Abstract
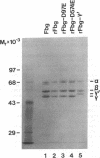
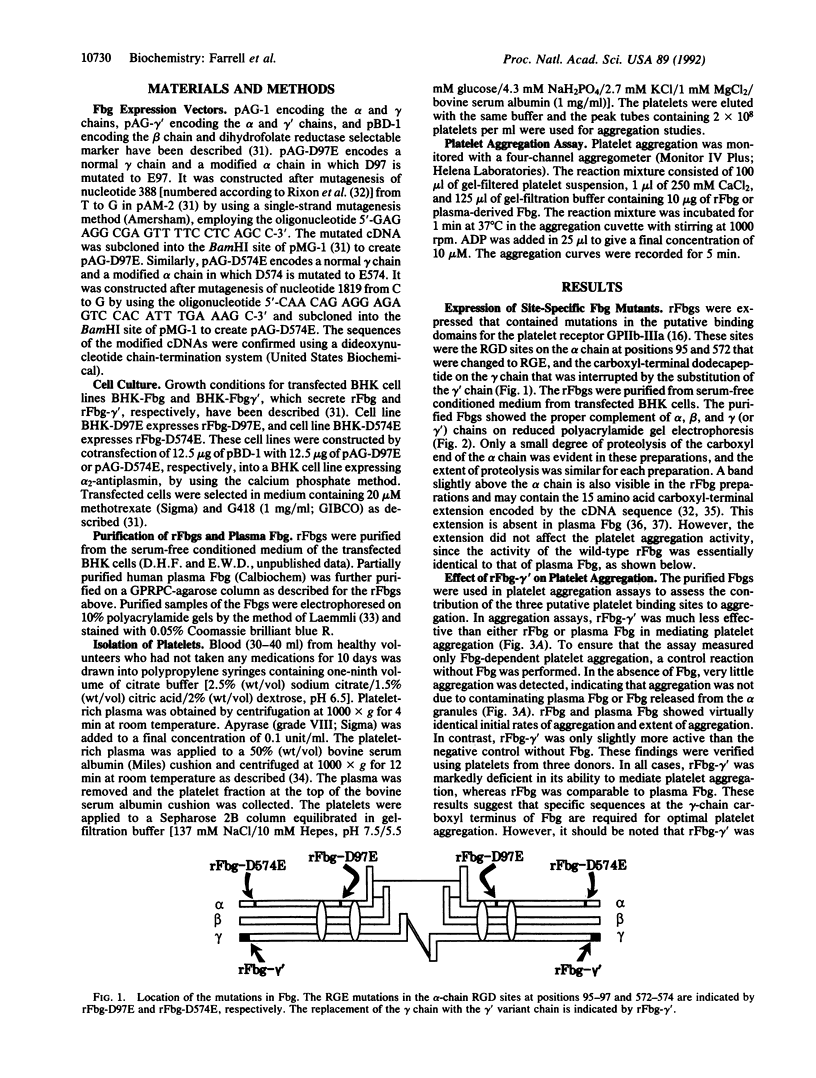
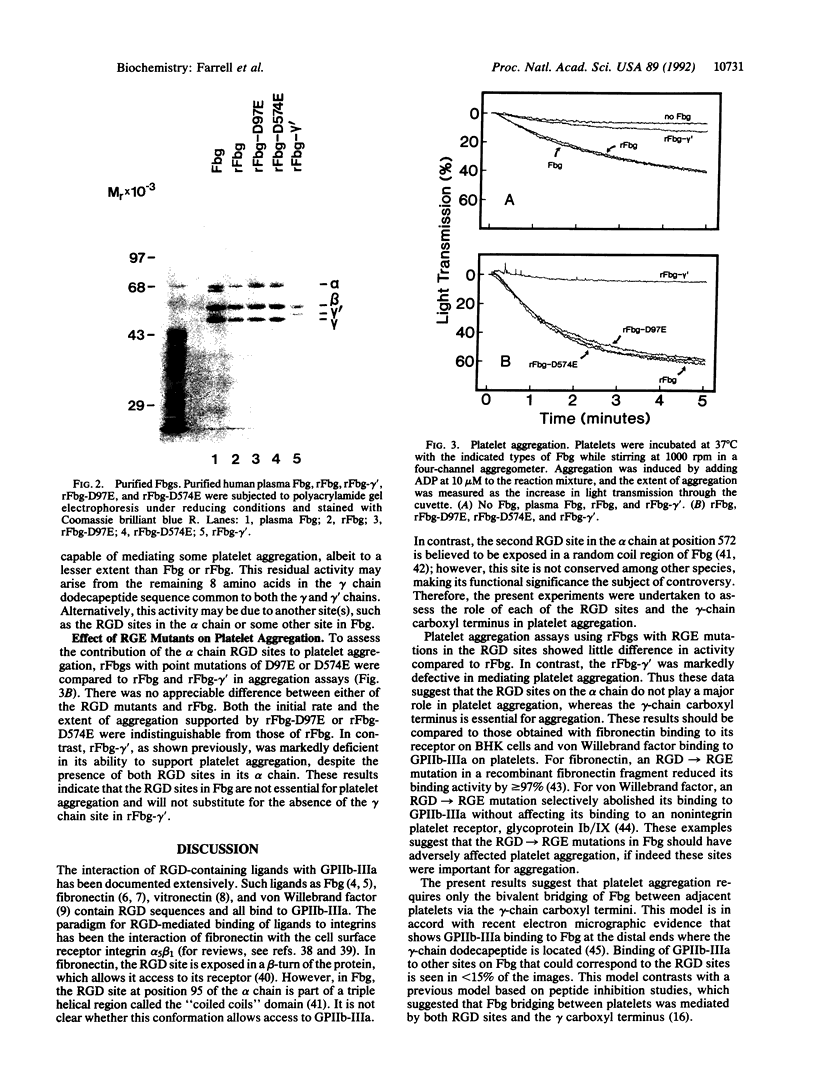
Fibrinogen (Fbg) mediates platelet aggregation by its interaction with the platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa (integrin alpha IIb beta 3). Peptides containing the amino acid sequence RGD derived from the alpha chain (residues alpha 95-97 and residues alpha 572-574) and the sequence HHLGGAKQAGDV derived from the carboxyl terminus of the gamma chain of Fbg (residues gamma 400-411) inhibit these interactions. To determine the role of these sequences in intact Fbg, recombinant human Fbg (rFbg), mutant rFbgs with an RGD-->RGE substitution at either position alpha 97 or alpha 574, and a rFbg gamma'-containing variant that has a carboxyl-terminal interruption in the HHLGGAKQAGDV sequence have been expressed in transfected BHK cells. Purified rFbg and the two RGE mutant Fbgs were similar to plasma Fbg in platelet aggregation assays. In contrast, the gamma' variant Fbg was markedly defective in platelet aggregation. These data support the proposals that the carboxyl-terminal region of the gamma chain of Fbg is essential for optimal platelet aggregation and that the alpha-chain RGD sequences are neither necessary nor sufficient for platelet aggregation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beacham D. A., Wise R. J., Turci S. M., Handin R. I. Selective inactivation of the Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDS) binding site in von Willebrand factor by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3409–3415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. S., Vilaire G. Exposure of platelet fibrinogen receptors by ADP and epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1393–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI109597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Nannizzi L., Phillips D. R., Hsu M. A., Scarborough R. M. Inhibition of fibrinogen binding to GP IIb-IIIa by a GP IIIa peptide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1415–1421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Berliner S. A., Vicente V., Ruggeri Z. M. Recognition of distinct adhesive sites on fibrinogen by related integrins on platelets and endothelial cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):945–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Davie E. W. gamma and gamma' chains of human fibrinogen are produced by alternative mRNA processing. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4232–4236. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Ginsberg M. H., Burke T. A., Lam S. C., Plow E. F. Localization of an Arg-Gly-Asp recognition site within an integrin adhesion receptor. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):91–93. doi: 10.1126/science.3262922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Ginsberg M. H., Matsueda G. R., Plow E. F. A discrete sequence in a platelet integrin is involved in ligand recognition. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):66–68. doi: 10.1038/350066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Goldbaum D. M., Doolittle L. R. Designation of sequences involved in the "coiled-coil" interdomainal connections in fibrinogen: constructions of an atomic scale model. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 5;120(2):311–325. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Watt K. W., Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Riley M. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):464–468. doi: 10.1038/280464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell D. H., Mulvihill E. R., Huang S. M., Chung D. W., Davie E. W. Recombinant human fibrinogen and sulfation of the gamma' chain. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 1;30(39):9414–9420. doi: 10.1021/bi00103a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Cummings D. E., Comeau C. M., Kant J. A., Crabtree G. R. Structure of the human gamma-fibrinogen gene. Alternate mRNA splicing near the 3' end of the gene produces gamma A and gamma B forms of gamma-fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12826–12830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Marder V. J., Martin S. E. Demonstration of a large molecular weight variant of the gamma chain of normal human plasma fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5599–5604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris P. J., Peerschke E. I., Marder V. J., Francis C. W. The C-terminal sequences of the gamma 57.5 chain of human fibrinogen constitute a plasmin sensitive epitope that is exposed in crosslinked fibrin. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2437–2444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Cowan J. F., Yamada K. M., Santoro S. A. Inhibition of platelet adhesion to fibronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor substrates by a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from the cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):946–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Kloczewiak M., Bednarek M. A., Timmons S. Platelet receptor recognition domains on the alpha chain of human fibrinogen: structure-function analysis. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2909–2914. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Timmons S., Kloczewiak M., Strong D. D., Doolittle R. F. gamma and alpha chains of human fibrinogen possess sites reactive with human platelet receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2068–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. C., Mahmoud M., Gaffney P. J. The ability of fibrinogen fragments to support ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Thromb Res. 1979;16(3-4):427–435. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kant J. A., Lord S. T., Crabtree G. R. Partial mRNA sequences for human A alpha, B beta, and gamma fibrinogen chains: evolutionary and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3953–3957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum N. E., Mosesson M. W., Amrani D. L. Characterization of the gamma chain platelet binding site on fibrinogen fragment D. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2643–2648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloczewiak M., Timmons S., Lukas T. J., Hawiger J. Platelet receptor recognition site on human fibrinogen. Synthesis and structure-function relationship of peptides corresponding to the carboxy-terminal segment of the gamma chain. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. Human platelets possess an inducible and saturable receptor specific for fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5357–5363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Budzynski A. Z., Lipinski B. Significance of the intact polypeptide chains of human fibrinogen in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Blood. 1977 Apr;49(4):635–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Yamada K. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin: separable, synergistic sites mediate adhesive function. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Francis C. W., Marder V. J. Fibrinogen binding to human blood platelets: effect of gamma chain carboxyterminal structure and length. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):385–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Galanakis D. K. The synthetic RGDS peptide inhibits the binding of fibrinogen lacking intact alpha chain carboxyterminal sequences to human blood platelets. Blood. 1987 Mar;69(3):950–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., McEver R. P., Coller B. S., Woods V. L., Jr, Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. Related binding mechanisms for fibrinogen, fibronectin, von Willebrand factor, and thrombospondin on thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid sequences and fibrinogen binding to platelets. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F., Ruoslahti E. Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa: member of a family of Arg-Gly-Asp--specific adhesion receptors. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1559–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.2420006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon M. W., Chan W. Y., Davie E. W., Chung D. W. Characterization of a complementary deoxyribonucleic acid coding for the alpha chain of human fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3237–3244. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A., Lawing W. J., Jr Competition for related but nonidentical binding sites on the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex by peptides derived from platelet adhesive proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Bednarek M. A., Kloczewiak M., Hawiger J. Antiplatelet "hybrid" peptides analogous to receptor recognition domains on gamma and alpha chains of human fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2919–2923. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Hawiger J. Isolation of human platelets by albumin gradient and gel filtration. Methods Enzymol. 1989;169:11–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)69046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisel J. W., Stauffacher C. V., Bullitt E., Cohen C. A model for fibrinogen: domains and sequence. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1388–1391. doi: 10.1126/science.4071058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Mosesson M. W. Carboxy-terminal amino acid sequence of a human fibrinogen gamma-chain variant (gamma'). Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6146–6149. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Mosesson M. W. Human plasma fibrinogen heterogeneity: evidence for an extended carboxyl-terminal sequence in a normal gamma chain variant (gamma'). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]