Abstract
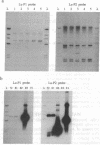
We have cloned two DNA elements (Lu-P1 and Lu-P2) from the Australian sheep blowfly Lucilia cuprina that are similar to the transposable P element of Drosophila melanogaster in both structure and sequence but have diverged from it and from each other considerably. Hybridization studies indicate that a third related element probably exists in another, as yet unsequenced, clone. Neither Lu-P1 nor Lu-P2 appears to be active in terms of mobility, and it is not known whether any transposition-competent copies of other related elements occur in the genome of the blowfly. However, the isolation of any P-like sequences from a species outside of the family Drosophilidae allows comparisons to be made of more widely divergent P-related elements than has been possible previously. We are unaware of any report of the presence of multiple P-like family members within a single species. The discovery of Lu-P1 and Lu-P2 in the blowfly fuels the possibility that similar elements may be widespread in insects, and perhaps in other orders of animals.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Wong J. K., Fitzpatrick V. D., Moyle M., Ingles C. J. The C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Drosophila melanogaster, and mammals: a conserved structure with an essential function. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):321–329. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Spierer P., Hogness D. S. Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Wilson A. C. Molecular evolution in Drosophila and the higher Diptera II. A time scale for fly evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02100622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvi B. R., Hong T. J., Findley S. D., Gelbart W. M. Evidence for a common evolutionary origin of inverted repeat transposons in Drosophila and plants: hobo, Activator, and Tam3. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):465–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capy P., Maruyama K., David J. R., Hartl D. L. Insertion sites of the transposable element mariner are fixed in the genome of Drosophila sechellia. J Mol Evol. 1991 Nov;33(5):450–456. doi: 10.1007/BF02103137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn A. F., Howells A. J., Whitten M. J. Recombinant DNA technology and genetic control of pest insects. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1984;2:69–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Kelley R., Spradling A. Insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila genome with single P elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1121–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.2830671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. B., Peterson K. R., Strausbaugh L. D., Kidwell M. G., Chovnick A. Evidence for horizontal transmission of the P transposable element between Drosophila species. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):339–355. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elizur A., Vacek A. T., Howells A. J. Cloning and characterization of the white and topaz eye color genes from the sheep blowfly Lucilia cuprina. J Mol Evol. 1990 Apr;30(4):347–358. doi: 10.1007/BF02101889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. W., Medhora M. M., Hartl D. L. Molecular structure of a somatically unstable transposable element in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8684–8688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi S., Liu X. J., Frommer W. B., Köster-Töpfer M., Willmitzer L. Identification and structural characterization of further DNA elements in the potato and pepper genomes homologous to the transposable element-like insertion Tst1. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Dec;230(3):494–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00280308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidholm D. A., Gudmundsson G. H., Boman H. G. A highly repetitive, mariner-like element in the genome of Hyalophora cecropia. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11518–11521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. J., Hagemann S., Reiter E., Pinsker W. P-element homologous sequences are tandemly repeated in the genome of Drosophila guanche. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4018–4022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawrath C., Schell J., Koncz C. Homologous domains of the largest subunit of eucaryotic RNA polymerase II are conserved in plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):65–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00315798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paricio N., Pérez-Alonso M., Martínez-Sebastián M. J., de Frutos R. P sequences of Drosophila subobscura lack exon 3 and may encode a 66 kd repressor-like protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6713–6718. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins H. D., Bedo D. G., Howells A. J. Characterization and chromosomal distribution of a tandemly repeated DNA sequence from the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Chromosoma. 1992 Mar;101(5-6):358–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00346015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Benkovic S. J., Schimmel P. R. A DNA fragment with an alpha-phosphorothioate nucleotide at one end is asymmetrically blocked from digestion by exonuclease III and can be replicated in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7350–7354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C. Regulation of Drosophila P element transposition. Trends Genet. 1991 Sep;7(9):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90309-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonelig M., Anxolabéhère D. A P element of Scaptomyza pallida is active in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6102–6106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streck R. D., Macgaffey J. E., Beckendorf S. K. The structure of hobo transposable elements and their insertion sites. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3615–3623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobus U., Bäumlein H., Bogachev S. S., Borisevich I. V., Panitz R., Kolesnikov N. N. A new transposable element in Chironomus thummi. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):311–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00633834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]