Abstract
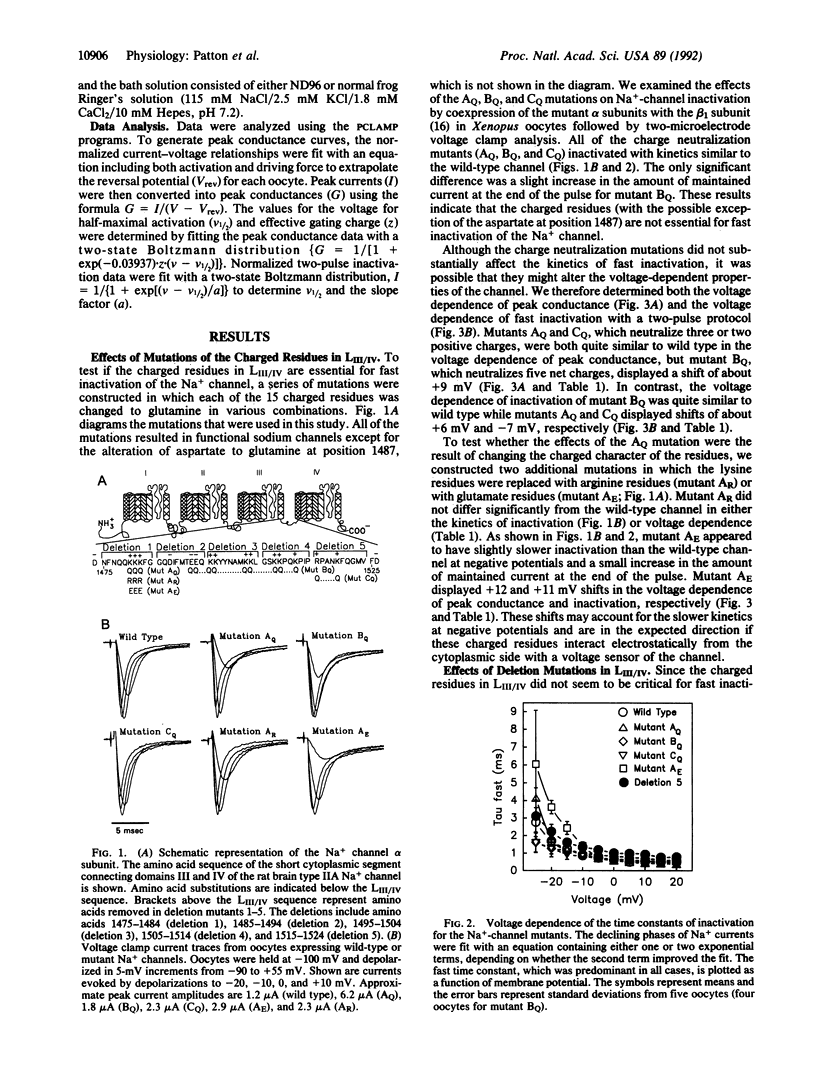
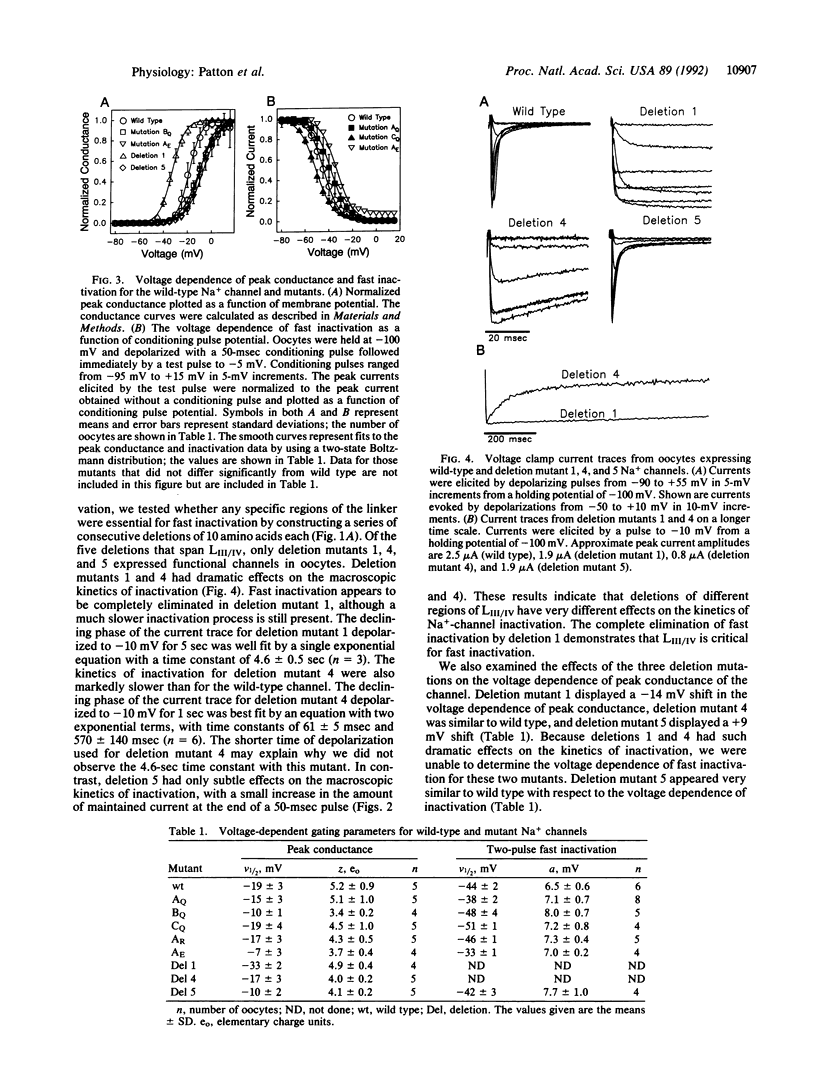
The cytoplasmic linker connecting domains III and IV of the voltage-gated Na+ channel is thought to be involved in fast inactivation. This linker is highly conserved among the various Na+ channels that have been cloned. In the rat brain IIA Na+ channel, it consists of 53 amino acids of which 15 are charged. To investigate the role of this linker in inactivation, we mutated all 15 of the charged residues in various combinations. All but one of these mutants expressed functional channels, and all of these inactivated with kinetics similar to the wild-type channel. We then constructed a series of deletion mutations that span the III-IV linker to determine if any region of the linker is essential for fast inactivation. Deletion of the first 10 amino acids completely eliminated fast inactivation in the channel, whereas deletion of the last 10 amino acids had no substantial effect on inactivation. These results demonstrate that some residues in the amino end of the III-IV linker are critical for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation, but that the highly conserved positively charged and paired negatively charged residues are not essential.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Hayflick J. S., Vasser M., Seeburg P. H. In vitro deletional mutagenesis for bacterial production of the 20,000-dalton form of human pituitary growth hormone. DNA. 1983;2(3):183–193. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Slow changes in currents through sodium channels in frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A neutral amino acid change in segment IIS4 dramatically alters the gating properties of the voltage-dependent sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Marshall J., Dunn J. M., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit with novel gating properties. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):449–461. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cota G., Armstrong C. M. Sodium channel gating in clonal pituitary cells. The inactivation step is not voltage dependent. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Aug;94(2):213–232. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukierman S. Asymmetric electrostatic effects on the gating of rat brain sodium channels in planar lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):845–855. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82118-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonoi T., Hille B. Gating of Na channels. Inactivation modifiers discriminate among models. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Feb;89(2):253–274. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafte D. S., Goldin A. L., Auld V. J., Dunn R. J., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Inactivation of cloned Na channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Oct;96(4):689–706. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafte D. S., Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Evidence for the involvement of more than one mRNA species in controlling the inactivation process of rat and rabbit brain Na channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci. 1988 Aug;8(8):2859–2868. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-02859.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. Changes in sodium channel gating produced by point mutations in a cytoplasmic linker. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):688–691. doi: 10.1126/science.2173138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman J. R., Kirsch G. E., VanDongen A. M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Fast and slow gating of sodium channels encoded by a single mRNA. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. E., Goldin A. L. A voltage-dependent gating transition induces use-dependent block by tetrodotoxin of rat IIA sodium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90376-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozo E., Bezanilla F. Phosphorylation affects voltage gating of the delayed rectifier K+ channel by electrostatic interactions. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):685–690. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Thornhill W. B., Duch D. S., Levinson S. R., Urban B. W. Neuraminidase treatment modifies the function of electroplax sodium channels in planar lipid bilayers. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90221-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P. M., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Inhibition of inactivation of single sodium channels by a site-directed antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8147–8151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Numann R., Murphy B. J., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. A phosphorylation site in the Na+ channel required for modulation by protein kinase C. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.1658937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Patton D. E., Scheuer T., Wang Y., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10910–10914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Aldrich R. W. Restoration of inactivation in mutants of Shaker potassium channels by a peptide derived from ShB. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.2122520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J. Y., Potts J. F., Trimmer J. S., Agnew W. S., Sigworth F. J. Multiple gating modes and the effect of modulating factors on the microI sodium channel. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90280-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


