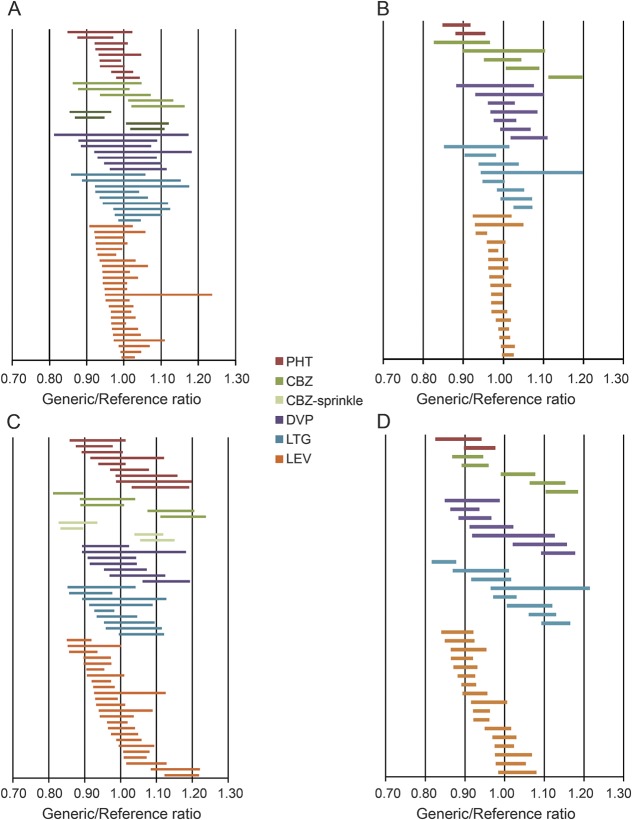
In the article “Assessing bioequivalence of generic modified-release antiepileptic drugs” by E.L. Johnson et al.,1 there is an error in figure 2, panels A and B (depicting lamotrigine 90% confidence intervals). Please find the corrected figure below, showing the area under the curve for lamotrigine bioequivalence studies conducted in the fasting (A) and fed (B) states. The authors regret the error.
Figure 2. Ninety percent confidence intervals for AUC and Cmax generic/reference ratios.
Ninety percent confidence intervals of generic/reference ratios for each product: total drug exposure (AUC) (A and B) and Cmax (C and D) under fed and fasting conditions ([A] AUC under fasting conditions; [B] AUC under fed conditions; [C] Cmax under fasting conditions; and [D] Cmax under fed conditions). The majority of confidence intervals include 1.00. AUC = area under the curve; CBZ = carbamazepine; Cmax = maximum concentration; DVP = divalproex; LEV = levetiracetam; LTG = lamotrigine; PHT = phenytoin.
REFERENCE
- 1.Johnson EL, Chang YT, Davit B, Gidal BE, Krauss GL. Assessing bioequivalence of generic modified-release antiepileptic drugs. Neurology 2016;86:1597–1604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]