Abstract
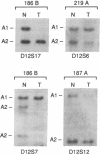
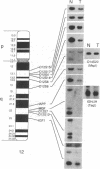
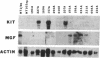
Human male germ cell tumors (GCTs) result from malignant transformation of premeiotic or early meiotic germ cells and exhibit embryonal-like differentiation of the three germinal layers. The genetic basis of origin and expression of differentiated phenotypes by GCTs are poorly understood. Our recent cytogenetic analysis of a large series of GCTs has shown that two chromosome 12 abnormalities, an isochromosome for the short arm [i(12p)] and deletions in the long arm [del(12q)], characterize these tumors, which led us to suggest that the deletions represent loss of one or more candidate tumor suppressor genes whose products regulate the normal proliferation of the spermatogonial stem cells. We undertook a molecular mapping of the deletions by comparing germ-line and tumor genotypes of eight polymorphic loci in paired normal/tumor DNA samples from 45 GCT patients. Analysis of loss of constitutional heterozygosity at these loci revealed two regions of frequent loss (> 40%), one at 12q13 and the other at 12q22, identifying the sites of the postulated tumor suppressor genes. One tumor (no. 143A) exhibited a homozygous deletion of a region of 12q22, which included the MGF gene. The KIT and MGF genes have been shown to play key roles in embryonal and postnatal development of germ cells; therefore, we evaluated their expression by Northern blot analysis in a panel of three GCT cell lines and 24 fresh GCT biopsies. Deregulated expression of MGF and KIT, which was discordant between seminomatous and nonseminomatous lesions, was observed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Williams D. E., Tushinski R., Gimpel S., Eisenman J., Cannizzaro L. A., Aronson M., Croce C. M., Huebner K., Cosman D. Alternate splicing of mRNAs encoding human mast cell growth factor and localization of the gene to chromosome 12q22-q24. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Aug;2(8):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arheden K., Nilbert M., Heim S., Mandahl N., Mitelman F. No amplification or rearrangement of INT1, GLI, or COL2A1 in uterine leiomyomas with t(12;14)(q14-15;q23-24). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Jun;39(2):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arheden K., Rønne M., Mandahl N., Heim S., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Mitelman F. In situ hybridization localizes the human putative oncogene GLI to chromosome subbands 12q13.3-14.1. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):1–2. doi: 10.1007/BF00288260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Murphy J. E., George P. C., Qiu F. H., Bergold P. J., Lederman L., Snyder H. W., Jr, Brodeur D., Zuckerman E. E., Hardy W. D. A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene family. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):415–421. doi: 10.1038/320415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannan C. I., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E., Eisenman J., Anderson D. M., Cosman D., Bedell M. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Steel-Dickie mutation encodes a c-kit ligand lacking transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4671–4674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Maze R., Miyazawa K., Carow C., Hendrie P. C., Cooper S., Hangoc G., Vadhan-Raj S., Lu L. The kit receptor and its ligand, steel factor, as regulators of hemopoiesis. Cancer Cells. 1991 Dec;3(12):480–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buroker N. E., Magenis R. E., Weliky K., Bruns G., Litt M. Four restriction fragment length polymorphisms revealed by probes from a single cosmid map to human chromosome 12q. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):86–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00278825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Dryja T. P., Phillips R. A., Benedict W. F., Godbout R., Gallie B. L., Murphree A. L., Strong L. C., White R. L. Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):779–784. doi: 10.1038/305779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey M. F., Hesketh C., Wainscoat J. S., Gendler S., Thein S. L. Clonal allele loss in gastrointestinal cancers. Br J Cancer. 1989 May;59(5):750–754. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Chan D. C., Leder P. Transmembrane form of the kit ligand growth factor is determined by alternative splicing and is missing in the Sld mutant. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90326-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Holmes L. B., Atkins L., Riccardi V. M. Aniridia-Wilms' tumor association: evidence for specific deletion of 11p13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;24(3):185–192. doi: 10.1159/000131375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera L., Kakati S., Gibas L., Pietrzak E., Sandberg A. A. Gardner syndrome in a man with an interstitial deletion of 5q. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Nov;25(3):473–476. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E., Anderson D. M., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Parada L. F. Embryonic RNA expression patterns of the c-kit receptor and its cognate ligand suggest multiple functional roles in mouse development. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2425–2435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Bigner S. H., Bigner D. D., Trent J. M., Law M. L., O'Brien S. J., Wong A. J., Vogelstein B. Identification of an amplified, highly expressed gene in a human glioma. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.3563490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manova K., Nocka K., Besmer P., Bachvarova R. F. Gonadal expression of c-kit encoded at the W locus of the mouse. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1057–1069. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Tumor suppressor genes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90641-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Nakamura Y., Hoff M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pCMM1.2) on chromosome 12q [D12S15]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3596–3596. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Zsebo K. M., Hogan B. L. Embryonic expression of a haematopoietic growth factor encoded by the Sl locus and the ligand for c-kit. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):667–669. doi: 10.1038/347667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens F., Johansson B., Mandahl N., Heim S., Bennet K., Rydholm A., Willén H., Mitelman F. Clonal chromosome abnormalities in two liposarcomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Sep;28(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton C. C., Byers M. G., Nakai H., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. Human genes for insulin-like growth factors I and II and epidermal growth factor are located on 12q22----q24.1, 11p15, and 4q25----q27, respectively. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(4):245–249. doi: 10.1159/000132237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A. B., Murty V. V., Rodriguez E., Reuter V. E., Bosl G. J., Chaganti R. S. Detection and analysis of origin of i(12p), a diagnostic marker of human male germ cell tumors, by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1991 Jul;3(4):300–307. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870030409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Ballard L., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pYNH15 on chromosome 12q [D12S17]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):779–779. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Fujimoto E., Martin C., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pEFD33.2 on chromosome 12 [D12S14]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):778–778. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P., Lathrop G. M., Law M., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., Hoff M., Kumlin E., Thomas W., Elsner T., Ballard L. A primary genetic linkage map for human chromosome 12. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P., Mosselman S., Höppener J. W., Jansz H. S., Clark A., O'Rahilly S., Turner R. C., Wainscoat J. S. An RFLP associated with insulinoma amyloid polypeptide locus (IAPP). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6758–6758. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulien S., Turc-Carel C., Dal Cin P., Jani-Sait S., Sreekantaiah C., Leong S. P., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W., Sandberg A. A., Gemmill R. M. Myxoid liposarcoma with t(12;16) (q13;p11) contains site-specific differences in methylation patterns surrounding a zinc-finger gene mapped to the breakpoint region on chromosome 12. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):7902–7907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Vande Woude G. F. Proto-oncogene expression in germ cell development. Trends Genet. 1988 Jul;4(7):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. H., Ray P., Brown K., Barker P. E., Jhanwar S., Ruddle F. H., Besmer P. Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family--oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Structure of the human immunoglobulin mu locus: characterization of embryonic and rearranged J and D genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Rottapel R., Giddens E., Brady C., Forrester L., Bernstein A. W mutant mice with mild or severe developmental defects contain distinct point mutations in the kinase domain of the c-kit receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):390–400. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez E., Mathew S., Mukherjee A. B., Reuter V. E., Bosl G. J., Chaganti R. S. Analysis of chromosome 12 aneuploidy in interphase cells from human male germ cell tumors by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Jul;5(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870050104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez E., Mathew S., Reuter V., Ilson D. H., Bosl G. J., Chaganti R. S. Cytogenetic analysis of 124 prospectively ascertained male germ cell tumors. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 15;52(8):2285–2291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropers H. H., Craig I. W. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 12 and 13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):259–279. doi: 10.1159/000132794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Albanesi C., Grimaldi P., Geremia R. Expression of the mRNA for the ligand of c-kit in mouse Sertoli cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):910–914. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80272-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmeyer T., Peter S., Hartmann M., Munemitsu S., Ackermann R., Ullrich A., Slamon D. J. Expression of the hst-1 and c-kit protooncogenes in human testicular germ cell tumors. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 1;51(7):1811–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. C., Nocka K., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. The dominant W42 spotting phenotype results from a missense mutation in the c-kit receptor kinase. Science. 1990 Jan 12;247(4939):209–212. doi: 10.1126/science.1688471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turc-Carel C., Dal Cin P., Boghosian L., Leong S. P., Sandberg A. A. Breakpoints in benign lipoma may be at 12q13 or 12q14. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Nov;36(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbright T. M., Roth L. M. Recent developments in the pathology of germ cell tumors. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1987 Nov;4(4):304–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfes H., Kogawa K., Millette C. F., Cooper G. M. Specific expression of nuclear proto-oncogenes before entry into meiotic prophase of spermatogenesis. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):740–743. doi: 10.1126/science.2475907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Ramsay N. Retinoblastoma and subband deletion of chromosome 13. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Feb;132(2):161–163. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120270059012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]