Abstract
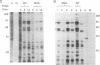
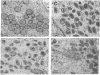
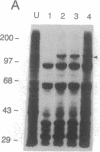
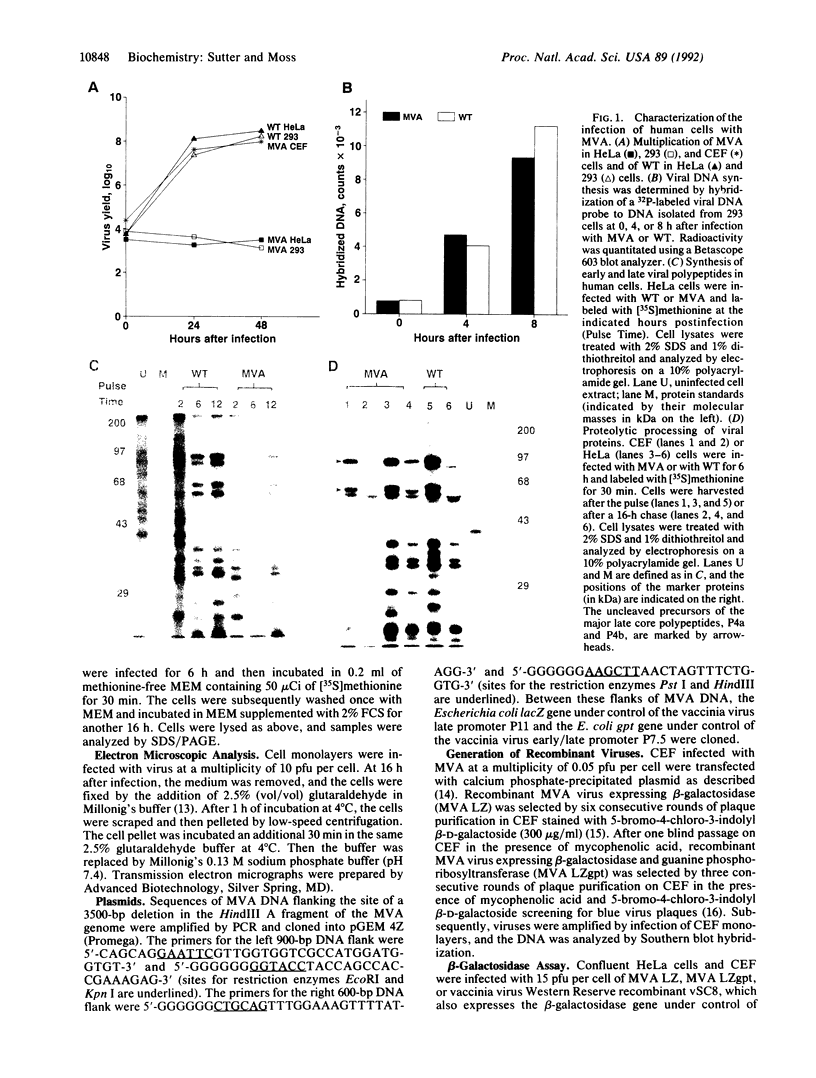
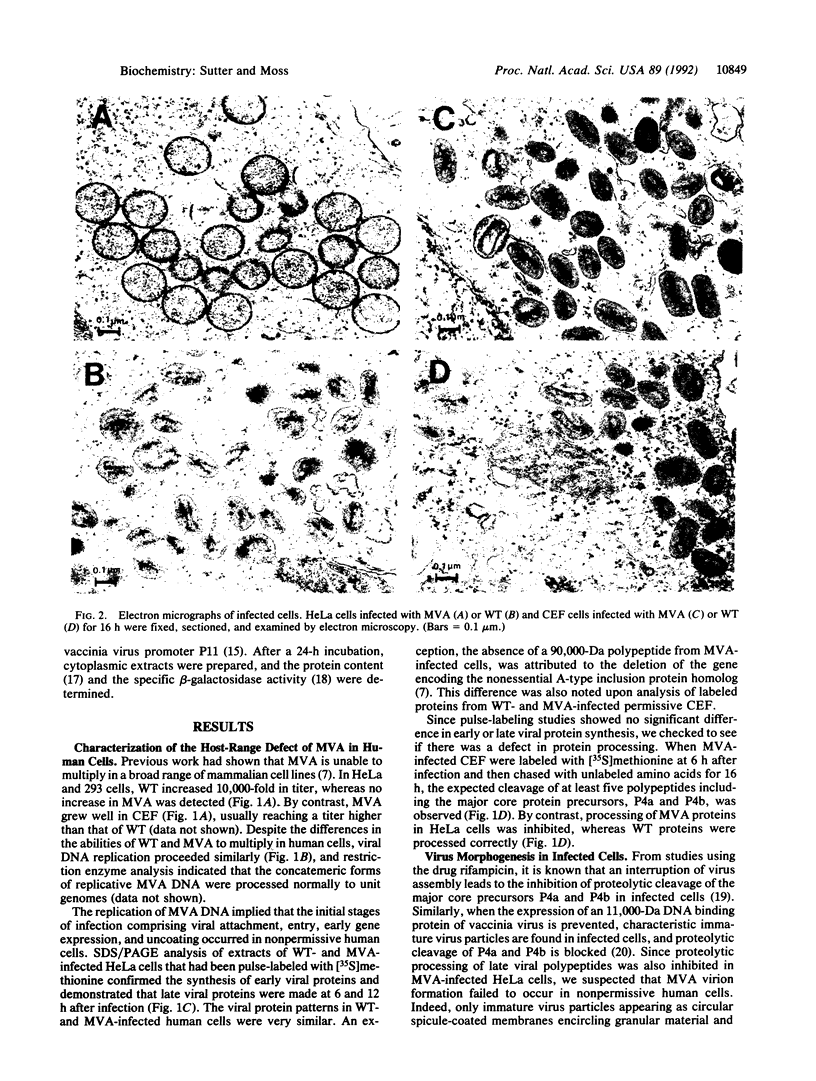
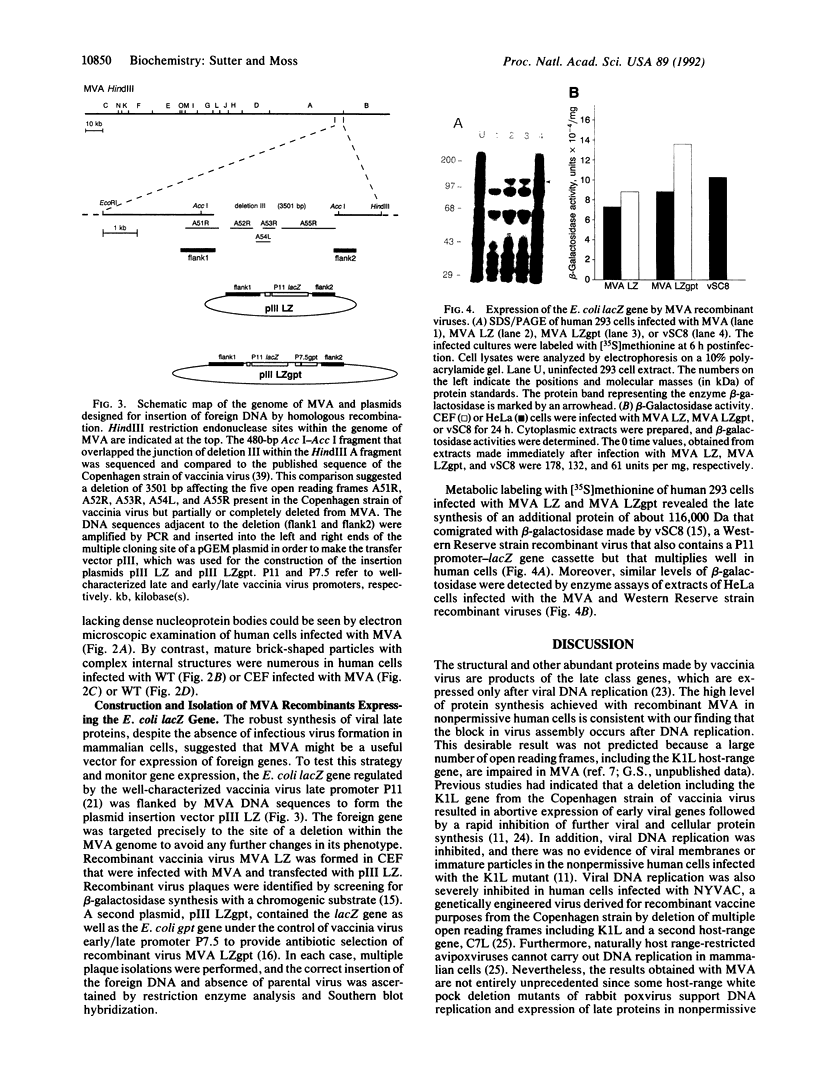
Modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA), a highly attenuated vaccinia virus strain that has been safety tested in humans, was evaluated for use as an expression vector. MVA has multiple genomic deletions and is severely host cell restricted: it grows well in avian cells but is unable to multiply in human and most other mammalian cells tested. Nevertheless, we found that replication of viral DNA appeared normal and that both early and late viral proteins were synthesized in human cells. Proteolytic processing of viral structural proteins was inhibited, however, and only immature virus particles were detected by electron microscopy. We constructed an insertion plasmid with the Escherichia coli lacZ gene under the control of the vaccinia virus late promoter P11, flanked by sequences of MVA DNA, to allow homologous recombination at the site of a naturally occurring 3500-base-pair deletion within the MVA genome. MVA recombinants were isolated and propagated in permissive avian cells and shown to express the enzyme beta-galactosidase upon infection of nonpermissive human cells. The amount of enzyme made was similar to that produced by a recombinant of vaccinia virus strain Western Reserve, which also had the lacZ gene under control of the P11 promoter, but multiplied to high titers. Since recombinant gene expression is unimpaired in nonpermissive human cells, MVA may serve as a highly efficient and exceptionally safe vector.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenburger W., Süter C. P., Altenburger J. Partial deletion of the human host range gene in the attenuated vaccinia virus MVA. Arch Virol. 1989;105(1-2):15–27. doi: 10.1007/BF01311113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxby D., Paoletti E. Potential use of non-replicating vectors as recombinant vaccines. Vaccine. 1992;10(1):8–9. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90411-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertholet C., Stocco P., Van Meir E., Wittek R. Functional analysis of the 5' flanking sequence of a vaccinia virus late gene. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1951–1957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom D. C., Edwards K. M., Hager C., Moyer R. W. Identification and characterization of two nonessential regions of the rabbitpox virus genome involved in virulence. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1530–1542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1530-1542.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Chakrabarti S., Cooper J. A., Twardzik D. R., Moss B. Deletion of the vaccinia virus growth factor gene reduces virus virulence. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):866–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.866-874.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Smith G. L., Cremer K., Notkins A. L., Moss B. Decreased virulence of recombinant vaccinia virus expression vectors is associated with a thymidine kinase-negative phenotype. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):813–815. doi: 10.1038/317813a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadoz M., Strady A., Meignier B., Taylor J., Tartaglia J., Paoletti E., Plotkin S. Immunisation with canarypox virus expressing rabies glycoprotein. Lancet. 1992 Jun 13;339(8807):1429–1432. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92027-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child S. J., Palumbo G. J., Buller R. M., Hruby D. E. Insertional inactivation of the large subunit of ribonucleotide reductase encoded by vaccinia virus is associated with reduced virulence in vivo. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):625–629. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90119-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallo S., Maa J. S., Rodriguez J. R., Rodriguez D., Esteban M. Humoral immune response elicited by highly attenuated variants of vaccinia virus and by an attenuated recombinant expressing HIV-1 envelope protein. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Koehren F., Kirn A. Host range deletion mutant of vaccinia virus defective in human cells. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):488–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Spehner D., Kirn A. Host range restriction of vaccinia virus in Chinese hamster ovary cells: relationship to shutoff of protein synthesis. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.843-850.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Moss B. Escherichia coli gpt gene provides dominant selection for vaccinia virus open reading frame expression vectors. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1849-1854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard S., Spehner D., Drillien R., Kirn A. Localization and sequence of a vaccinia virus gene required for multiplication in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5573–5577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel S. J., Johnson G. P., Perkus M. E., Davis S. W., Winslow J. P., Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):247-66, 517-63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs S. N., Kotwal G. J., Moss B. Vaccinia virus complement-control protein prevents antibody-dependent complement-enhanced neutralization of infectivity and contributes to virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Moss B. Formation of a vaccinia virus structural polypeptide from a higher molecular weight precursor: inhibition by rifampicin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):677–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Hügin A. W., Moss B. Mapping and insertional mutagenesis of a vaccinia virus gene encoding a 13,800-Da secreted protein. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90627-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Roos J. M., McGuigan L. C., Smith K. A., Cormier N., Cohen L. K., Roberts B. E., Payne L. G. Molecular attenuation of vaccinia virus: mutant generation and animal characterization. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2617–2630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2617-2630.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. General method for production and selection of infectious vaccinia virus recombinants expressing foreign genes. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.857-864.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr A., Stickl H., Müller H. K., Danner K., Singer H. Der Pockenimpfstamm MVA: Marker, genetische Struktur, Erfahrungen mit der parenteralen Schutzimpfung und Verhalten im abwehrgeschwächten Organismus. Zentralbl Bakteriol B. 1978 Dec;167(5-6):375–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M., Moss B. Resolution of vaccinia virus DNA concatemer junctions requires late-gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1595–1603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1595-1603.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H., Sutter G., Mayr A. Mapping of deletions in the genome of the highly attenuated vaccinia virus MVA and their influence on virulence. J Gen Virol. 1991 May;72(Pt 5):1031–1038. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-5-1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Regulation of vaccinia virus transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:661–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Vaccinia virus: a tool for research and vaccine development. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1662–1667. doi: 10.1126/science.2047875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Graves R. L. The white pock mutants of rabbit poxvirus. IV. The late white pock (mu) host range (hr) mutants of rabbit poxvirus are blocked in morphogenesis. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):332–346. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shida H., Hinuma Y., Hatanaka M., Morita M., Kidokoro M., Suzuki K., Maruyama T., Takahashi-Nishimaki F., Sugimoto M., Kitamura R. Effects and virulences of recombinant vaccinia viruses derived from attenuated strains that express the human T-cell leukemia virus type I envelope gene. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4474–4480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4474-4480.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickl H., Hochstein-Mintzel V., Mayr A., Huber H. C., Schäfer H., Holzner A. MVA-Stufenimpfung gegen Pocken. Klinische Erprobung des attenuierten Pocken-Lebendimpfstoffes, Stamm MVA. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1974 Nov 22;99(47):2386–2392. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1108143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia J., Perkus M. E., Taylor J., Norton E. K., Audonnet J. C., Cox W. I., Davis S. W., van der Hoeven J., Meignier B., Riviere M. NYVAC: a highly attenuated strain of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):217–232. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90752-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Trimarchi C., Weinberg R., Languet B., Guillemin F., Desmettre P., Paoletti E. Efficacy studies on a canarypox-rabies recombinant virus. Vaccine. 1991 Mar;9(3):190–193. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90152-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Weinberg R., Tartaglia J., Richardson C., Alkhatib G., Briedis D., Appel M., Norton E., Paoletti E. Nonreplicating viral vectors as potential vaccines: recombinant canarypox virus expressing measles virus fusion (F) and hemagglutinin (HA) glycoproteins. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90321-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. F., Moss B. Vaccinia virus morphogenesis is interrupted when expression of the gene encoding an 11-kilodalton phosphorylated protein is prevented by the Escherichia coli lac repressor. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6101–6110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6101-6110.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]