Abstract
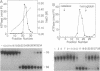
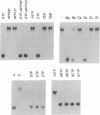
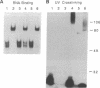
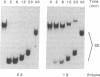
Three distinct nucleic acid-dependent ATPases are packaged within infectious vaccinia virus particles; one of these enzymes (nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase II or NPH-II) is activated by single-stranded RNA. Purified NPH-II is now shown to be an NTP-dependent RNA helicase. RNA unwinding requires a divalent cation and any one of the eight common ribo- or deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates. The enzyme acts catalytically to displace an estimated 10-fold molar excess of duplex RNA under in vitro reaction conditions. NPH-II binds to single-stranded RNA. Turnover of the bound enzyme is stimulated by and coupled to hydrolysis of NTP. Photocrosslinking of radiolabeled RNA to NPH-II results in label transfer to a single 73-kDa polypeptide. The sedimentation properties of the helicase are consistent with NPH-II being a monomer of this protein. Immunoblotting experiments identify NPH-II as the product of the vaccinia virus I8 gene. The I8-encoded protein displays extensive sequence similarity to members of the DE-H family of RNA-dependent NTPases. Mutations in the NPH-II gene [Fathi, Z. & Condit, R.C. (1991) Virology 181, 258-272] define the vaccinia helicase as essential for virus replication in vivo. Encapsidation of NPH-II in the virus particle suggests a role for the enzyme in synthesis of early messenger RNAs by the virion-associated transcription machinery.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Purification and characterization of a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4372–4380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone R. F., Parr R. P., Moss B. Intermolecular duplexes formed from polyadenylylated vaccinia virus RNA. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):365–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.365-374.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. DNA-dependent ATPase activity associated with vaccinia virus early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10761–10765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Yuen L., Shuman S., Moss B. Purification of a factor required for transcription of vaccinia virus early genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10754–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess S., Couto J. R., Guthrie C. A putative ATP binding protein influences the fidelity of branchpoint recognition in yeast splicing. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90086-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Lin R. J. The yeast PRP2 protein, a putative RNA-dependent ATPase, shares extensive sequence homology with two other pre-mRNA splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6447–6447. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Company M., Arenas J., Abelson J. Requirement of the RNA helicase-like protein PRP22 for release of messenger RNA from spliceosomes. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):487–493. doi: 10.1038/349487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathi Z., Condit R. C. Genetic and molecular biological characterization of a vaccinia virus temperature-sensitive complementation group affecting a virion component. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):258–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90491-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathi Z., Condit R. C. Phenotypic characterization of a vaccinia virus temperature-sensitive complementation group affecting a virion component. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90492-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel S. J., Johnson G. P., Perkus M. E., Davis S. W., Winslow J. P., Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):247-66, 517-63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Satler C. A., Merrick W. C. RNA-stimulated ATPase activity of eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8648–8654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler J., Shuman S. Ternary complex formation by vaccinia virus RNA polymerase at an early viral promoter: analysis by native gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2982–2989. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2982-2989.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J., Beeson J. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in vaccinia virus. I. The mechanism of synthesis and release of RNA in vaccinia cores. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Smith J., Claude A., Lin R. J. The purified yeast pre-mRNA splicing factor PRP2 is an RNA-dependent NTPase. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2319–2326. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V., Senkevich T. G. Vaccinia virus encodes four putative DNA and/or RNA helicases distantly related to each other. J Gen Virol. 1992 Apr;73(Pt 4):989–993. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M. I., Kernan M. J., Kreber R., Ganetzky B., Baker B. S. The maleless protein associates with the X chromosome to regulate dosage compensation in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):935–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90439-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. G., Hurwitz J. A new RNA helicase isolated from HeLa cells that catalytically translocates in the 3' to 5' direction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4398–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery C., Richardson J. P. Characterization of the nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase (ATPase) activity of RNA synthesi termination factor p. I. Enzymatic properties and effects of inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1375–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Kaiser-Rogers K. A. DNA helicases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:289–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolette E., Rosemond-Hornbeak H., Moss B. Two nucleid acid-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolases from vaccinia virus. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3273–3280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Two nucleic acid-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolases from vaccinia virus. Nucleotide substrate and polynucleotide cofactor specificities. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3281–3286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. R., Linder P. D-E-A-D protein family of putative RNA helicases. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwer B., Guthrie C. PRP16 is an RNA-dependent ATPase that interacts transiently with the spliceosome. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):494–499. doi: 10.1038/349494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Broyles S. S., Moss B. Purification and characterization of a transcription termination factor from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12372–12380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Moss B. Bromouridine triphosphate inhibits transcription termination and mRNA release by vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21356–21360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Spencer E., Furneaux H., Hurwitz J. The role of ATP in in vitro vaccinia virus RNA synthesis effects of AMP-PNP and ATP gamma S. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5396–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E., Shuman S., Hurwitz J. Purification and properties of vaccinia virus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5388–5395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]