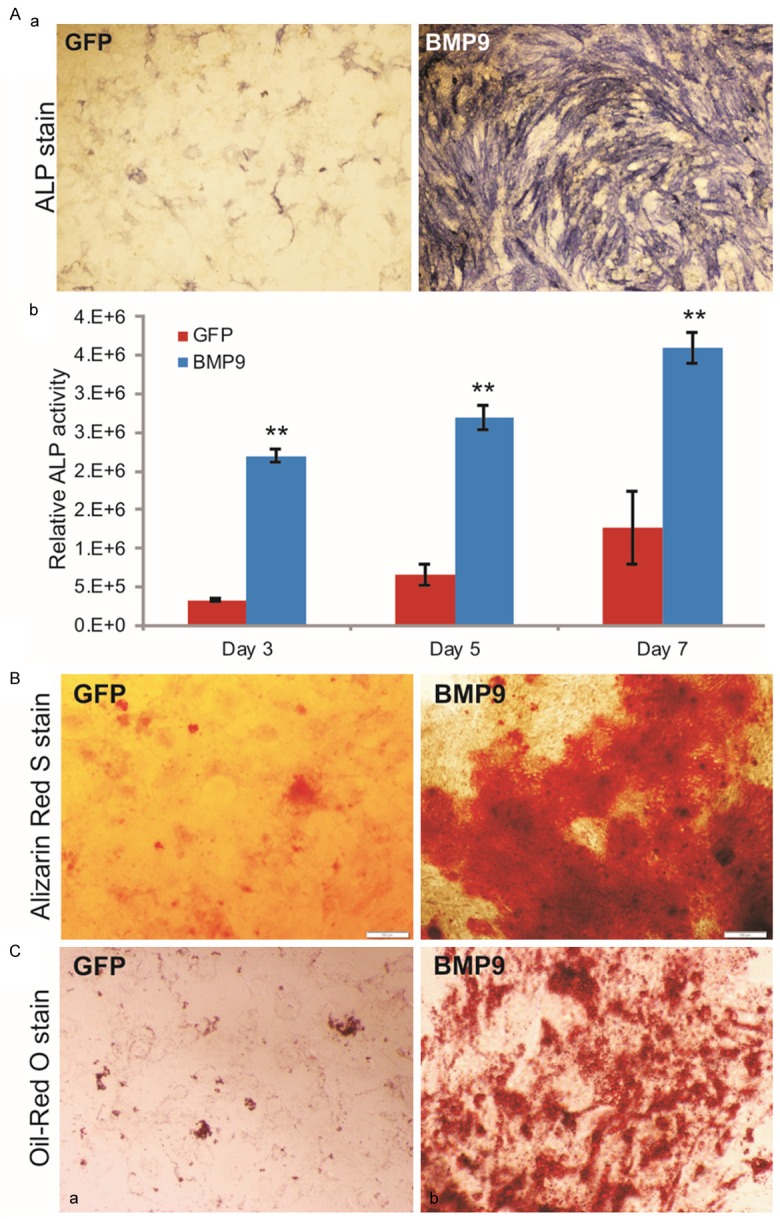
BMP9 induces osteogenic differentiation in iMADs in vitro. (A) BMP9 effectively induces osteogenic marker alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in iMADs. Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP. At 5 days after infection, cells were fixed for histochemical staining for ALP activity (a). Quantitative measurement of relative ALP activity was also determined at 3, 5, and 7 days after infection (b). Assays were done in triplicate and representative images are shown. “**”, p<0.001. (B) BMP9 induces robust matrix mineralization. Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP infected iMADs were cultured in mineralization medium for 10 days and stained with Alizarin Red S. Assays were done in triplicate and representative images are shown. (C) BMP9 has limited effect on adipogenic differentiation, Ad-GFP (a) or Ad-BMP9 (b) infected iMADs were cultured in complete DMEM. At 10 days after infection, the cells were fixed and stained with Oil Red O solution. Assays were done in triplicate and representative images are shown.
We also assessed the adipogenic potential of the iMADs. When the iMADs were stimulated with BMP9 for 10 days, the cells exhibited a modest but significantly higher level of lipid droplet formation as revealed by Oil-red O staining, compared with that of the control cells (Figure 5C). Interestingly, the BMP-induced in vitro adipogenic differentiation in the iMADs is somewhat less pronounced than that in other sources of mesenchymal stem cells, such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts, C3H10T1/2 cells or C2C12 cells [29,41,79,94,95]. This is rather surprising given the fact that the iMADs were derived from adipose tissue. Nonetheless, these in vitro results further demonstrate that the iMADs are responsive to BMP9 stimulation and exhibit the characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells.
BMP9 induces robust ectopic bone formation from by iMADs implanted with scaffold materials
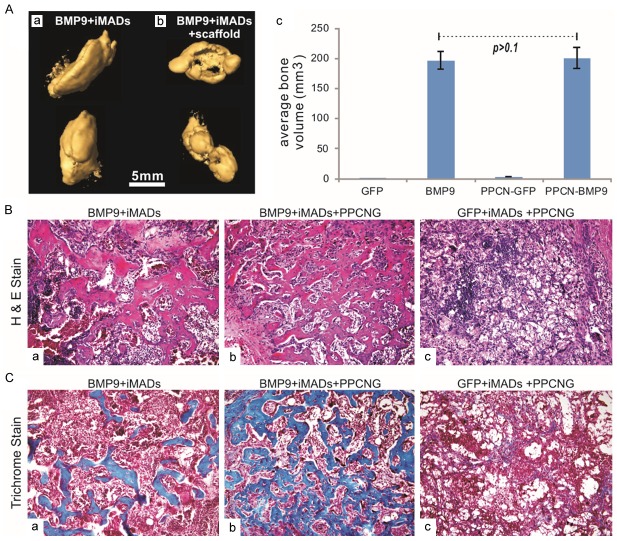
We next determined the iMADs’ ability to form ectopic bone using the stem cell implantation model with or without scaffold materials, as previously reported [34,36,83,87,96]. The iMADs were first transduced with Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP for 30 h. The cells were then collected, mixed with PBS or the scaffold material PPCN/gelatin and injected subcutaneously into athymic nude mice. PPCN polymer is a thermoresponsive, injectable, biodegradable and highly biocompatible scaffolding material [56]. At 4 weeks after implantation, subcutaneous masses at the injection sites were retrieved from the BMP9-transduced groups, while no apparent masses were formed in the animals injected with GFP-treated iMADs only. When subjected to µCT imaging analysis, the masses retrieved from the BMP9-treated groups (either injected with the iMAD cells only or the iMADs mixed with the scaffold material) exhibited significant mineralization (Figure 6Aa & 6Ab). Quantitative analysis indicates that the bony masses formed in the direct cell injection group were volumetrically similar to that formed in the cells mixed with the PPCN-gelatin interpenetrating network group (p>0.1) (Figure 6Ac). However, histologic evaluation indicates that the BMP9-stimulated iMADs mixed with the scaffold material underwent rather complete osteogenic differentiation and formed well-networked woven bone structures, whereas the bony masses retrieved from the direct cell injection group contained regions of undifferentiated cells and unevenly distributed bony trabeculae (Figure 6Ba vs. 6Bb). The masses retrieved from the iMADs transduced with Ad-GFP and mixed with the scaffold material did not form any detectable bony structure upon histologic examination (Figure 6Bc). Trichrome staining further confirmed that the bony structures formed in BMP9-transduced iMADs mixed with PPCN/gelatin scaffold material exhibited higher maturity and greater mineralization, compared with those of the direct BMP9-iMAD cell injection; no mineralization was observed in the GFP-treated iMADs group (Figure 6Cb vs. 6Ca & 6Cc). Interestingly, no apparent adipogenic differentiation and adipocyte formation were observed in the masses formed with BMP9-transduced iMADs, which is consistent with the modest adipogenic activity shown in vitro. These in vivo results strongly indicate that BMP9 induces robust bone formation from the iMADs.
Figure 6.
BMP9 induces robust ectopic bone formation from the iMADs implanted with scaffold materials. (A) Subconfluent iMADs were infected with Ad-BMP9 or Ad-GFP for 30 h, and implanted into athymic nude mice subcutaneously either by direct cell injection or mixing with thermoresponsive biodegradable scaffold material PPCN-gelatin (5x106 cells per injection, n=5 per group). After 4 weeks, the subcutaneous masses at the injection sites were collected and fixed for microCT imaging (a & b). Average bone volumes were calculated using Amira software (c). No masses were retrieved from the group injected with Ad-GFP infected iMAD cells only, nor were bony masses recovered from the group injected with Ad-GFP infected iMADs mixed with PPCN-gelatin scaffold material. (B) H&E staining of the masses retrieved from subcutaneous injection with Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cell only (a), Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (b) or Ad-GFP infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (c). Representative images are shown. (C) Trichrome staining of the masses retrieved from subcutaneous injection with Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cell only (a), Ad-BMP9 infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (b) or Ad-GFP infected iMAD cells mixed with PPCN scaffold (c). Representative images are shown.
Discussion
AD-MSCs are important sources of multipotent progenitor cells for regenerative medicine although the biological features and regulatory circuitries of these progenitors remain to be fully understood
Adipose tissue controls a myriad of biological actions, including appetite, glucose homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, aging, fertility and fecundity, as well as buffering body temperature [43,44]. In mammals, adipose tissue is typically classified by morphological appearance as being either white adipose tissue (WAT) or brown adipose tissue (BAT). WAT (the primary site of energy storage) is mostly composed of adipocytes and is found throughout the body [44]. The anatomical location of WAT is often classified as being visceral or subcutaneous. In rodents, WAT depots include the anterior subcutaneous WATs (asWATs) (such as interscapular and axillary WAT), inguinal WAT, perigonadal WAT, retroperitoneal WAT, and mesenteric WAT. Thus, adipose tissue is complex and heterogeneous [42]. It is conceivable that AD-MSCs derived from different anatomical locations may exhibit different progenitor characteristics.
The cellular diversity of adipose tissue has become more appreciated over the past few decades. This leads to the increased interest in its potential use as a cell source [46]. The dissociation and separation of adipose tissue into a single cell suspension was first described in the 1990s [97,98], ushering in a new era of study of the different cellular components of adipose tissue and the subsequent identification of the adipocyte precursor cell or the preadipocyte [99,101]. Ultimately, the preadipocyte became a focal point for the emerging field of tissue engineering [46,48]. Adipose tissue is dynamic, responding to homeostatic and external cues. The formation and maintenance of adipose tissue is essential to many biological processes and when perturbed leads to significant diseases. Nonetheless, the molecular mechanisms underlying adipose tissue development and regulation of adipose stem cells remain to be fully understood [42,47].
Although AD-MSCs are extensively used in experimental tissue engineering, optimal and effective regulators for AD-MSC-based bone tissue engineering remain to be thoroughly characterized
AD-MSCs have been shown to undergo osteogenic differentiation upon dexamethasone treatment [102]. AD-MSCs can also differentiate into bone cells in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional tissue engineered constructs using various scaffold materials, including collagen, poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), carbon nanotubes, silk sponges, or self-assembling spheroids [103,108]. Pretreated AD-MSCs with dexamethasone/VD3 (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) greatly improved their osteogenic capabilities [109]. The feasibility of in vivo bone regeneration by transplantation of ADSCs without prior in vitro osteogenic differentiation was demonstrated [110]. Local transplantation of human multipotent adipose-derived stem cells was shown to accelerate fracture healing via enhanced osteogenesis and angiogenesis [111]. Interestingly, dura mater was shown to stimulate human adipose-derived stromal cells to undergo bone formation in mouse calvarial defects [112]. Consistent with our prior reported results [30], silencing noggin expression significantly increased osteogenic differentiation in in human AD-MSCs [113,114]. Similar to what we found in other sources of MSCs [115], histone deacetylase inhibitors can promote the osteogenic potential of adipose-derived stem cells [116]. BMPs, mostly BMP2, was shown to improve bone formation from AD-MSCs although it remains to be determined if efficient bone formation can be achieved by using BMP alone [103,117-125].
Although numerous studies have shown that AD-MSCs can be induced to undergo osteogenic differentiation by different biological factors with or without scaffold materials, the efficiency for bone tissue engineering using AD-MSCs needs to be optimized. In this study, we have demonstrated that BMP9 can induce robust ectopic bone formation in the iMADs. Our findings are supported by two recent studies that showed that BMP9 is highly effective in inducing osteogenic differentiation of rabbit and human adipose-derived progenitor cells in vitro [126,127]. Our results also demonstrated that the thermoresponsive biodegradable scaffold PPCN may be used as a valuable and versatile vehicle for cell-based therapies and tissue engineering [56]. Furthermore, the established iMAD cells should provide a valuable resource for the study of AD-MSC biology, which will subsequently enable us to develop novel and efficacious strategies for bone tissue engineering.
Acknowledgements
The reported work was supported in part by research grants from the National Institutes of Health (AT004418, DE020140 to TCH and RRR), the Chicago Biomedical Consortium (RRR, GAA and TCH), the Scoliosis Research Society (to MJL), and the 973 Program of Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of China (#2011CB707900 to TCH). SL was a recipient of the pre-doctoral fellowship from the China Scholarship Council. MKM was a recipient of Howard Hughes Medical Institute Medical Research Fellowship. This work was also supported in part by The University of Chicago Core Facility Subsidy grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) of the National Institutes of Health through Grant UL1 TR000430. All authors have read the journal’s authorship agreement and the manuscript has been reviewed and approved by all the authors.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
Abbreviations
- ALP
alkaline phosphatase
- BMP
bone morphogenetic protein
- MAD
multipotent adipose-derived cells
- iMADs
immortalized MADs
- MSCs
mesenchymal stem cells
Supporting Information
References
- 1.Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276:71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5309.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–147. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5411.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Luo J, Sun MH, Kang Q, Peng Y, Jiang W, Luu HH, Luo Q, Park JY, Li Y, Haydon RC, He TC. Gene therapy for bone regeneration. Curr Gene Ther. 2005;5:167–179. doi: 10.2174/1566523053544218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Luther G, Wagner ER, Zhu G, Kang Q, Luo Q, Lamplot J, Bi Y, Luo X, Luo J, Teven C, Shi Q, Kim SH, Gao JL, Huang E, Yang K, Rames R, Liu X, Li M, Hu N, Liu H, Su Y, Chen L, He BC, Zuo GW, Deng ZL, Reid RR, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. BMP-9 Induced Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Potential. Curr Gene Ther. 2011;11:229–240. doi: 10.2174/156652311795684777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lamplot JD, Qin J, Nan G, Wang J, Liu X, Yin L, Tomal J, Li R, Shui W, Zhang H, Kim SH, Zhang W, Zhang J, Kong Y, Denduluri S, Rogers MR, Pratt A, Haydon RC, Luu HH, Angeles J, Shi LL, He TC. BMP9 signaling in stem cell differentiation and osteogenesis. Am J Stem Cells. 2013;2:1–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ishihara A, Bertone AL. Cell-mediated and direct gene therapy for bone regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12:411–423. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.661709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kimelman Bleich N, Kallai I, Lieberman JR, Schwarz EM, Pelled G, Gazit D. Gene therapy approaches to regenerating bone. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:1320–1330. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wilson CG, Martin-Saavedra FM, Vilaboa N, Franceschi RT. Advanced BMP gene therapies for temporal and spatial control of bone regeneration. J Dent Res. 2013;92:409–417. doi: 10.1177/0022034513483771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Tang N, Song WX, Luo J, Luo X, Chen J, Bennett E, Reid R, Manning D, Xue A, Montag AG, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. Regulation of osteogenic differentiation during skeletal development. Front Biosci. 2008;13:2001–2021. doi: 10.2741/2819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rastegar F, Shenaq D, Huang J, Zhang W, Zhang BQ, He BC, Chen L, Zuo GW, Luo Q, Shi Q, Wagner ER, Huang E, Gao Y, Gao JL, Kim SH, Zhou JZ, Bi Y, Su Y, Zhu G, Luo J, Luo X, Qin J, Reid RR, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Deng ZL, He TC. Mesenchymal stem cells: Molecular characteristics and clinical applications. World J Stem Cells. 2010;2:67–80. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v2.i4.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shenaq DS, Rastegar F, Petkovic D, Zhang BQ, He BC, Chen L, Zuo GW, Luo Q, Shi Q, Wagner ER, Huang E, Gao Y, Gao JL, Kim SH, Yang K, Bi Y, Su Y, Zhu G, Luo J, Luo X, Qin J, Reid RR, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells and Their Orthopedic Applications: Forging a Path towards Clinical Trials. Stem Cells Int. 2010;2010:519028. doi: 10.4061/2010/519028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Teven CM, Liu X, Hu N, Tang N, Kim SH, Huang E, Yang K, Li M, Gao JL, Liu H, Natale RB, Luther G, Luo Q, Wang L, Rames R, Bi Y, Luo J, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Reid RR, He TC. Epigenetic regulation of mesenchymal stem cells: a focus on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2011;2011:201371. doi: 10.4061/2011/201371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Green JD, Tollemar V, Dougherty M, Yan Z, Yin L, Ye J, Collier Z, Mohammed MK, Haydon RC, Luu HH, Kang R, Lee MJ, Ho SH, He TC, Shi LL, Athiviraham A. Multifaceted signaling regulators of chondrogenesis: Implications in cartilage regeneration and tissue engineering. Genes Dis. 2015;2:307–327. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2015.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Olsen BR, Reginato AM, Wang W. Bone development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:191–220. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berendsen AD, Olsen BR. Bone development. Bone. 2015;80:14–18. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.04.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Raucci A, Bellosta P, Grassi R, Basilico C, Mansukhani A. Osteoblast proliferation or differentiation is regulated by relative strengths of opposing signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 2008;215:442–451. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kim JH, Liu X, Wang J, Chen X, Zhang H, Kim SH, Cui J, Li R, Zhang W, Kong Y, Zhang J, Shui W, Lamplot J, Rogers MR, Zhao C, Wang N, Rajan P, Tomal J, Statz J, Wu N, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. Wnt signaling in bone formation and its therapeutic potential for bone diseases. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013;5:13–31. doi: 10.1177/1759720X12466608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yang K, Wang X, Zhang H, Wang Z, Nan G, Li Y, Zhang F, Mohammed MK, Haydon RC, Luu HH, Bi Y, He TC. The evolving roles of canonical WNT signaling in stem cells and tumorigenesis: implications in targeted cancer therapies. Lab Invest. 2016;96:116–36. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Denduluri SK, Olumuyiwa Idowu O, Wang Z, Liao Z, Yan Z, Mohammed MK, Ye J, Wei Q, Wang J, Zhao L, Luu HH. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling in tumorigenesis and the development of cancer drug resistance. Genes Dis. 2015;2:13–25. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Teven CM, Farina EM, Rivas J, Reid RR. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling in development and skeletal diseases. Genes Dis. 2014;1:199–213. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jo A, Denduluri SK, Zhang B, Wang Z, Yin L, Yan Z, Kang R, Shi LL, Mok J, Lee MJ, Haydon RC. The Versatile Functions of Sox9 in Development, Stem Cells, and Human Diseases. Genes Dis. 2014;1:149–161. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Louvi A, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Notch and disease: a growing field. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23:473–480. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zanotti S, Canalis E. Notch and the skeleton. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:886–896. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01285-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guruharsha KG, Kankel MW, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The Notch signalling system: recent insights into the complexity of a conserved pathway. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:654–666. doi: 10.1038/nrg3272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Varga AC, Wrana JL. The disparate role of BMP in stem cell biology. Oncogene. 2005;24:5713–5721. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Luu HH, Song WX, Luo X, Manning D, Luo J, Deng ZL, Sharff KA, Montag AG, Haydon RC, He TC. Distinct roles of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2007;25:665–677. doi: 10.1002/jor.20359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M, Peabody M, Zhang Q, Ye J, Yan Z, Denduluri S, Idowu O, Li M, Shen C, Hu A, Haydon RC, Kang R, Mok J, Lee MJ, Luu HL, Shi LL. Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes Dis. 2014;1:87–105. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cheng H, Jiang W, Phillips FM, Haydon RC, Peng Y, Zhou L, Luu HH, An N, Breyer B, Vanichakarn P, Szatkowski JP, Park JY, He TC. Osteogenic activity of the fourteen types of human bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A:1544–1552. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200308000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kang Q, Sun MH, Cheng H, Peng Y, Montag AG, Deyrup AT, Jiang W, Luu HH, Luo J, Szatkowski JP, Vanichakarn P, Park JY, Li Y, Haydon RC, He TC. Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. Gene Ther. 2004;11:1312–1320. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y, Hong S, Li M, Zhang J, Bi Y, He Y, Liu X, Nan G, Su Y, Zhu G, Li R, Zhang W, Wang J, Zhang H, Kong Y, Shui W, Wu N, He Y, Chen X, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Shi LL, He TC, Qin J. Noggin resistance contributes to the potent osteogenic capability of BMP9 in mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2013;31:1796–1803. doi: 10.1002/jor.22427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Peng Y, Kang Q, Cheng H, Li X, Sun MH, Jiang W, Luu HH, Park JY, Haydon RC, He TC. Transcriptional characterization of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)-mediated osteogenic signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:1149–1165. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Peng Y, Kang Q, Luo Q, Jiang W, Si W, Liu BA, Luu HH, Park JK, Li X, Luo J, Montag AG, Haydon RC, He TC. Inhibitor of DNA binding/differentiation helix-loop-helix proteins mediate bone morphogenetic protein-induced osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:32941–32949. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403344200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Luo Q, Kang Q, Si W, Jiang W, Park JK, Peng Y, Li X, Luu HH, Luo J, Montag AG, Haydon RC, He TC. Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) Is Regulated by Wnt and Bone Morphogenetic Proteins Signaling in Osteoblast Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:55958–55968. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407810200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sharff KA, Song WX, Luo X, Tang N, Luo J, Chen J, Bi Y, He BC, Huang J, Li X, Jiang W, Zhu GH, Su Y, He Y, Shen J, Wang Y, Chen L, Zuo GW, Liu B, Pan X, Reid RR, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. Hey1 Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein Plays an Important Role in Mediating BMP9-induced Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:649–659. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806389200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huang E, Zhu G, Jiang W, Yang K, Gao Y, Luo Q, Gao JL, Kim SH, Liu X, Li M, Shi Q, Hu N, Wang L, Liu H, Cui J, Zhang W, Li R, Chen X, Kong YH, Zhang J, Wang J, Shen J, Bi Y, Statz J, He BC, Luo J, Wang H, Xiong F, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Yang L, He TC. Growth hormone synergizes with BMP9 in osteogenic differentiation by activating the JAK/STAT/IGF1 pathway in murine multilineage cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27:1566–1575. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tang N, Song WX, Luo J, Luo X, Chen J, Sharff KA, Bi Y, He BC, Huang JY, Zhu GH, Su YX, Jiang W, Tang M, He Y, Wang Y, Chen L, Zuo GW, Shen J, Pan X, Reid RR, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors requires functional canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13:2448–2464. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen L, Jiang W, Huang J, He BC, Zuo GW, Zhang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Wagner ER, Luo J, Tang M, Wietholt C, Luo X, Bi Y, Su Y, Liu B, Kim SH, He CJ, Hu Y, Shen J, Rastegar F, Huang E, Gao Y, Gao JL, Zhou JZ, Reid RR, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Deng ZL. Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF-2) potentiates BMP-9-induced osteogenic differentiation and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:2447–2459. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang W, Deng ZL, Chen L, Zuo GW, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Wagner ER, Rastegar F, Kim SH, Jiang W, Shen J, Huang E, Gao Y, Gao JL, Zhou JZ, Luo J, Huang J, Luo X, Bi Y, Su Y, Yang K, Liu H, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, He BC. Retinoic acids potentiate BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hu N, Jiang D, Huang E, Liu X, Li R, Liang X, Kim SH, Chen X, Gao JL, Zhang H, Zhang W, Kong YH, Zhang J, Wang J, Shui W, Luo X, Liu B, Cui J, Rogers MR, Shen J, Zhao C, Wang N, Wu N, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Huang W. BMP9-regulated angiogenic signaling plays an important role in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. J Cell Sci. 2013;126:532–541. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu X, Qin J, Luo Q, Bi Y, Zhu G, Jiang W, Kim SH, Li M, Su Y, Nan G, Cui J, Zhang W, Li R, Chen X, Kong Y, Zhang J, Wang J, Rogers MR, Zhang H, Shui W, Zhao C, Wang N, Liang X, Wu N, He Y, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Shi LL, Li T, He TC, Li M. Cross-talk between EGF and BMP9 signalling pathways regulates the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17:1160–1172. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang H, Wang J, Deng F, Huang E, Yan Z, Wang Z, Deng Y, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Ye J, Qiao M, Li R, Wang J, Wei Q, Zhou G, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Deng F. Canonical Wnt signaling acts synergistically on BMP9-induced osteo/odontoblastic differentiation of stem cells of dental apical papilla (SCAPs) Biomaterials. 2015;39:145–154. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.11.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sanchez-Gurmaches J, Guertin DA. Adipocyte lineages: tracing back the origins of fat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842:340–351. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.05.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zeve D, Tang W, Graff J. Fighting fat with fat: the expanding field of adipose stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5:472–481. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Berry DC, Stenesen D, Zeve D, Graff JM. The developmental origins of adipose tissue. Development. 2013;140:3939–3949. doi: 10.1242/dev.080549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nordberg RC, Loboa EG. Our Fat Future: Translating Adipose Stem Cell Therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4:974–979. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kapur SK, Dos-Anjos Vilaboa S, Llull R, Katz AJ. Adipose tissue and stem/progenitor cells: discovery and development. Clin Plast Surg. 2015;42:155–167. doi: 10.1016/j.cps.2014.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Huang SJ, Fu RH, Shyu WC, Liu SP, Jong GP, Chiu YW, Wu HS, Tsou YA, Cheng CW, Lin SZ. Adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential. Cell Transplant. 2013;22:701–709. doi: 10.3727/096368912X655127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Halvorsen YC, Wilkison WO, Gimble JM. Adipose-derived stromal cells--their utility and potential in bone formation. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000;24(Suppl 4):S41–44. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP, Hedrick MH. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell- based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7:211–228. doi: 10.1089/107632701300062859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gimble JM, Guilak F. Differentiation potential of adipose derived adult stem (ADAS) cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2003;58:137–160. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(03)58005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wu N, Zhang H, Deng F, Li R, Zhang W, Chen X, Wen S, Wang N, Zhang J, Yin L, Liao Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Yan Z, Liu W, Wu D, Ye J, Deng Y, Yang K, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. Overexpression of Ad5 precursor terminal protein accelerates recombinant adenovirus packaging and amplification in HEK-293 packaging cells. Gene Ther. 2014;21:629–637. doi: 10.1038/gt.2014.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wen S, Zhang H, Li Y, Wang N, Zhang W, Yang K, Wu N, Chen X, Deng F, Liao Z, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Yan Z, Liu W, Zhang Z, Ye J, Deng Y, Zhou G, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Shi LL, He TC, Wei G. Characterization of constitutive promoters for piggyBac transposon-mediated stable transgene expression in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) PLoS One. 2014;9:e94397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Deng Y, Zhang J, Wang Z, Yan Z, Qiao M, Ye J, Wei Q, Wang J, Wang X, Zhao L, Lu S, Tang S, Mohammed MK, Liu H, Fan J, Zhang F, Zou Y, Liao J, Qi H, Haydon RC, Luu HH, He TC, Tang L. Antibiotic monensin synergizes with EGFR inhibitors and oxaliplatin to suppress the proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17523. doi: 10.1038/srep17523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chen X, Cui J, Yan Z, Zhang H, Chen X, Wang N, Shah P, Deng F, Zhao C, Geng N, Li M, Denduluri SK, Haydon RC, Luu HH, Reid RR, He TC. Sustained high level transgene expression in mammalian cells mediated by the optimized piggyBac transposon system. Genes Dis. 2015;2:96–105. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Li Y, Wagner ER, Yan Z, Wang Z, Luther G, Jiang W, Ye J, Wei Q, Wang J, Zhao L, Lu S, Wang X, Mohammed MK, Tang S, Liu H, Fan J, Zhang F, Zou Y, Song D, Liao J, Haydon RC, Luu HH, He TC. The Calcium-Binding Protein S100A6 Accelerates Human Osteosarcoma Growth by Promoting Cell Proliferation and Inhibiting Osteogenic Differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37:2375–2392. doi: 10.1159/000438591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yang J, van Lith R, Baler K, Hoshi RA, Ameer GA. A thermoresponsive biodegradable polymer with intrinsic antioxidant properties. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15:3942–3952. doi: 10.1021/bm5010004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.He TC. Adenoviral Vectors in Current Protocols in Human Genetics. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2004. Adenoviral Vectors; pp. 12.14.11–12.14.25. [Google Scholar]
- 58.He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:2509–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Luo J, Deng ZL, Luo X, Tang N, Song WX, Chen J, Sharff KA, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, He TC. A protocol for rapid generation of recombinant adenoviruses using the AdEasy system. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:1236–1247. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kong Y, Zhang H, Chen X, Zhang W, Zhao C, Wang N, Wu N, He Y, Nan G, Zhang H, Wen S, Deng F, Liao Z, Wu D, Zhang J, Qin X, Haydon RC, Luu HH, He TC, Zhou L. Destabilization of Heterologous Proteins Mediated by the GSK3beta Phosphorylation Domain of the beta-Catenin Protein. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32:1187–1199. doi: 10.1159/000354518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Li R, Zhang W, Cui J, Shui W, Yin L, Wang Y, Zhang H, Wang N, Wu N, Nan G, Chen X, Wen S, Deng F, Zhou G, Liao Z, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Yan Z, Liu W, Zhang Z, Ye J, Deng Y, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Deng ZL. Targeting BMP9-promoted human osteosarcoma growth by inactivation of notch signaling. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014;14:274–285. doi: 10.2174/1568009614666140305105805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zhang W, Zhang H, Wang N, Zhao C, Zhang H, Deng F, Wu N, He Y, Chen X, Zhang J, Wen S, Liao Z, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Liu W, Yan Z, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Zhou L, He TC. Modulation of beta-Catenin Signaling by the Inhibitors of MAP Kinase, Tyrosine Kinase, and PI3-Kinase Pathways. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10:1888–1898. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wang N, Zhang W, Cui J, Zhang H, Chen X, Li R, Wu N, Chen X, Wen S, Zhang J, Yin L, Deng F, Liao Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Yan Z, Liu W, Ye J, Deng Y, Wang Z, Qiao M, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Shi LL, Liang H, He TC. The piggyBac Transposon-Mediated Expression of SV40 T Antigen Efficiently Immortalizes Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) PLoS One. 2014;9:e97316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Huang E, Bi Y, Jiang W, Luo X, Yang K, Gao JL, Gao Y, Luo Q, Shi Q, Kim SH, Liu X, Li M, Hu N, Liu H, Cui J, Zhang W, Li R, Chen X, Shen J, Kong Y, Zhang J, Wang J, Luo J, He BC, Wang H, Reid RR, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Yang L, He TC. Conditionally Immortalized Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts Retain Proliferative Activity without Compromising Multipotent Differentiation Potential. PLoS One. 2012;7:e32428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yang K, Chen J, Jiang W, Huang E, Cui J, Kim SH, Hu N, Liu H, Zhang W, Li R, Chen X, Kong Y, Zhang J, Wang J, Wang L, Shen J, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Lian X, Yang T, He TC. Conditional Immortalization Establishes a Repertoire of Mouse Melanocyte Progenitors with Distinct Melanogenic Differentiation Potential. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:2479–2483. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gao Y, Huang E, Zhang H, Wang J, Wu N, Chen X, Wang N, Wen S, Nan G, Deng F, Liao Z, Wu D, Zhang B, Zhang J, Haydon RC, Luu HH, Shi LL, He TC. Crosstalk between Wnt/beta-Catenin and Estrogen Receptor Signaling Synergistically Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e82436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Westerman KA, Leboulch P. Reversible immortalization of mammalian cells mediated by retroviral transfer and site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:8971–8976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.17.8971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Li M, Chen Y, Bi Y, Jiang W, Luo Q, He Y, Su Y, Liu X, Cui J, Zhang W, Li R, Kong Y, Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang H, Shui W, Wu N, Zhu J, Tian J, Yi QJ, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Zhu GH. Establishment and characterization of the reversibly immortalized mouse fetal heart progenitors. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10:1035–1046. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bi Y, He Y, Huang J, Su Y, Zhu GH, Wang Y, Qiao M, Zhang BQ, Zhang H, Wang Z, Liu W, Cui J, Kang Q, Zhang Z, Deng Y, Li R, Zhang Q, Yang K, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Tang N. Functional characteristics of reversibly immortalized hepatic progenitor cells derived from mouse embryonic liver. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:1318–1338. doi: 10.1159/000366340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lamplot JD, Liu B, Yin L, Zhang W, Wang Z, Luther G, Wagner E, Li R, Nan G, Shui W, Yan Z, Rames R, Deng F, Zhang H, Liao Z, Liu W, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Ye J, Deng Y, Qiao M, Haydon RC, Luu HH, Angeles J, Shi LL, He TC, Ho SH. Reversibly Immortalized Mouse Articular Chondrocytes Acquire Long-Term Proliferative Capability while Retaining Chondrogenic Phenotype. Cell Transplant. 2015;24:1053–1066. doi: 10.3727/096368914X681054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.He BC, Chen L, Zuo GW, Zhang W, Bi Y, Huang J, Wang Y, Jiang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Liu B, Lei X, Luo J, Luo X, Wagner ER, Kim SH, He CJ, Hu Y, Shen J, Zhou Q, Rastegar F, Deng ZL, Luu HH, He TC, Haydon RC. Synergistic antitumor effect of the activated PPARgamma and retinoid receptors on human osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:2235–2245. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.He BC, Gao JL, Zhang BQ, Luo Q, Shi Q, Kim SH, Huang E, Gao Y, Yang K, Wagner ER, Wang L, Tang N, Luo J, Liu X, Li M, Bi Y, Shen J, Luther G, Hu N, Zhou Q, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Zhao Y, He TC. Tetrandrine inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and suppresses tumor growth of human colorectal cancer. Mol Pharmacol. 2011;79:211–219. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.068668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Chen X, Luther G, Zhang W, Nan G, Wagner ER, Liao Z, Wu N, Zhang H, Wang N, Wen S, He Y, Deng F, Zhang J, Wu D, Zhang B, Haydon RC, Zhou L, Luu HH, He TC. The E-F Hand Calcium-Binding Protein S100A4 Regulates the Proliferation, Survival and Differentiation Potential of Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32:1083–1096. doi: 10.1159/000354508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Li R, Hu Z, Sun SY, Chen ZG, Owonikoko TK, Sica GL, Ramalingam SS, Curran WJ, Khuri FR, Deng X. Niclosamide overcomes acquired resistance to erlotinib through suppression of STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12:2200–2212. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gao JL, Lv GY, He BC, Zhang BQ, Zhang H, Wang N, Wang CZ, Du W, Yuan CS, He TC. Ginseng saponin metabolite 20(S)-protopanaxadiol inhibits tumor growth by targeting multiple cancer signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:292–298. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Liao Z, Nan G, Yan Z, Zeng L, Deng Y, Ye J, Zhang Z, Qiao M, Li R, Denduluri S, Wang J, Wei Q, Geng N, Zhao L, Lu S, Wang X, Zhou G, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Wang Z. The Anthelmintic Drug Niclosamide Inhibits the Proliferative Activity of Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting Multiple Signal Pathways. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15:726–738. doi: 10.2174/1568009615666150629132157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG. Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Zhang Q, Wang J, Deng F, Yan Z, Xia Y, Wang Z, Ye J, Deng Y, Zhang Z, Qiao M, Li R, Denduluri SK, Wei Q, Zhao L, Lu S, Wang X, Tang S, Liu H, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Jiang L. TqPCR: A Touchdown qPCR Assay with Significantly Improved Detection Sensitivity and Amplification Efficiency of SYBR Green qPCR. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0132666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kang Q, Song WX, Luo Q, Tang N, Luo J, Luo X, Chen J, Bi Y, He BC, Park JK, Jiang W, Tang Y, Huang J, Su Y, Zhu GH, He Y, Yin H, Hu Z, Wang Y, Chen L, Zuo GW, Pan X, Shen J, Vokes T, Reid RR, Haydon RC, Luu HH, He TC. A comprehensive analysis of the dual roles of BMPs in regulating adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18:545–559. doi: 10.1089/scd.2008.0130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Si W, Kang Q, Luu HH, Park JK, Luo Q, Song WX, Jiang W, Luo X, Li X, Yin H, Montag AG, Haydon RC, He TC. CCN1/Cyr61 Is Regulated by the Canonical Wnt Signal and Plays an Important Role in Wnt3A-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:2955–2964. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.2955-2964.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zhang J, Weng Y, Liu X, Wang J, Zhang W, Kim SH, Zhang H, Li R, Kong Y, Chen X, Shui W, Wang N, Zhao C, Wu N, He Y, Nan G, Chen X, Wen S, Zhang H, Deng F, Wan L, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Shi LL, He TC, Shi Q. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inducible factor cysteine-rich with EGF-like domains 2 (Creld2) is an important mediator of BMP9-regulated osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Li R, Yan Z, Ye J, Huang H, Wang Z, Wei Q, Wang J, Zhao L, Lu S, Wang X, Tang S, Fan J, Zhang F, Zou Y, Song D, Liao J, Lu M, Liu F, Shi LL, Athiviraham A, Lee MJ, He TC, Zhang Z. The Prodomain-Containing BMP9 Produced from a Stable Line Effectively Regulates the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Med Sci. 2016;13:8–18. doi: 10.7150/ijms.13333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Luo J, Tang M, Huang J, He BC, Gao JL, Chen L, Zuo GW, Zhang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Bi Y, Luo X, Jiang W, Su Y, Shen J, Kim SH, Huang E, Gao Y, Zhou JZ, Yang K, Luu HH, Pan X, Haydon RC, Deng ZL, He TC. TGFbeta/BMP type I receptors ALK1 and ALK2 are essential for BMP9-induced osteogenic signaling in mesenchymal stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:29588–29598. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Bi Y, Huang J, He Y, Zhu GH, Su Y, He BC, Luo J, Wang Y, Kang Q, Luo Q, Chen L, Zuo GW, Jiang W, Liu B, Shi Q, Tang M, Zhang BQ, Weng Y, Huang A, Zhou L, Feng T, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Tang N. Wnt antagonist SFRP3 inhibits the differentiation of mouse hepatic progenitor cells. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108:295–303. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Huang J, Bi Y, Zhu GH, He Y, Su Y, He BC, Wang Y, Kang Q, Chen L, Zuo GW, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Huang A, Zhou L, Feng T, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Tang N. Retinoic acid signalling induces the differentiation of mouse fetal liver-derived hepatic progenitor cells. Liver Int. 2009;29:1569–1581. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Rastegar F, Gao JL, Shenaq D, Luo Q, Shi Q, Kim SH, Jiang W, Wagner ER, Huang E, Gao Y, Shen J, Yang K, He BC, Chen L, Zuo GW, Luo J, Luo X, Bi Y, Liu X, Li M, Hu N, Wang L, Luther G, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC. Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase beta (LPAATbeta) promotes the tumor growth of human osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 2010;5:e14182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Shui W, Zhang W, Yin L, Nan G, Liao Z, Zhang H, Wang N, Wu N, Chen X, Wen S, He Y, Deng F, Zhang J, Luu HH, Shi LL, Hu Z, Haydon RC, Mok J, He TC. Characterization of scaffold carriers for BMP9-transduced osteoblastic progenitor cells in bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102:3429–38. doi: 10.1002/jbma.35006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Luo X, Chen J, Song WX, Tang N, Luo J, Deng ZL, Sharff KA, He G, Bi Y, He BC, Bennett E, Huang J, Kang Q, Jiang W, Su Y, Zhu GH, Yin H, He Y, Wang Y, Souris JS, Chen L, Zuo GW, Montag AG, Reid RR, Haydon RC, Luu HH, He TC. Osteogenic BMPs promote tumor growth of human osteosarcomas that harbor differentiation defects. Lab Invest. 2008;88:1264–1277. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2008.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A, Prockop D, Horwitz E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8:315–317. doi: 10.1080/14653240600855905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Takata Y, Kondo S, Goda N, Kanegae Y, Saito I. Comparison of efficiency between FLPe and Cre for recombinase-mediated cassette exchange in vitro and in adenovirus vector production. Genes Cells. 2011;16:765–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2011.01526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Anderson RP, Voziyanova E, Voziyanov Y. Flp and Cre expressed from Flp-2A-Cre and Flp-IRES-Cre transcription units mediate the highest level of dual recombinase-mediated cassette exchange. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Turan S, Galla M, Ernst E, Qiao J, Voelkel C, Schiedlmeier B, Zehe C, Bode J. Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE): traditional concepts and current challenges. J Mol Biol. 2011;407:193–221. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Zuo GW, Kohls CD, He BC, Chen L, Zhang W, Shi Q, Zhang BQ, Kang Q, Luo J, Luo X, Wagner ER, Kim SH, Restegar F, Haydon RC, Deng ZL, Luu HH, He TC, Luo Q. The CCN proteins: important signaling mediators in stem cell differentiation and tumorigenesis. Histol Histopathol. 2010;25:795–806. doi: 10.14670/hh-25.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang W, Huang E, Wang N, Wu N, Wen S, Chen X, Liao Z, Deng F, Yin L, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Yan Z, Liu W, Zhang Z, Ye J, Deng Y, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Deng F. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-9 (BMP9) Effectively Induces Osteo/Odontoblastic Differentiation of the Reversibly Immortalized Stem Cells of Dental Apical Papilla. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:1405–1416. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD. Commitment of C3H10T1/2 pluripotent stem cells to the adipocyte lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:9607–9611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403100101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Shui W, Yin L, Luo J, Li R, Zhang W, Zhang J, Huang W, Hu N, Liang X, Deng ZL, Hu Z, Shi LL, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Ho SH. Characterization of chondrocyte scaffold carriers for cell-based gene therapy in articular cartilage repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;101:3542–3550. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Rodbell M. Metabolism of Isolated Fat Cells. I. Effects of Hormones on Glucose Metabolism and Lipolysis. J Biol Chem. 1964;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Rodbell M. Localization of Lipoprotein Lipase in Fat Cells of Rat Adipose Tissue. J Biol Chem. 1964;239:753–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Loffler G, Hauner H. Adipose tissue development: the role of precursor cells and adipogenic factors. Part II: The regulation of the adipogenic conversion by hormones and serum factors. Klin Wochenschr. 1987;65:812–817. doi: 10.1007/BF01727475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Teichert-Kuliszewska K, Hamilton BS, Deitel M, Roncari DA. Augmented production of heparin-binding mitogenic proteins by preadipocytes from massively obese persons. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:1226–1231. doi: 10.1172/JCI115984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Petruschke T, Hauner H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha prevents the differentiation of human adipocyte precursor cells and causes delipidation of newly developed fat cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993;76:742–747. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.3.8445033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Desai HV, Voruganti IS, Jayasuriya C, Chen Q, Darling EM. Live-cell, temporal gene expression analysis of osteogenic differentiation in adipose-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19:40–48. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2012.0127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 103.Peterson B, Zhang J, Iglesias R, Kabo M, Hedrick M, Benhaim P, Lieberman JR. Healing of critically sized femoral defects, using genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:120–129. doi: 10.1089/ten.2005.11.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Hao W, Hu YY, Wei YY, Pang L, Lv R, Bai JP, Xiong Z, Jiang M. Collagen I gel can facilitate homogenous bone formation of adipose-derived stem cells in PLGA-beta-TCP scaffold. Cells Tissues Organs. 2008;187:89–102. doi: 10.1159/000109946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Li X, Liu H, Niu X, Yu B, Fan Y, Feng Q, Cui FZ, Watari F. The use of carbon nanotubes to induce osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived MSCs in vitro and ectopic bone formation in vivo. Biomaterials. 2012;33:4818–4827. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Shi Y, Niedzinski JR, Samaniego A, Bogdansky S, Atkinson BL. Adipose-derived stem cells combined with a demineralized cancellous bone substrate for bone regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18:1313–1321. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2011.0357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Lee JW, Kim KJ, Kang KS, Chen S, Rhie JW, Cho DW. Development of a bone reconstruction technique using a solid free-form fabrication (SFF)-based drug releasing scaffold and adipose-derived stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101:1865–1875. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Atluri K, Seabold D, Hong L, Elangovan S, Salem AK. Nanoplex-Mediated Codelivery of Fibroblast Growth Factor and Bone Morphogenetic Protein Genes Promotes Osteogenesis in Human Adipocyte-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol Pharm. 2015;12:3032–3042. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Yoon E, Dhar S, Chun DE, Gharibjanian NA, Evans GR. In vivo osteogenic potential of human adipose-derived stem cells/poly lactide-co-glycolic acid constructs for bone regeneration in a rat critical-sized calvarial defect model. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:619–627. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Jeon O, Rhie JW, Kwon IK, Kim JH, Kim BS, Lee SH. In vivo bone formation following transplantation of human adipose-derived stromal cells that are not differentiated osteogenically. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14:1285–1294. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2007.0253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Shoji T, Ii M, Mifune Y, Matsumoto T, Kawamoto A, Kwon SM, Kuroda T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M, Asahara T. Local transplantation of human multipotent adipose-derived stem cells accelerates fracture healing via enhanced osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Lab Invest. 2010;90:637–649. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Levi B, Nelson ER, Li S, James AW, Hyun JS, Montoro DT, Lee M, Glotzbach JP, Commons GW, Longaker MT. Dura mater stimulates human adipose-derived stromal cells to undergo bone formation in mouse calvarial defects. Stem Cells. 2011;29:1241–1255. doi: 10.1002/stem.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Levi B, Hyun JS, Nelson ER, Li S, Montoro DT, Wan DC, Jia FJ, Glotzbach JC, James AW, Lee M, Huang M, Quarto N, Gurtner GC, Wu JC, Longaker MT. Nonintegrating knockdown and customized scaffold design enhances human adipose-derived stem cells in skeletal repair. Stem Cells. 2011;29:2018–2029. doi: 10.1002/stem.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Fan J, Park H, Tan S, Lee M. Enhanced osteogenesis of adipose derived stem cells with Noggin suppression and delivery of BMP-2. PLoS One. 2013;8:e72474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Hu N, Wang C, Liang X, Yin L, Luo X, Liu B, Zhang H, Shui W, Nan G, Wang N, Wu N, Chen X, He Y, Wen S, Deng F, Zhang H, Liao Z, Luu HH, Haydon RC, He TC, Huang W. Inhibition of histone deacetylases potentiates BMP9-induced osteogenic signaling in mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32:486–498. doi: 10.1159/000354453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Hu X, Zhang X, Dai L, Zhu J, Jia Z, Wang W, Zhou C, Ao Y. Histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A promotes the osteogenic differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells by altering the epigenetic modifications on Runx2 promoter in a BMP signaling-dependent manner. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22:248–255. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Cowan CM, Aalami OO, Shi YY, Chou YF, Mari C, Thomas R, Quarto N, Nacamuli RP, Contag CH, Wu B, Longaker MT. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 and retinoic acid accelerate in vivo bone formation, osteoclast recruitment, and bone turnover. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:645–658. doi: 10.1089/ten.2005.11.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Dudas JR, Marra KG, Cooper GM, Penascino VM, Mooney MP, Jiang S, Rubin JP, Losee JE. The osteogenic potential of adipose-derived stem cells for the repair of rabbit calvarial defects. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56:543–548. doi: 10.1097/01.sap.0000210629.17727.bd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Hsu WK, Wang JC, Liu NQ, Krenek L, Zuk PA, Hedrick MH, Benhaim P, Lieberman JR. Stem cells from human fat as cellular delivery vehicles in an athymic rat posterolateral spine fusion model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:1043–1052. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.00292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Chen Q, Yang Z, Sun S, Huang H, Sun X, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang B. Adipose-derived stem cells modified genetically in vivo promote reconstruction of bone defects. Cytotherapy. 2010;12:831–840. doi: 10.3109/14653249.2010.495980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.De Francesco F, Ricci G, D’Andrea F, Nicoletti GF, Ferraro GA. Human Adipose Stem Cells: From Bench to Bedside. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2015;21:572–584. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2014.0608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Fan J, Im CS, Cui ZK, Guo M, Bezouglaia O, Fartash A, Lee JY, Nguyen J, Wu BM, Aghaloo T, Lee M. Delivery of Phenamil Enhances BMP-2-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Bone Formation in Calvarial Defects. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21:2053–2065. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2014.0489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Almubarak S, Nethercott H, Freeberg M, Beaudon C, Jha A, Jackson W, Marcucio R, Miclau T, Healy K, Bahney C. Tissue engineering strategies for promoting vascularized bone regeneration. Bone. 2016;83:197–209. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Zuk P, Chou YF, Mussano F, Benhaim P, Wu BM. Adipose-derived stem cells and BMP2: part 2. BMP2 may not influence the osteogenic fate of human adipose-derived stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2011;52:119–132. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2010.484515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Smith DM, Cooper GM, Afifi AM, Mooney MP, Cray J, Rubin JP, Marra KG, Losee JE. Regenerative surgery in cranioplasty revisited: the role of adipose-derived stem cells and BMP-2. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128:1053–1060. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31822b65e4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Chai Y, Liu F, Li Q, Shen Y, Ding WY. BMP-9 induces rabbit adipose-derived stem cells to differentiation into osteoblasts via BMP signaling pathway. Anal Quant Cytopathol Histpathol. 2013;35:171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Rivera JC, Strohbach CA, Wenke JC, Rathbone CR. Beyond osteogenesis: an in vitro comparison of the potentials of six bone morphogenetic proteins. Front Pharmacol. 2013;4:125. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.