Abstract
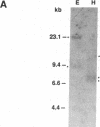
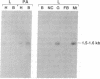
We have isolated a cDNA clone encoding a precursor form of the diuretic hormone from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta (Mas-DH). Translation of the cDNA revealed a 138-amino acid precursor consisting of the Mas-DH amino acid sequence bounded by dibasic amino acid processing sites, a putative signal sequence, and additional peptide sequence on either side of the Mas-DH coding sequence. The region of the precursor upstream of the mature Mas-DH sequence shows limited (28%) homology to the cryptic region of the ovine corticotropin-releasing factor precursor. The Mas-DH RNA is 1.5-1.6 kilobases long; it is present in both the heads and bodies of adult and larval insects. In prewandering fifth stadium larvae, Mas-DH mRNA is expressed in brain, nerve cord, gut, and Malpighian tubules, but not in the fat body. There is a single genomic copy of the Mas-DH gene; the message is multiply spliced.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn M. B., Kingan T. G., Bodnar W., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Kempe T., Wagner R. M., Raina A. K., Schnee M. E., Ma M. C. Isolation and identification of a new diuretic peptide from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):927–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92025-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury A. F., Finnie M. D., Smyth D. G. Mechanism of C-terminal amide formation by pituitary enzymes. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):686–688. doi: 10.1038/298686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield J. Y., Keeley L. L. Adipokinetic hormone gene sequence from Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12791–12793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi L. Consensus sequence for processing of peptide precursors at monobasic sites. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80290-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. H., Shannon J. M., Hofmann T., Mason R. J. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of the hydrophobic surfactant protein SP-C from rat: expression in alveolar type II cells and homology with SP-C from other species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 1;995(3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furutani Y., Morimoto Y., Shibahara S., Noda M., Takahashi H., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Hayashida H., Miyata T. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for ovine corticotropin-releasing factor precursor. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):537–540. doi: 10.1038/301537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka H., Toschi A., Li J. P., Carney R. L., Schooley D. A., Kramer S. J. Identification of an allatotropin from adult manduca sexta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1481–1483. doi: 10.1126/science.243.4897.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka H., Troetschler R. G., Li J. P., Kramer S. J., Carney R. L., Schooley D. A. Isolation and identification of a diuretic hormone from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2976–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami A., Kataoka H., Oka T., Mizoguchi A., Kimura-Kawakami M., Adachi T., Iwami M., Nagasawa H., Suzuki A., Ishizaki H. Molecular cloning of the Bombyx mori prothoracicotropic hormone. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1333–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.2315701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay I., Coast G. M., Cusinato O., Wheeler C. H., Totty N. F., Goldsworthy G. J. Isolation and characterization of a diuretic peptide from Acheta domesticus. Evidence for a family of insect diuretic peptides. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Jul;372(7):505–512. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.2.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay I., Wheeler C. H., Coast G. M., Totty N. F., Cusinato O., Patel M., Goldsworthy G. J. Characterization of a diuretic peptide from Locusta migratoria. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Oct;372(10):929–934. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1991.372.2.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. J., Toschi A., Miller C. A., Kataoka H., Quistad G. B., Li J. P., Carney R. L., Schooley D. A. Identification of an allatostatin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9458–9462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G. Processing of precursors by dipeptidylaminopeptidases: a case of molecular ticketing. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jan;15(1):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90126-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmberg E., Ota R. B., Furuya K., King D. S., Applebaum S. W., Ferenz H. J., Schooley D. A. Identification of a diuretic hormone of Locusta migratoria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 16;179(2):1036–1041. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91923-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S. Increased insecticidal effect by a recombinant baculovirus carrying a synthetic diuretic hormone gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1177–1183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92726-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]