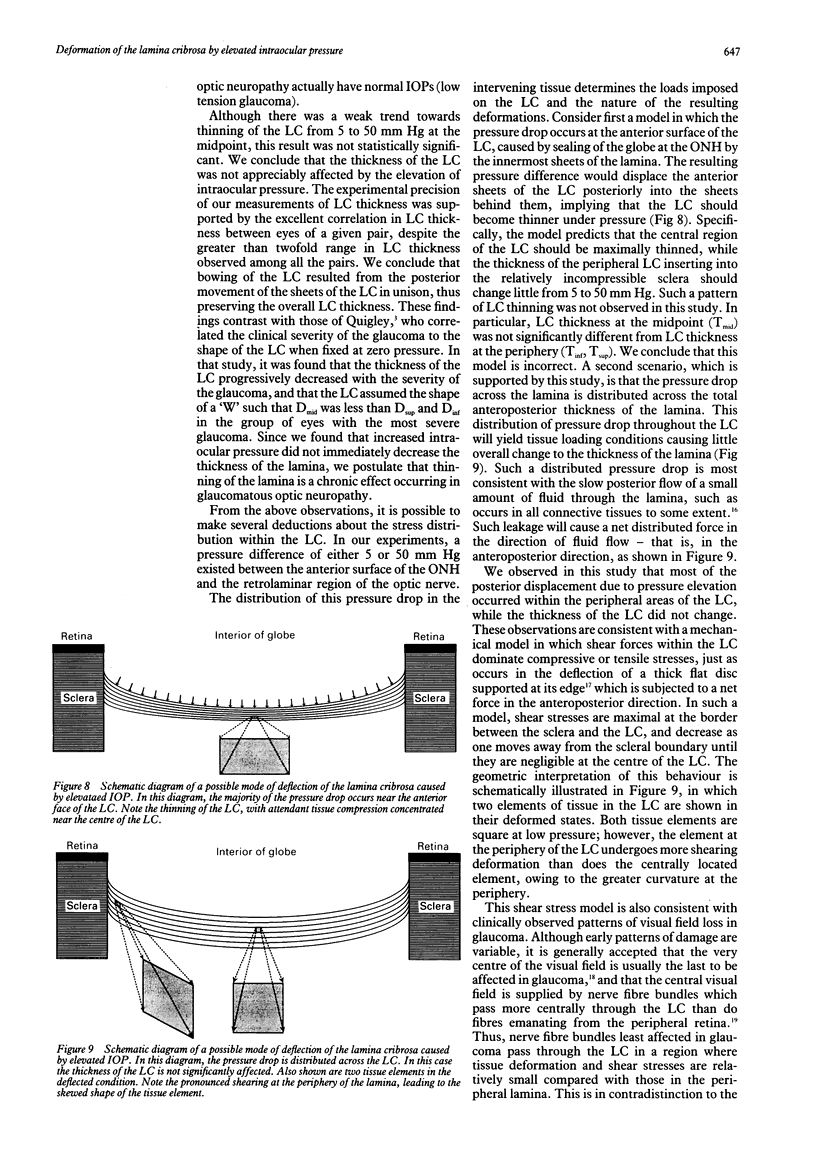
Abstract
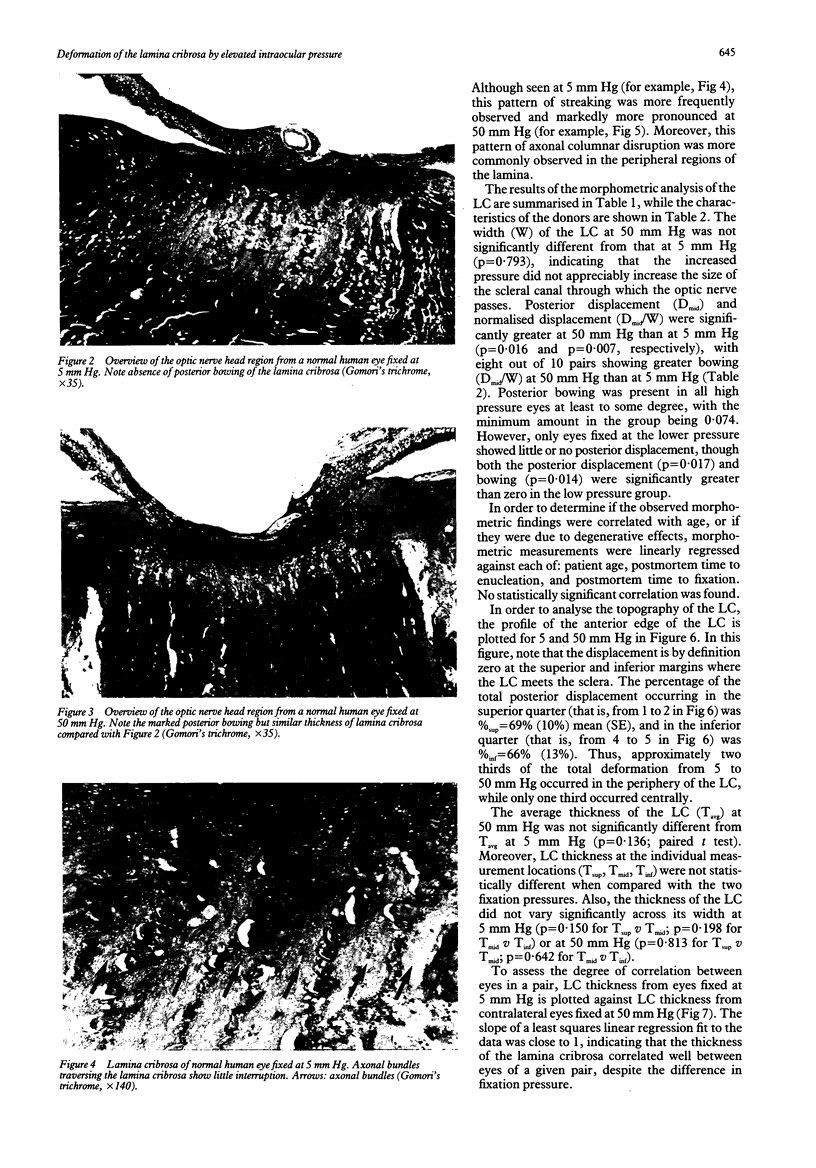
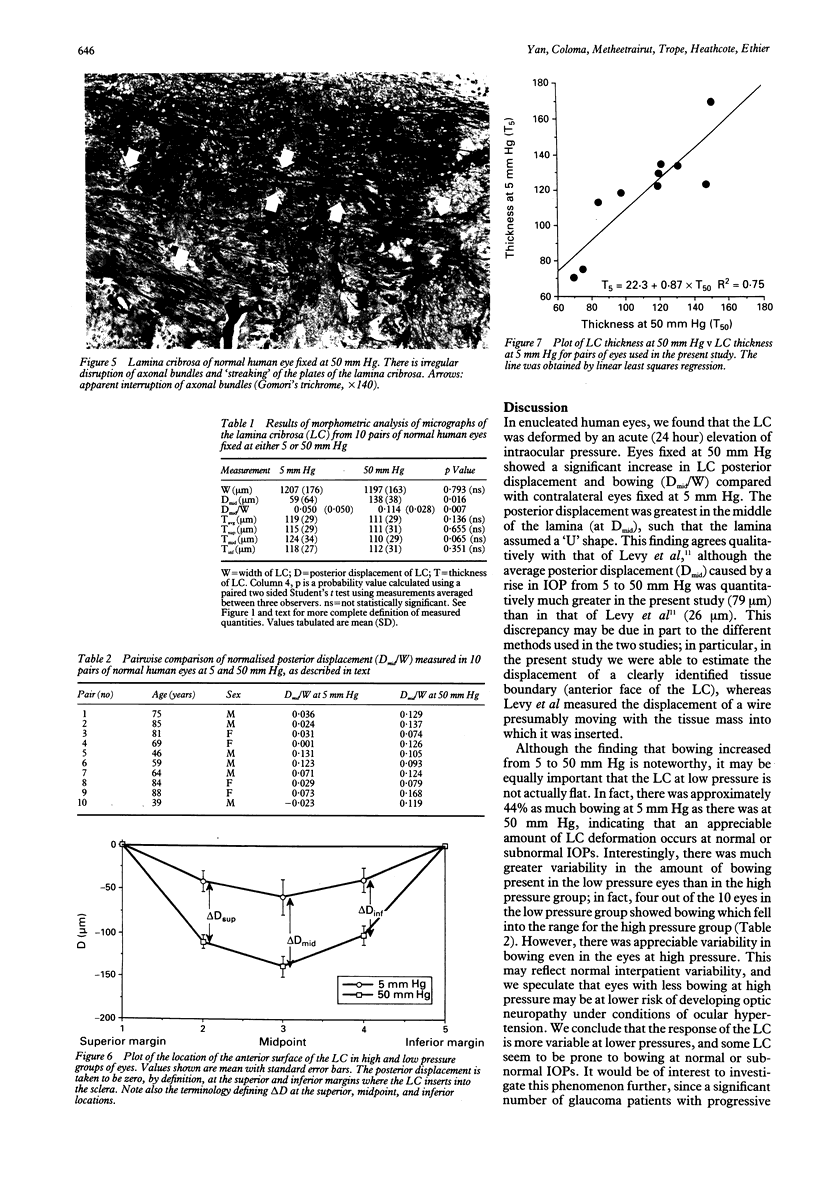
The purpose of this study was to determine the mechanical response of the lamina cribrosa (LC) to elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) so as to identify possible mechanisms of optic nerve damage in early glaucoma. Ten pairs of normal human eyes were fixed after 24 hours' exposure to 50 mm Hg pressure (experimental eyes) or 5 mm Hg pressure (contralateral control eyes). Photomicrographs of the central region of the optic nerve head (ONH) were taken to examine the LC morphologically and to measure the dimensions of the LC. It was found that elevated IOP caused the LC to deflect posteriorly without affecting its thickness. The majority of the posterior displacement in the LC occurred near the periphery of the ONH. This shape change is consistent with a model of force distribution within the LC in which shear stresses are dominant; such stresses are maximal at the periphery and minimal at the centre of the ONH. These findings support a model in which mechanical forces, specifically shearing stresses within the peripheral lamina, play a direct role in the pathology of glaucomatous optic neuropathy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. R., Hendrickson A. Effect of intraocular pressure on rapid axoplasmic transport in monkey optic nerve. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Oct;13(10):771–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman A. L., Quigley H. A., Vitale S., Dunkelberger G. Displacement of the optic nerve head by acute changes in intraocular pressure in monkey eyes. Ophthalmology. 1991 Jan;98(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(91)32345-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. H., Tschumper R. C. Human trabecular meshwork organ culture. A new method. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Jun;28(6):945–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick J. R. Flow through interstitium and other fibrous matrices. Q J Exp Physiol. 1987 Oct;72(4):409–437. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1987.sp003085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. S., Crapps E. E., Bonney R. C. Displacement of the optic nerve head. Response to acute intraocular pressure elevation in primate eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Dec;99(12):2166–2174. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930021042012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. S., Crapps E. E. Displacement of optic nerve head in response to short-term intraocular pressure elevation in human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984 May;102(5):782–786. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030630037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maumenee A. E. Causes of optic nerve damage in glaucoma. Robert N. Shaffer lecture. Ophthalmology. 1983 Jul;90(7):741–752. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(83)34493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minckler D. S., Bunt A. H., Klock I. B. Radioautographic and cytochemical ultrastructural studies of axoplasmic transport in the monkey optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978 Jan;17(1):33–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minckler D. S. The organization of nerve fiber bundles in the primate optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980 Sep;98(9):1630–1636. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1980.01020040482019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Addicks E. M., Green W. R., Maumenee A. E. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. II. The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Apr;99(4):635–649. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930010635009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Addicks E. M. Regional differences in the structure of the lamina cribrosa and their relation to glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Jan;99(1):137–143. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930010139020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Flower R. W., Addicks E. M., McLeod D. S. The mechanism of optic nerve damage in experimental acute intraocular pressure elevation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980 May;19(5):505–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Hohman R. M., Addicks E. M., Massof R. W., Green W. R. Morphologic changes in the lamina cribrosa correlated with neural loss in open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 May;95(5):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(83)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H., Anderson D. R. The dynamics and location of axonal transport blockade by acute intraocular pressure elevation in primate optic nerve. Invest Ophthalmol. 1976 Aug;15(8):606–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radius R. L., Gonzales M. Anatomy of the lamina cribrosa in human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Dec;99(12):2159–2162. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930021035010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeimer R. C., Ogura Y. The relation between glaucomatous damage and optic nerve head mechanical compliance. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 Aug;107(8):1232–1234. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1989.01070020298042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]