Abstract
The accuracy and reproducibility of the optic nerve head analyser (ONHA) and the Heidelberg retina tomograph (HRT) were compared and the performance of the HRT in measuring fundus elevations was evaluated. The coefficient of variation of three repeated measurements in a model eye and in volunteers and the relative error in a model eye was calculated. With ONHA measurements the pooled coefficient of variation in volunteers was 9.3% in measuring cup areas and 8.4% in measuring the cup volume. In a model eye the pooled coefficient of variation was 7.6% for the parameter 'cup area' and 9.9% for the parameter 'cup volume'. The pooled relative error in the model eye was 6.6% for the parameter 'cup area' and 5.1% for the parameter 'cup volume'. With HRT measurements in volunteers the pooled coefficient of variation of both the parameters 'volume below contour' and 'volume below surface' was 6.9%. In the model eye the pooled coefficient of variation was 2.4% for the 'volume below contour' and 4.1% for the parameter 'volume below surface'. The pooled relative error in the model eye was 11.3% for the 'volume below contour' and 11% for the 'volume below surface'. The pooled relative error in measuring retinal elevations in the model eye was 3.8%. The coefficient of variation was 3.5%. The accuracies of the HRT and ONHA were similar. However, as the ONHA 'cup volume' is unreliable in patients because of the design of the ONHA whereas the HRT volume parameters are reliable it seems reasonable to assume that the HRT is superior to the ONHA. Only the HRT is capable of quantifying retinal elevations.
Full text
PDF

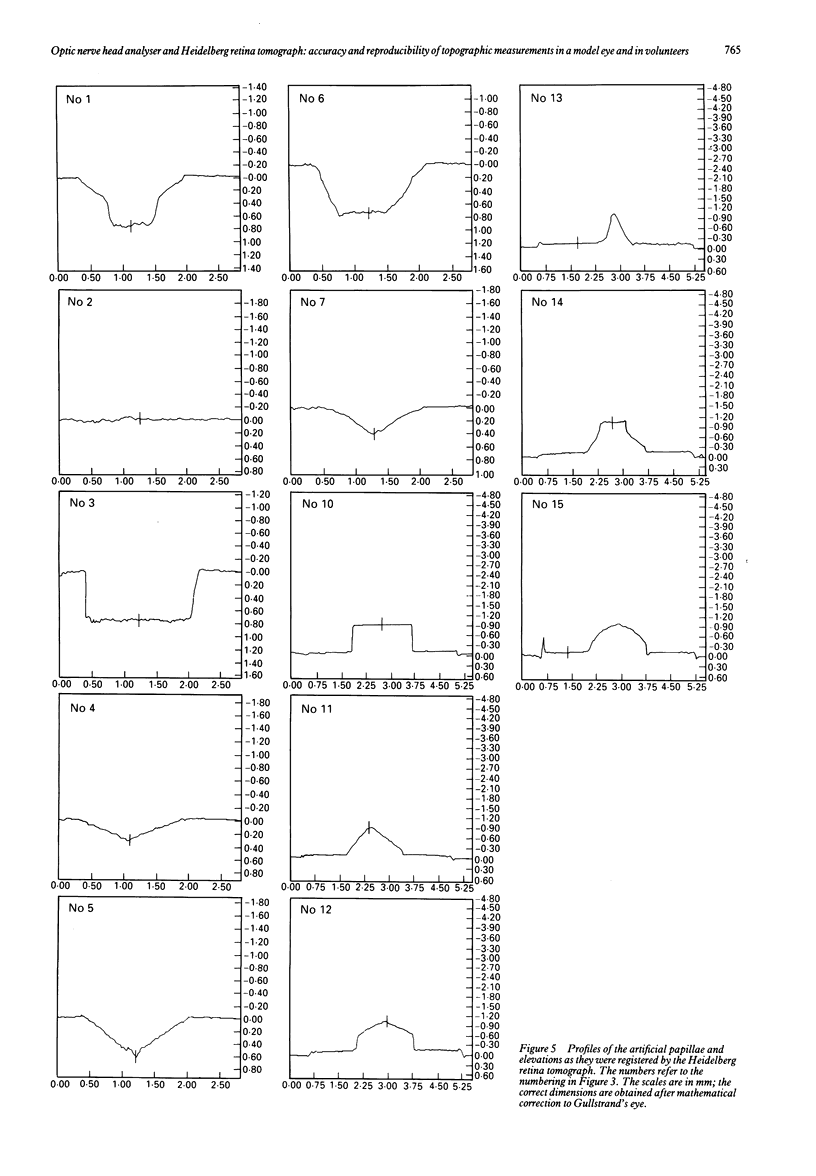



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop K. I., Werner E. B., Krupin T., Kozart D. M., Beck S. R., Nunan F. A., Wax M. B. Variability and reproducibility of optic disk topographic measurements with the Rodenstock Optic Nerve Head Analyzer. Am J Ophthalmol. 1988 Dec 15;106(6):696–702. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(88)90703-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli J., Klingbeil U., Sears M., Pope B. Reproducibility of optic disc measurements with computerized analysis of stereoscopic video images. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Jul;104(7):1035–1039. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050190093046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannheim F., Klingbeil U. Die Bestimmung räumlicher Papillendaten mit dem "Fundusanalysator". Fortschr Ophthalmol. 1986;83(5):527–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher A. W., Tso P. C., Weinreb R. N. Reproducibility of topographic measurements of the normal and glaucomatous optic nerve head with the laser tomographic scanner. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991 Feb 15;111(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreher A. W., Weinreb R. N. Accuracy of topographic measurements in a model eye with the laser tomographic scanner. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991 Oct;32(11):2992–2996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk J., Steeb R. Verbesserte Reproduzierbarkeit der computergesteuerten Papillenstrukturanalyse. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1991 Jun;199(1):25–29. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1046041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F. E., Burk R. O., Völcker H. E., Zinser G., Harbarth U. Reproducibility of topographic measurements of the optic nerve head with laser tomographic scanning. Ophthalmology. 1989 Sep;96(9):1320–1324. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32719-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikelberg F. S., Douglas G. R., Schulzer M., Cornsweet T. N., Wijsman K. Reliability of optic disk topographic measurements recorded with a video-ophthalmograph. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Jul 15;98(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider K., Burk R. O., Völcker H. E. Reproducibility of topometric data acquisition in normal and glaucomatous optic nerve heads with the laser tomographic scanner. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1993 Aug;231(8):457–464. doi: 10.1007/BF02044232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider K., Burk R. O., Völcker H. E. Vergleich von zwei Laser-Scanning-Tomographie-Systemen zur dreidimensionalen Papillenanalyse. Ophthalmologe. 1993 Dec;90(6):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. B., Martone J. F., Shelton A. R., Ollie A. R., MacMillan J. Reproducibility of topographic measurements with the optic nerve head analyzer. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987 Dec 15;104(6):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. B., Tiedeman J. S., Miller K. N., Hickingbotham D., Ollie A. R. Accuracy of topographic measurements with the Optic Nerve Head Analyzer. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989 Mar 15;107(3):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(89)90312-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb R. N., Lusky M., Bartsch D. U., Morsman D. Effect of repetitive imaging on topographic measurements of the optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993 May;111(5):636–638. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1993.01090050070031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]