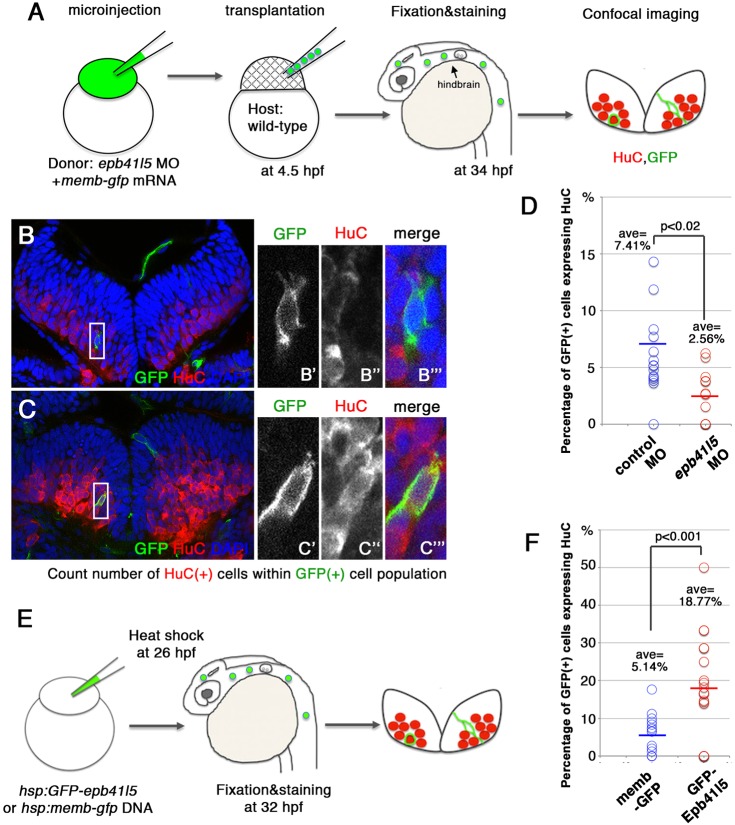
Fig. 5.
Epb41l5 facilitates differentiation of neurons. (A) Schematic of the experiment. epb41l5 morpholino was injected into one-cell-stage embryos with memb-gfp mRNA. Twenty to thirty cells were transplanted to wild-type embryos. Ratios of HuC-expressing cells within total GFP-expressing transplanted cells were analyzed in individual confocal images. (B,C) Representative images of HuC-positive neurons in the hindbrain. Boxed areas in B and C are enlarged in the right-hand panels. The cell in B does not express HuC, suggesting an undifferentiated NPC. The cell in C does express HuC, suggesting a differentiated neuron. (D) Reduced expression of epb41l5 attenuates differentiation of neurons. Out of the 428 control transplanted cells in 16 embryos that were analyzed, 7.41% cells expressed HuC. Out of the 221 epb41l5-deficient transplanted cells in 12 embryos that were analyzed, 2.56% cells expressed HuC. ave, average. (E) Schematic of the experiment. Plasmid DNAs encoding membGFP or GFP-Epb41l5 were microinjected. At 6 h after heat-shock treatment, HuC expression in GFP-expressing cells was analyzed at 32 hpf. (F) GFP-Epb41l5 facilitated differentiation of neurons. Out of the 623 membGFP-expressing cells in eight embryos that were analyzed, 5.14% cells expressed HuC. Out of the 277 cells overexpressing GFP-Epb41l5 in six embryos that were analyzed, 18.77% cells expressed HuC.