Abstract
Sixty two females at 50% carrier risk were assessed from 19 families affected by X linked ocular albinism (OA1). Twenty nine (47%) had definite fundus changes of the carrier state with a mud splattered fundus appearance and 23 (37%) had a normal ophthalmic examination. Ten (16%) had mild peripheral retinal pigmentary changes so that it was difficult to exclude the carrier state; six of these females were shown to be at low risk and only one at high risk of being a carrier by DNA analysis using linked DNA polymorphisms, including a highly informative dinucleotide repeat at the Kallmann locus. Mild peripheral retinal pigmentary changes are not a definite indication of carrier status and in 45 age matched female controls five (11%) had similar changes. No female with a clinically normal fundus was found to be at high risk by DNA analysis. Molecular genetic analysis improves the accuracy of carrier detection in OA1 families and should be considered if the clinical findings are equivocal.
Full text
PDF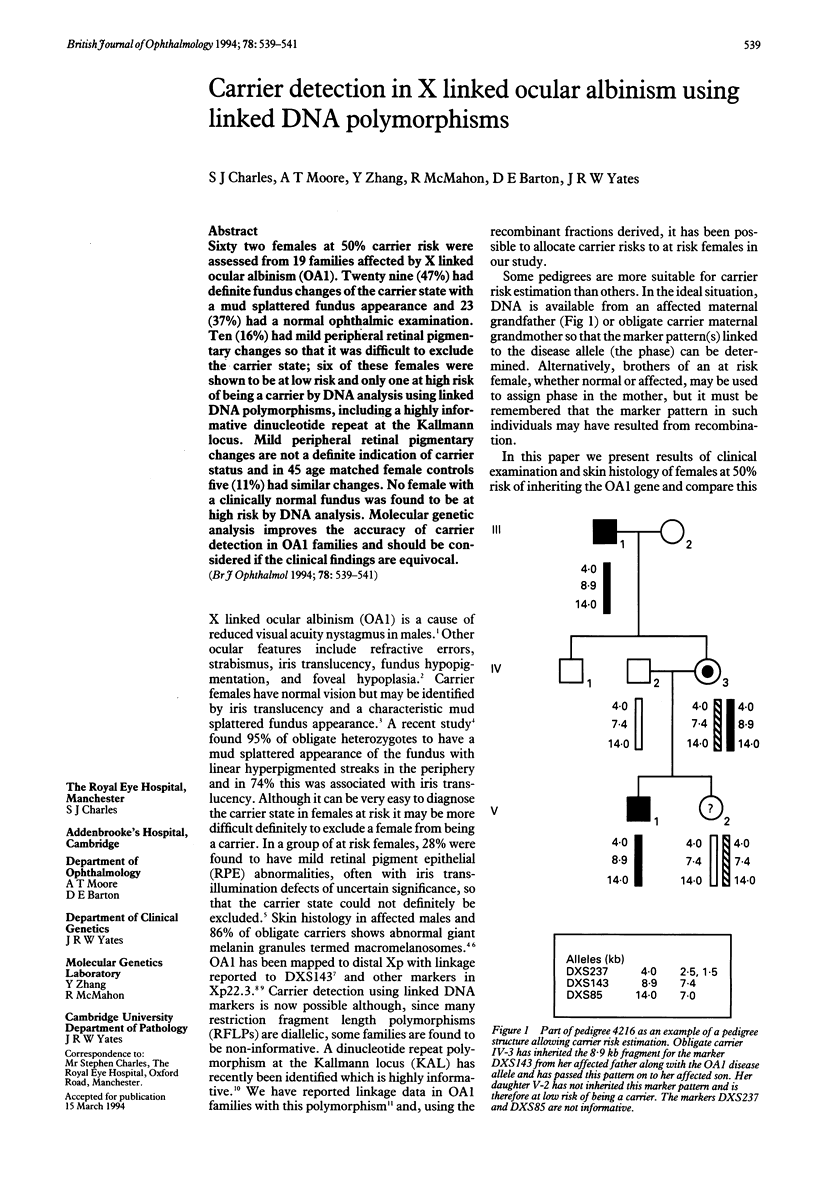


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouloux P. M., Hardelin J. P., Munroe P., Kirk J. M., Legouis R., Levilliers J., Hazan J., Weissenbach J., Petit C. A dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the Kallmann locus (Xp22.3). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5453–5453. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles S. J., Green J. S., Grant J. W., Yates J. R., Moore A. T. Clinical features of affected males with X linked ocular albinism. Br J Ophthalmol. 1993 Apr;77(4):222–227. doi: 10.1136/bjo.77.4.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles S. J., Green J. S., Moore A. T., Barton D. E., Yates J. R. Genetic mapping of X-linked ocular albinism: linkage analysis in a large Newfoundland kindred. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):259–261. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles S. J., Moore A. T., Grant J. W., Yates J. R. Genetic counselling in X-linked ocular albinism: clinical features of the carrier state. Eye (Lond) 1992;6(Pt 1):75–79. doi: 10.1038/eye.1992.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles S. J., Moore A. T., Yates J. R. Genetic mapping of X linked ocular albinism: linkage analysis in British families. J Med Genet. 1992 Aug;29(8):552–554. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.8.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALLS H. F. Sex-linked ocular albinism displaying typical fundus changes in the female heterozygote. Am J Ophthalmol. 1951 May;34(5 2):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(51)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay B., Carruthers J., Treplin M. C., Winder A. F. Human albinism. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1976;12(3):415–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnear P. E., Jay B., Witkop C. J., Jr Albinism. Surv Ophthalmol. 1985 Sep-Oct;30(2):75–101. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(85)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell F. E., Jr, Hambrick G. W., Jr, Green W. R., Iliff W. J., Stone D. L. X-linked ocular albinism. An oculocutaneous macromelanosomal disorder. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Nov;94(11):1883–1892. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910040593001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnur R. E., Nussbaum R. L., Anson-Cartwright L., McDowell C., Worton R. G., Musarella M. A. Linkage analysis in X-linked ocular albinism. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90353-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., McMahon R., Charles S. J., Green J. S., Moore A. T., Barton D. E., Yates J. R. Genetic mapping of the Kallmann syndrome and X linked ocular albinism gene loci. J Med Genet. 1993 Nov;30(11):923–925. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.11.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



