Abstract
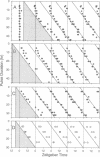
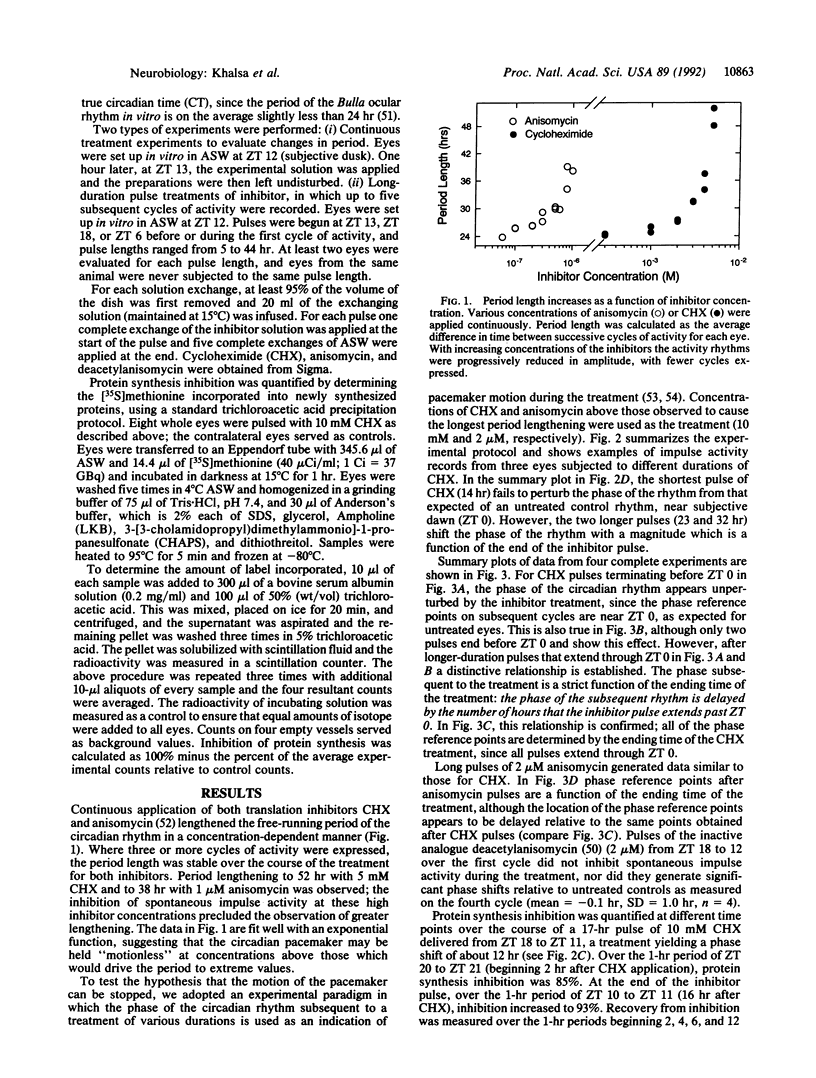
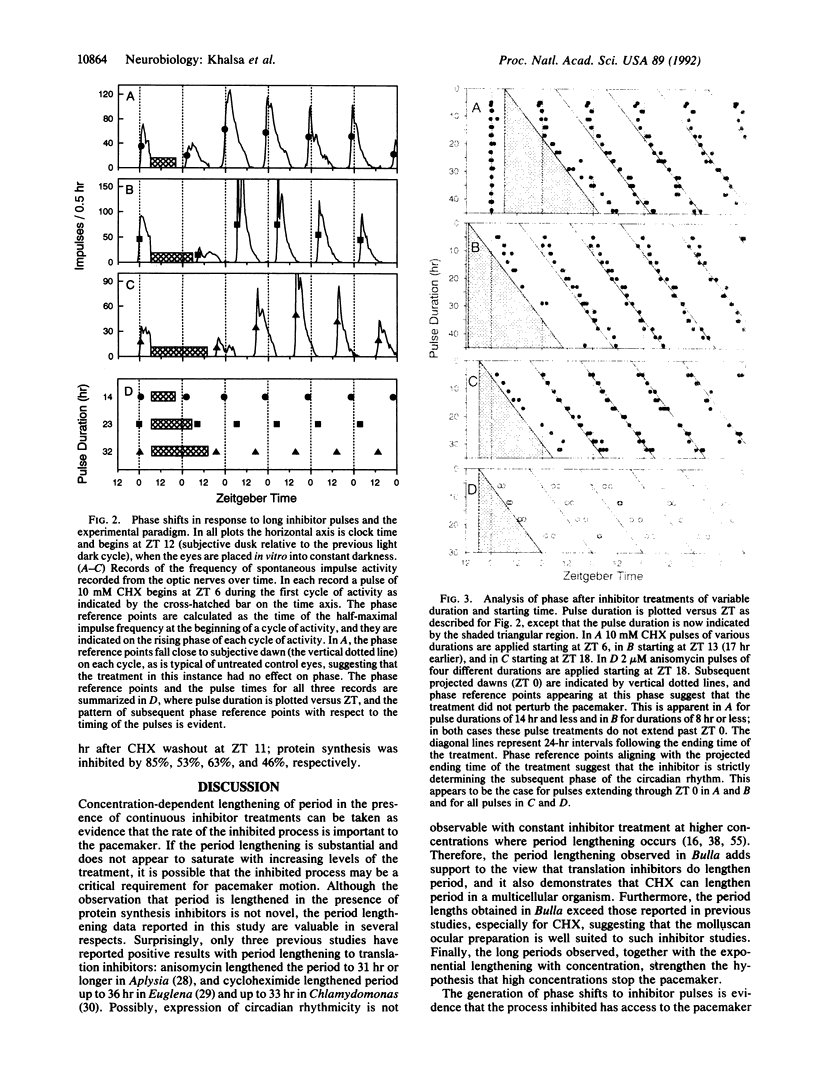
The requirement for protein synthesis in the mechanism of a circadian pacemaker was investigated by using inhibitors of protein synthesis. Continuous treatment of the ocular circadian pacemaker of the mollusc Bulla gouldiana with anisomycin or cycloheximide substantially lengthened (up to 39 and 52 hr, respectively) the free-running period of the rhythm. To determine whether high concentrations of inhibitor could stop the pacemaker, long pulse treatments of various durations (up to 44 hr) were applied and the subsequent phase of the rhythm was assayed. The observed phases of the rhythm after the treatments were a function of the time of the end of the treatment pulse, but only for treatments which spanned subjective dawn. The results provide evidence that protein synthesis is required in a phase-dependent manner for motion of the circadian pacemaker to continue.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronin N., Sagar S. M., Sharp F. R., Schwartz W. J. Light regulates expression of a Fos-related protein in rat suprachiasmatic nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5959–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broda H., Johnson C. H., Taylor W. R., Hastings J. W. Temperature dependence of phase response curves for drug-induced phase shifts. J Biol Rhythms. 1989 Fall;4(3):327–333. doi: 10.1177/074873048900400302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronelius G., Rensing L. Can phase response curves of various treatments of circadian rhythms be explained by effects on protein synthesis and degradation? Biosystems. 1982;15(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(82)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap J. C. Closely watched clocks: molecular analysis of circadian rhythms in Neurospora and Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1990 May;6(5):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90151-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap J. C., Feldman J. F. On the role of protein synthesis in the circadian clock of Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1096–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehret C. F., Trucco E. Molecular models for the circadian clock. I. The chronon concept. J Theor Biol. 1967 May;15(2):240–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. F. Lengthening the period of a biological clock in Euglena by cycloheximide, an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1080–1087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Mutations and molecules influencing biological rhythms. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:373–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin P. E., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Feedback of the Drosophila period gene product on circadian cycling of its messenger RNA levels. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):536–540. doi: 10.1038/343536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig R., Schweiger M., Schweiger R., Schweiger H. G. Identification of a high molecular weight polypeptide that may be part of the circadian clockwork in Acetabularia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6899–6902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S. T., Takahashi J. S., Wollnik F., Turek F. W. Inhibitor of protein synthesis phase shifts a circadian pacemaker in mammalian SCN. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):R1055–R1058. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1988.255.6.R1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacklet J. W. Circadian rhythm from the eye of Aplysia: temperature compensation of the effects of protein synthesis inhibitors. J Exp Biol. 1980 Feb;84:1–15. doi: 10.1242/jeb.84.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacklet J. W. Neuronal circadian rhythm: phase shifting by a protein synthesis inhibitor. Science. 1977 Oct 7;198(4312):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.897685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacklet J. W. Protein synthesis requirement of the Aplysia circadian clock. Tested by active and inactive derivatives of the inhibitor anisomycin. J Exp Biol. 1980 Apr;85:33–42. doi: 10.1242/jeb.85.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAKASHIAN M. W., HASTINGS J. W. The inhibition of a biological clock by actinomycin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2130–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakashian M. W., Schweiger H. G. Evidence for a cycloheximide-sensitive component in the biological clock of Acetabularia. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Mar 15;98(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakashian M. W., Schweiger H. G. Temperature dependence of cycloheximide-sensitive phase of circadian cycle in Acetabularia mediterranea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3216–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalsa S. B., Ralph M. R., Block G. D. Does low intracellular pH stop the motion of the Bulla circadian pacemaker? J Neurosci. 1991 Sep;11(9):2672–2679. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-09-02672.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornhauser J. M., Nelson D. E., Mayo K. E., Takahashi J. S. Photic and circadian regulation of c-fos gene expression in the hamster suprachiasmatic nucleus. Neuron. 1990 Aug;5(2):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90303-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergenhagen D., Schweiger H. G. The effect of different inhibitors of transcription and translation on the expression and control of circadian rhythm in individual cells of Acetabularia. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Sep;94(2):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90499-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima H., Perlman J., Feldman J. F. Cycloheximide-induced phase shifting of circadian clock of Neurospora. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):R31–R35. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1981.241.1.R31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima H., Perlman J., Feldman J. F. Genetic evidence that protein synthesis is required for the circadia clock of neurospora. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):361–362. doi: 10.1126/science.212.4492.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesiak W., Ungar A., Johnson C. H., Hastings J. W. Are protein synthesis inhibition and phase shifting of the circadian clock in Gonyaulax correlated? J Biol Rhythms. 1987 Summer;2(2):121–138. doi: 10.1177/074873048700200204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTENDRIGH C. S. Circadian rhythms and the circadian organization of living systems. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1960;25:159–184. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1960.025.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard R. G., Lickey M. E. In vitro resetting of the circadian clock in the Aplysia eye. I. Importance of efferent activity in optic nerve. J Neurosci. 1981 Aug;1(8):835–839. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-08-00835.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju U., Koumenis C., Nunez-Regueiro M., Eskin A. Alteration of the phase and period of a circadian oscillator by a reversible transcription inhibitor. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.1871602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju U., Yeung S. J., Eskin A. Involvement of proteins in light resetting ocular circadian oscillators of Aplysia. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):R256–R262. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.258.1.R256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rensing L., Hardeland R. The cellular mechanism of circadian rhythms--a view on evidence, hypotheses and problems. Chronobiol Int. 1990;7(5-6):353–370. doi: 10.3109/07420529009059146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Hall J. C. The molecular biology of circadian rhythms. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman B. S., Strumwasser F. Manipulation of a neuronal circadian oscillator with inhibitors of macromolecular synthesis. Fed Proc. 1977 Jun;36(7):2050–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman B. S., Strumwasser F. Phase shifting the circadian rhythm of neuronal activity in the isolated Aplysia eye with puromycin and cycloheximide. Electrophysiological and biochemical studies. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Oct;68(4):359–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.4.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusak B., Robertson H. A., Wisden W., Hunt S. P. Light pulses that shift rhythms induce gene expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1237–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2112267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger H. G., Hartwig R., Schweiger M. Cellular aspects of circadian rhythms. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:181–200. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siwicki K. K., Eastman C., Petersen G., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. Antibodies to the period gene product of Drosophila reveal diverse tissue distribution and rhythmic changes in the visual system. Neuron. 1988 Apr;1(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strumwasser F. A short history of the second messenger concept in neurons and lessons from long lasting changes in two neuronal systems producing afterdischarge and circadian oscillations. J Physiol (Paris) 1988;83(3):246–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi J. S. Circadian rhythms: from gene expression to behavior. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Dec;1(4):556–561. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(05)80028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi J. S., Murakami N., Nikaido S. S., Pratt B. L., Robertson L. M. The avian pineal, a vertebrate model system of the circadian oscillator: cellular regulation of circadian rhythms by light, second messengers, and macromolecular synthesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1989;45:279–352. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571145-6.50010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi J. S., Turek F. W. Anisomycin, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, perturbs the phase of a mammalian circadian pacemaker. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 3;405(1):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Dunlap J. C., Hastings J. W. Inhibitors of protein synthesis on 80S ribosomes phase shift the Gonyaulax clock. J Exp Biol. 1982 Apr;97:121–136. doi: 10.1242/jeb.97.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollnik F., Turek F. W., Majewski P., Takahashi J. S. Phase shifting the circadian clock with cycloheximide: response of hamsters with an intact or a split rhythm of locomotor activity. Brain Res. 1989 Sep 4;496(1-2):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung S. J., Eskin A. Involvement of a specific protein in the regulation of a circadian rhythm in Aplysia eye. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):279–283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]