Abstract
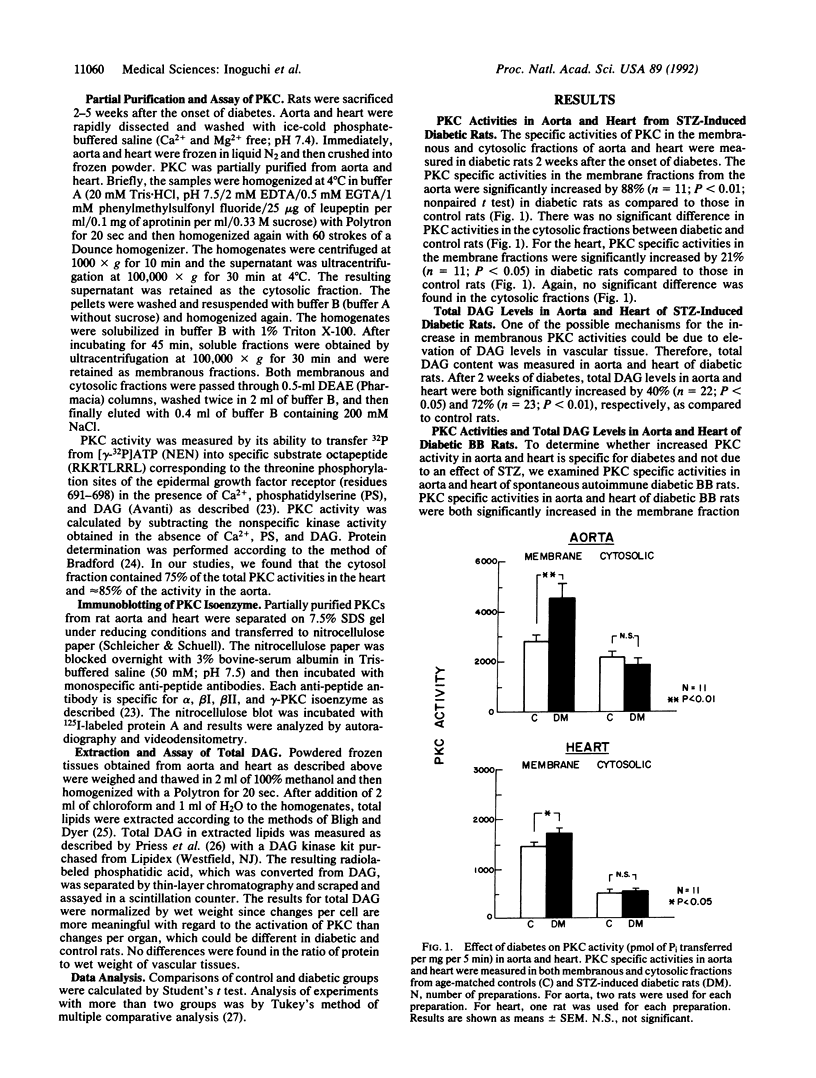
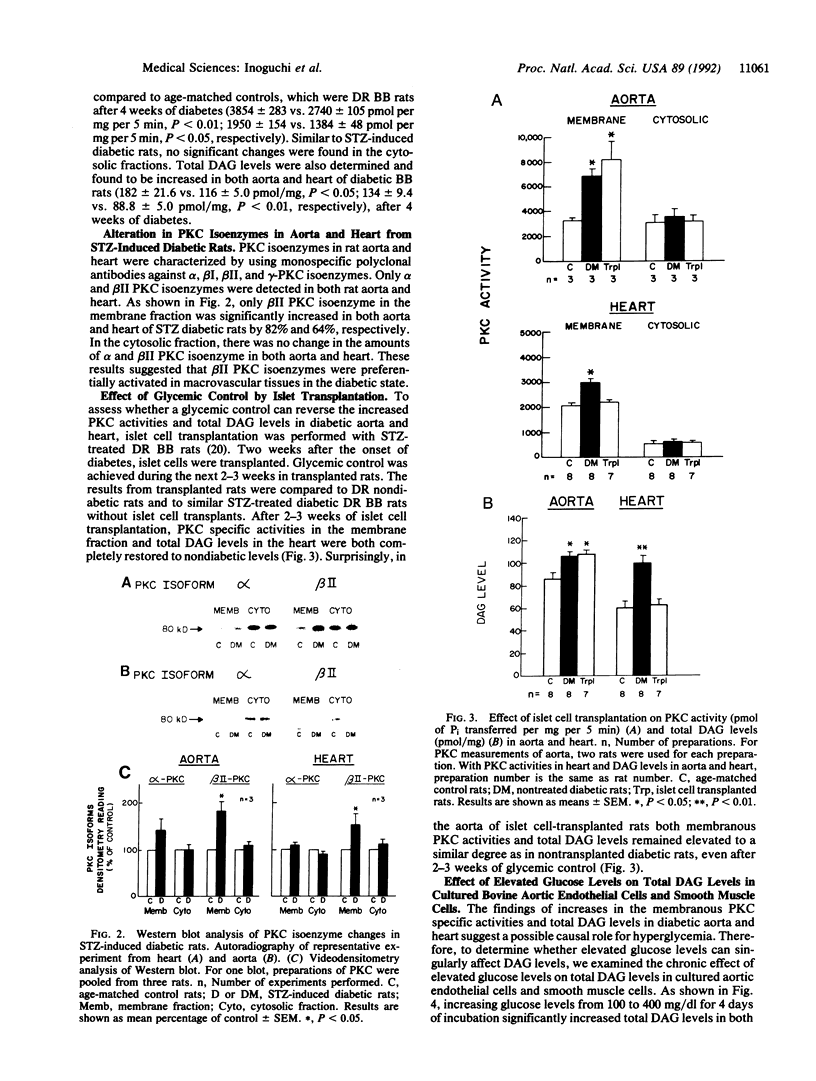
In the present study, we have measured protein kinase C (PKC) specific activities and total diacylglycerol (DAG) level in the aorta and heart of rats, which showed that after 2 weeks of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, membranous PKC specific activity and total DAG content were increased significantly by 88% and 40% in the aorta and by 21% and 72% in the heart, respectively. Hyperglycemia was identified as being a causal factor since elevated glucose levels increased DAG levels in cultured aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Analysis by immunoblotting revealed that only alpha and beta II PKC isoenzymes are detected in these two tissues and vascular cells among those studied. In STZ-induced diabetic rats, beta II isoenzyme is preferentially increased in both aorta and heart, whereas PKC alpha did not change significantly. The increases in membranous PKC specific activity and DAG level are observed in both spontaneous diabetes-prone diabetic BB rats as well as in STZ-induced diabetic BB and Sprague-Dawley rats, which persisted for up to 5 weeks. After 2 weeks of diabetes without treatment, the normalization of blood glucose levels for up to 3 weeks with islet cell transplants in STZ-induced diabetic BB rats reversed the biochemical changes only in the heart, but not in the aorta. These results suggest that PKC activity and DAG level may be persistently activated in the macrovascular tissues from diabetic animals and indicate a possible role for these biochemical parameters in the development of diabetic chronic vascular complications.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne C. The metabolism of lipids in mouse pancreatic islets. The biosynthesis of triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):667–673. doi: 10.1042/bj1520667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1315–1321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., Davidson C. M., DeRubertis F. R. Increase in diacylglycerol mass in isolated glomeruli by glucose from de novo synthesis of glycerolipids. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):667–674. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Protein kinase C is activated in glomeruli from streptozotocin diabetic rats. Possible mediation by glucose. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1667–1675. doi: 10.1172/JCI114066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danthuluri N. R., Deth R. C. Phorbol ester-induced contraction of arterial smooth muscle and inhibition of alpha-adrenergic response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):1103–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91397-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. Pancreatic islets synthesize phospholipids de novo from glucose via acyl-dihydroxyacetone phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engerman R. L., Kern T. S. Progression of incipient diabetic retinopathy during good glycemic control. Diabetes. 1987 Jul;36(7):808–812. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.7.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein F. S., Sonnenblick E. H. Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;27(4):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(85)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Shipley M. J., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Coronary-heart-disease risk and impaired glucose tolerance. The Whitehall study. Lancet. 1980 Jun 28;1(8183):1373–1376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92651-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Shipley M. J., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in relation to degree of glycaemia: the Whitehall study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 24;287(6396):867–870. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6396.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P. A., Berrios J. P., Mariani G., Handler E. S., Greiner D., Mordes J. P., Rossini A. A. Autoimmune destruction of islets transplanted into RT6-depleted diabetes-resistant BB/Wor rats. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):643–645. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Lattimer S. A., Sima A. A. Sorbitol, phosphoinositides, and sodium-potassium-ATPase in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 5;316(10):599–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703053161007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gøtzsche O., Gundersen H. J., Osterby R. Irreversibility of glomerular basement membrane accumulation despite reversibility of renal hypertrophy with islet transplantation in early experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):481–485. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachiya H. L., Takayama S., White M. F., King G. L. Regulation of insulin receptor internalization in vascular endothelial cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6417–6424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Yoshida Y., Cunha-Melo J. R., Beaven M. A., Huang K. P. Differential down-regulation of protein kinase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4238–4243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya K. I., Kawahara Y., Tsuda T., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Possible involvement of protein kinase C in platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated DNA synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Feb;63(2-3):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz H., Homan M., Velosa J., Robertson P., Rizza R. Effects of pancreas transplantation on postprandial glucose metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 31;325(18):1278–1283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110313251804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler I. I. Mortality experience of diabetic patients. A twenty-six-year follow-up study. Am J Med. 1971 Dec;51(6):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Goodman A. D., Buzney S., Moses A., Kahn C. R. Receptors and growth-promoting effects of insulin and insulinlike growth factors on cells from bovine retinal capillaries and aorta. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1028–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI111764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok C. F., Goldstein B. J., Muller-Wieland D., Lee T. S., Kahn C. R., King G. L. Identification of persistent defects in insulin receptor structure and function capillary endothelial cells from diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):127–136. doi: 10.1172/JCI113848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leatherman G. F., Kim D., Smith T. W. Effect of phorbol esters on contractile state and calcium flux in cultured chick heart cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):H205–H209. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.1.H205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. J., Ferro T. J., Blumenstock F. A., Brockenauer A. M., Malik A. B. Increased endothelial albumin permeability mediated by protein kinase C activation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1991–1998. doi: 10.1172/JCI114663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jr, Sahyoun N., Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P. Role of intracellular calcium mobilization in the regulation of protein kinase C-mediated membrane processes. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):549–551. doi: 10.1038/317549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordes J. P., Desemone J., Rossini A. A. The BB rat. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jul;3(3):725–750. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Akiyama N., Hashimoto H., Ogawa K., Satake T. Alteration of 1,2-diacylglycerol content in myocardium from diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Sep;37(9):1168–1172. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.9.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Nishiura T., Awaji Y., Kondo J., Hashimoto H., Ito T. 1,2-diacylglycerol content and its fatty acid composition in thoracic aorta of diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1991 Jul;40(7):820–824. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.7.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver F. J., de la Rubia G., Feener E. P., Lee M. E., Loeken M. R., Shiba T., Quertermous T., King G. L. Stimulation of endothelin-1 gene expression by insulin in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23251–23256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter-Riesch B., Fathi M., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Glucose and carbachol generate 1,2-diacylglycerols by different mechanisms in pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI113430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J. E., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:294–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugliese G., Tilton R. G., Chang K., Speedy A., Province M., Eades D. M., Lacy P. E., Kilo C., Williamson J. R. Effects of islet isografts on hemodynamic and vascular filtration changes in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1990 Mar;39(3):323–332. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugliese G., Tilton R. G., Williamson J. R. Glucose-induced metabolic imbalances in the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular disease. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1991 Mar;7(1):35–59. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610070106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. C., Goetz F. C., Sutherland D. E., Mauer S. M., Robison L. L., Cantrill H. L., Knobloch W. H., Najarian J. S. Progression of diabetic retinopathy after pancreas transplantation for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jan 28;318(4):208–214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198801283180403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Forder J., Kojima I., Scriabine A. TPA-induced contraction of isolated rabbit vascular smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):776–784. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilton B. H., Walton D. J. Sites of glycation of human and horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5587–5592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Peters M., McShane P., Gray D. W., Morris P. J. Isolation of rat pancreatic islets by ductal injection of collagenase. Transplantation. 1986 Dec;42(6):689–691. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198612000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesfamariam B., Brown M. L., Cohen R. A. Elevated glucose impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation by activating protein kinase C. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1643–1648. doi: 10.1172/JCI115179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Williamson J. R., Easom R. A., Chang K., Sherman W. R., Turk J. Diacylglycerol accumulation and microvascular abnormalities induced by elevated glucose levels. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI114988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




