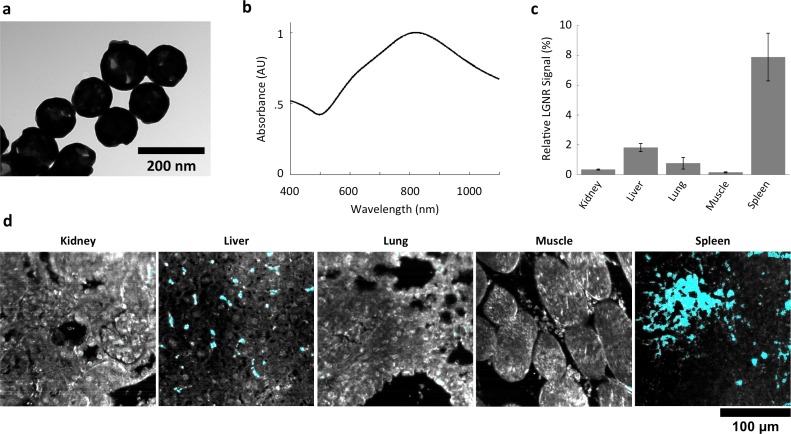
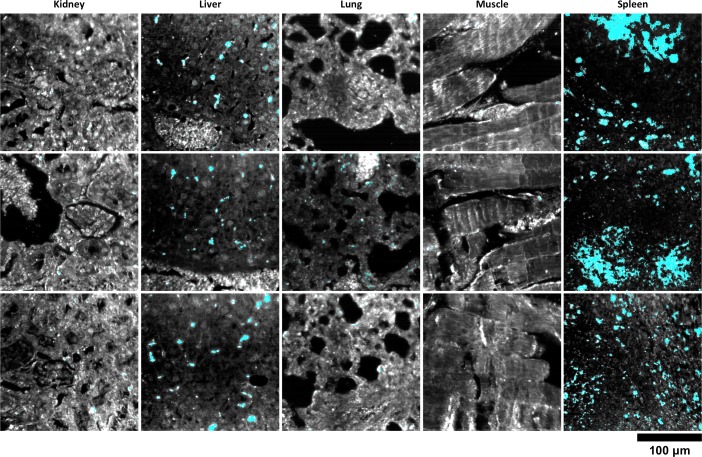
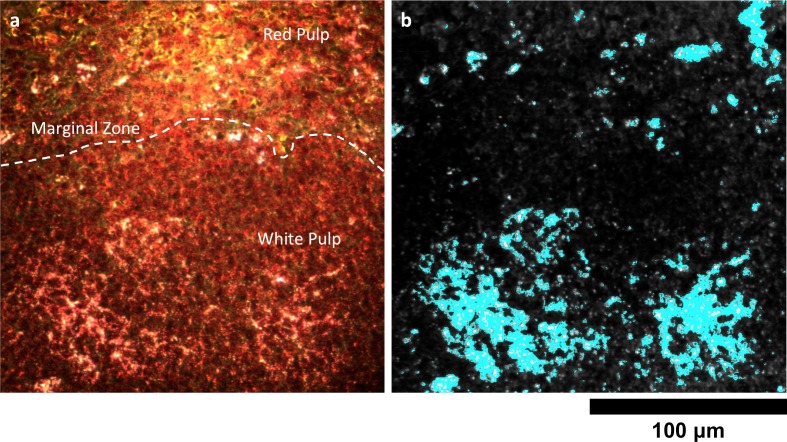
Figure 6. Characterization of gold nanoshell uptake after intravenous administration.
(a,b) Nanoshells (119 nm silica core with 14 nm-thick gold coating) exhibit distinct particle morphology and composition (a) that (like LGNRs) yield a near-infrared (~800 nm) spectral peak (b). However, the Nanoshell spectrum is markedly broader than the resonance observed for LGNRs. (c,d) HSM-AD revealed that Nanoshell uptake displays inter-organ distribution patterns somewhat similar to those observed for LGNRs, with maximal accumulation in the spleen (c). Values are represented as mean ± s.e.m. from four FOVs per tissue. However, there are notable distinctions including minimal Nanoshell uptake within kidney tissue and concentration of Nanoshells within splenic white pulp (d) (Nanoshell+ pixels are depicted in cyan).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.16352.033