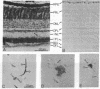
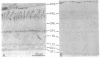
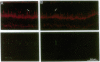
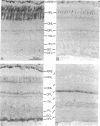
Abstract
Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) involved in transmembrane signal-transduction processes are heterotrimers composed of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. The alpha subunit shows great diversity and is thought to confer functional specificity to a particular G protein. By contrast, the beta and gamma subunits appear much less diverse; in particular, the beta subunit is believed to have no role in G protein specificity. Using immunocytochemistry, we found distinct distribution patterns for different beta and gamma subunits in the retina. In particular, rod and cone photoreceptors, which both subserve phototransduction but differ in light-response properties, have different beta and gamma subunits in their outer segments. Thus, the G protein mediating phototransduction shows cell-specific forms of the beta and gamma subunits in addition to the alpha subunit. This surprising finding supports the hypothesis that these subunits may also contribute to functional specificity of a G protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Gautam N., Fong H. K., Northup J. K., Simon M. I. The 35- and 36-kDa beta subunits of GTP-binding regulatory proteins are products of separate genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5008–5011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boycott B. B., Dowling J. E., Fisher S. K., Kolb H., Laties A. M. Interplexiform cells of the mammalian retina and their comparison with catecholamine-containing retinal cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Dec 2;191(1104):353–368. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Ionic channels and their regulation by G protein subunits. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:197–213. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Graziano M. P., Gilman A. G. G protein beta gamma subunits from bovine brain and retina: equivalent catalytic support of ADP-ribosylation of alpha subunits by pertussis toxin but differential interactions with Gs alpha. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):611–616. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Gierschik P., Staniszewski C., Benovic J. L., Codina J., Somers R., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Functional differences in the beta gamma complexes of transducin and the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1485–1491. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Stengel D., Woo S. L., Birnbaumer L. Beta-subunits of the human liver Gs/Gi signal-transducing proteins and those of bovine retinal rod cell transducin are identical. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 27;207(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81486-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehinger B. Neurotransmitter systems in the retina. Retina. 1982;2(4):305–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Fawzi A., Fraser E. D., Brown M. L., Northup J. K. Purification of a beta 35 form of the beta gamma complex common to G-proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher K. J., Aronson N. N., Jr Characterization of the cDNA and genomic sequence of a G protein gamma subunit (gamma 5). Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1585–1591. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Birren B. W., Simon M. I. Distinct forms of the beta subunit of GTP-binding regulatory proteins identified by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3792–3796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Hurley J. B., Hopkins R. S., Miake-Lye R., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F., Simon M. I. Repetitive segmental structure of the transducin beta subunit: homology with the CDC4 gene and identification of related mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao B., Gilman A. G., Robishaw J. D. A second form of the beta subunit of signal-transducing G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6122–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao B., Mumby S., Gilman A. G. The G protein beta 2 complementary DNA encodes the beta 35 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17254–17257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam N., Northup J., Tamir H., Simon M. I. G protein diversity is increased by associations with a variety of gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7973–7977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greferath U., Grünert U., Wässle H. Rod bipolar cells in the mammalian retina show protein kinase C-like immunoreactivity. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Nov 15;301(3):433–442. doi: 10.1002/cne.903010308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Rosenthal W., Birnbaumer L., Neer E. J., Yamazaki A., Bitensky M. W. Characterization by two-dimensional peptide mapping of the gamma subunits of Ns and Ni, the regulatory proteins of adenylyl cyclase, and of transducin, the guanine nucleotide-binding protein of rod outer segments of the eye. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14867–14872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. R., Blanks J. C., Fong H. K., Casey P. J., Hildebrandt E., Simons M. I. Novel localization of a G protein, Gz-alpha, in neurons of brain and retina. J Neurosci. 1990 Aug;10(8):2763–2770. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-08-02763.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipase A2 activity in bovine rod outer segments by the beta gamma subunits of transducin and its inhibition by the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L. Regulation of phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C in rod outer segments of bovine retina involves a common GTP-binding protein but different mechanisms of action. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;559:158–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaho Y., Tsai S. C., Adamik R., Hewlett E. L., Moss J., Vaughan M. Rhodopsin-enhanced GTPase activity of the inhibitory GTP-binding protein of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7378–7381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D., Lewis D. L., Graziadei L., Neer E. J., Bar-Sagi D., Clapham D. E. G-protein beta gamma-subunits activate the cardiac muscarinic K+-channel via phospholipase A2. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):557–560. doi: 10.1038/337557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea C. L., Bunt-Milam A. H., Hurley J. B. Alpha transducin is present in blue-, green-, and red-sensitive cone photoreceptors in the human retina. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea C. L., Somers D. E., Hurley J. B., Klock I. B., Bunt-Milam A. H. Identification of specific transducin alpha subunits in retinal rod and cone photoreceptors. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3529395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. A., Smallwood P. M., Moen P. T., Jr, Helman L. J., Ahn T. G. Molecular cloning of beta 3 subunit, a third form of the G protein beta-subunit polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2329–2333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Entine G. Visual pigments of frog and tadpole (Rana pipiens). Vision Res. 1968 Jul;8(7):761–775. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(68)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews G. Physiological characteristics of single green rod photoreceptors from toad retina. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:347–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire B. A., Stevens J. K., Sterling P. Microcircuitry of bipolar cells in cat retina. J Neurosci. 1984 Dec;4(12):2920–2938. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-12-02920.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kahn R. A., Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. Antisera of designed specificity for subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):265–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani K., Yau K. W. Sodium-dependent calcium extrusion and sensitivity regulation in retinal cones of the salamander. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:525–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawy S., Copenhagen D. R. Multiple classes of glutamate receptor on depolarizing bipolar cells in retina. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):56–58. doi: 10.1038/325056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi K., Kato S., Teranishi T. Dopamine cells and rod bipolar cells contain protein kinase C-like immunoreactivity in some vertebrate retinas. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Dec 5;94(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R., Famiglietti E. V., Jr, Kolb H. Intracellular staining reveals different levels of stratification for on- and off-center ganglion cells in cat retina. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Mar;41(2):472–483. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.2.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y. W., Sharp A. H., Snyder S. H., Yau K. W. Localization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in synaptic terminals in the vertebrate retina. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):525–531. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronin A. N., Gautam N. Interaction between G-protein beta and gamma subunit types is selective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6220–6224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Kalman V. K., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C. A. Existence of two gamma subunits of the G proteins in brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. J., Applebury M. L., Sternweis P. C. Relationships within the family of GTP-binding proteins isolated from bovine central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16242–16249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M. Signal sorting and amplification through G protein-coupled receptors. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M. GTP-binding proteins and their regulatory actions on ion channels. Jpn J Physiol. 1989;39(4):461–474. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.39.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Thomas T. C., Levine M. A., Neer E. J. Specificity of G protein beta and gamma subunit interactions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13807–13810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G., Rosenthal W., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. Role of G proteins in calcium channel modulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiells R. A., Falk G. Glutamate receptors of rod bipolar cells are linked to a cyclic GMP cascade via a G-protein. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Nov 22;242(1304):91–94. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11517–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Pang I. H. The G protein-channel connection. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Apr;13(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90002-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The purified alpha subunits of Go and Gi from bovine brain require beta gamma for association with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):631–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Nukada T., Tanabe T., Takahashi H., Noda M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of the beta-subunit of bovine transducin deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Kaneko A. Identification of bipolar cell subtypes by protein kinase C-like immunoreactivity in the goldfish retina. Vis Neurosci. 1990 Sep;5(3):223–230. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800000298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szél A., Diamantstein T., Röhlich P. Identification of the blue-sensitive cones in the mammalian retina by anti-visual pigment antibody. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 22;273(4):593–602. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1500–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.1962211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikler K. C., Rakic P. Distribution of photoreceptor subtypes in the retina of diurnal and nocturnal primates. J Neurosci. 1990 Oct;10(10):3390–3401. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-10-03390.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita M., Wässle H. Responses of rod bipolar cells isolated from the rat retina to the glutamate agonist 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (APB). J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2372–2382. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02372.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarfitz S., Niemi G. A., McConnell J. L., Fitch C. L., Hurley J. B. A G beta protein in the Drosophila compound eye is different from that in the brain. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90295-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Weizsäcker E., Strathmann M. P., Simon M. I. Diversity among the beta subunits of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins: characterization of a novel beta-subunit cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91650-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]