Abstract
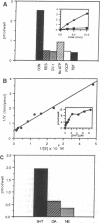
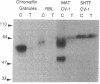
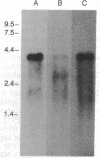
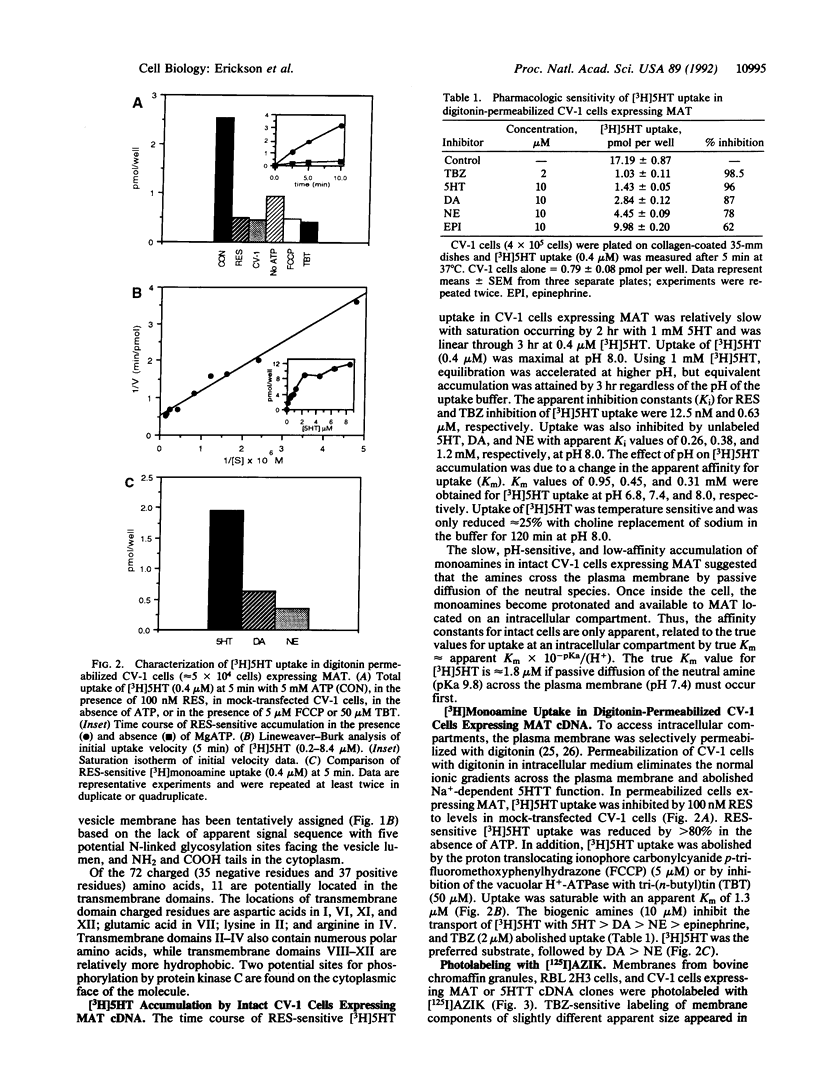
A cDNA for a rat vesicular monoamine transporter, designated MAT, was isolated by expression cloning in a mammalian cell line (CV-1). The cDNA sequence predicts a protein of 515 amino acids with 12 putative membrane-spanning domains. The characteristics of [3H]serotonin accumulation by CV-1 cells expressing the cDNA clone suggested sequestration by an intracellular compartment. In cells permeabilized with digitonin, uptake was ATP dependent with an apparent Km of 1.3 microM. Uptake was abolished by the proton-translocating ionophore carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone and with tri-(n-butyl)tin, an inhibitor of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. The rank order of potency to inhibit uptake was reserpine > tetrabenazine > serotonin > dopamine > norepinephrine > epinephrine. Direct comparison of [3H]monoamine uptake indicated that serotonin was the preferred substrate. Photolabeling of membranes prepared from CV-1 cells expressing MAT with 7-azido-8-[125I]iodoketanserin revealed a predominant tetrabenazine-sensitive photolabeled glycoprotein with an apparent molecular mass of approximately 75 kDa. The mRNA that encodes MAT was present specifically in monoamine-containing cells of the locus coeruleus, substantia nigra, and raphe nucleus of rat brain, each of which expresses a unique plasma membrane reuptake transporter. The MAT cDNA clone defines a vesicular monoamine transporter representing a distinct class of neurotransmitter transport molecules.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. Noradrenaline: fate and control of its biosynthesis. Science. 1971 Aug 13;173(3997):598–606. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3997.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely R. D., Berson H. E., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Caron M. G., Peek M. M., Prince H. K., Bradley C. C. Cloning and expression of a functional serotonin transporter from rat brain. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):66–70. doi: 10.1038/354066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. P., Gasnier B., Roisin M. P., Isambert M. F., Scherman D. Molecular pharmacology of the monoamine transporter of the chromaffin granule membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:194–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. P., Scherman D. Radioligands of the vesicular monoamine transporter and their use as markers of monoamine storage vesicles. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 1;38(15):2395–2404. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. J., Mezey E., Brownstein M. J. Cloning of a serotonin transporter affected by antidepressants. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):579–580. doi: 10.1126/science.1948036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isambert M. F., Gasnier B., Botton D., Henry J. P. Characterization and purification of the monoamine transporter of bovine chromaffin granules. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):1980–1986. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isambert M. F., Gasnier B., Laduron P. M., Henry J. P. Photoaffinity labeling of the monoamine transporter of bovine chromaffin granules and other monoamine storage vesicles using 7-azido-8-[125I]iodoketanserin. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2265–2270. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Jr Accumulation of biological amines into chromaffin granules: a model for hormone and neurotransmitter transport. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jan;68(1):232–307. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Schuldiner S. Mechanism of transport and storage of neurotransmitters. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238709082546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilty J. E., Lorang D., Amara S. G. Cloning and expression of a cocaine-sensitive rat dopamine transporter. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):578–579. doi: 10.1126/science.1948035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Njus D., Kelley P. M., Harnadek G. J. Bioenergetics of secretory vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;853(3-4):237–265. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(87)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacholczyk T., Blakely R. D., Amara S. G. Expression cloning of a cocaine- and antidepressant-sensitive human noradrenaline transporter. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):350–354. doi: 10.1038/350350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada S., Kitayama S., Lin C. L., Patel A., Nanthakumar E., Gregor P., Kuhar M., Uhl G. Cloning and expression of a cocaine-sensitive dopamine transporter complementary DNA. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):576–578. doi: 10.1126/science.1948034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Putative neurotransmitters in the brain: selective neuronal uptake, subcellular localization, and interactions with centrally acting drugs. Biol Psychiatry. 1970 Oct;2(4):367–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern-Bach Y., Greenberg-Ofrath N., Flechner I., Schuldiner S. Identification and purification of a functional amine transporter from bovine chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3961–3966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Proteins of synaptic vesicles involved in exocytosis and membrane recycling. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):665–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]