Abstract
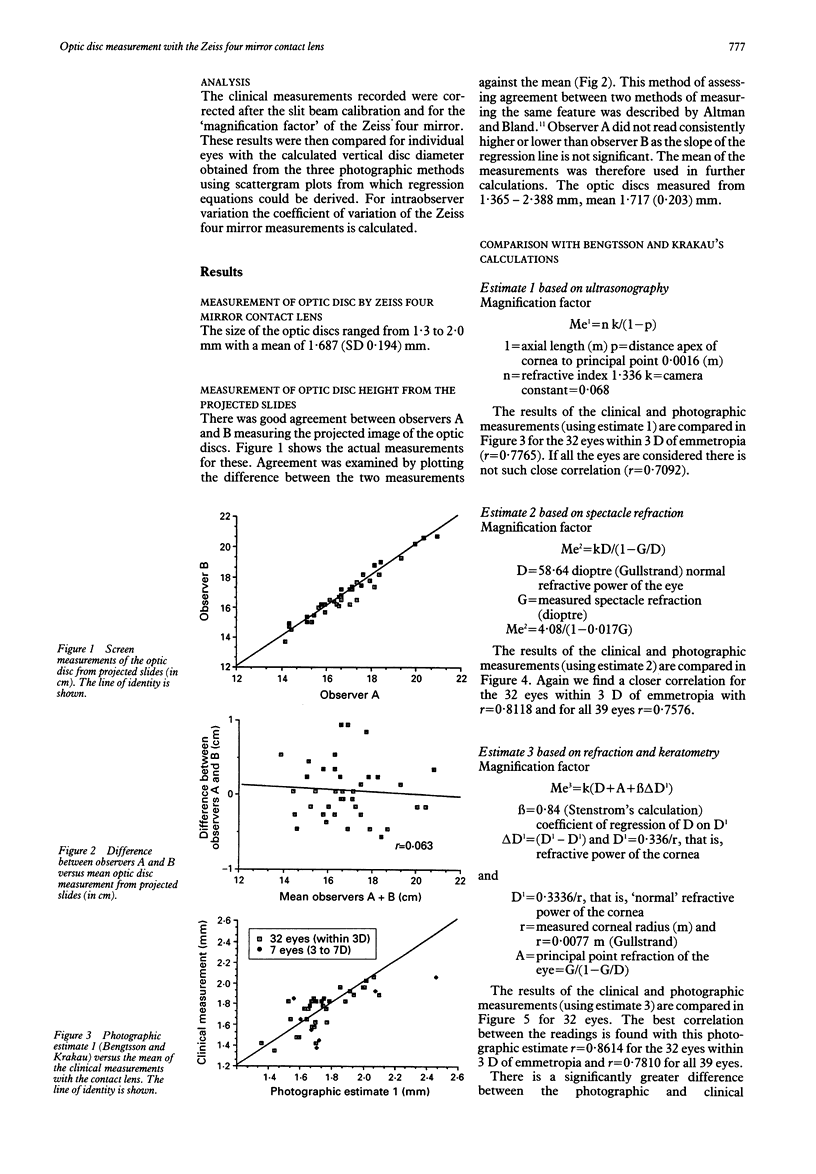
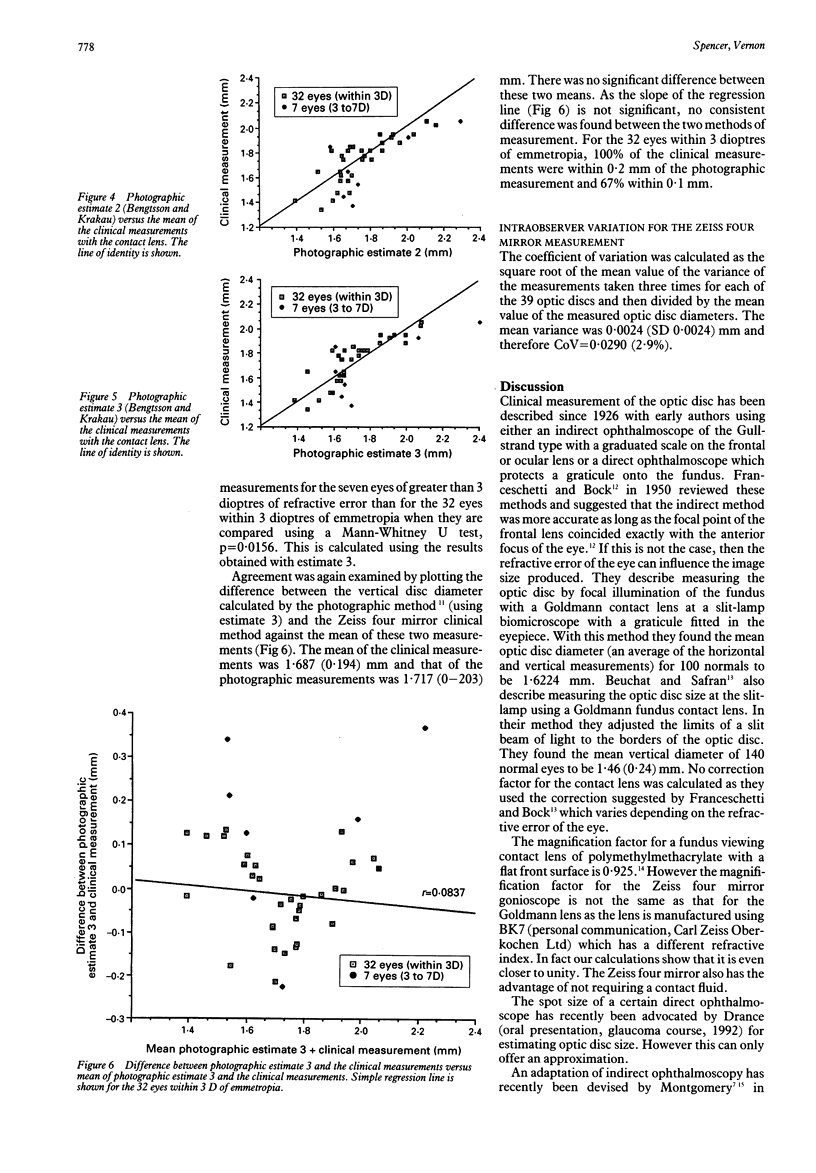
A knowledge of the optic disc size may be of value when assessing the glaucoma suspect. The vertical diameter of the optic disc was measured using a Zeiss four mirror gonioscope and a 900 Haag-Streit slit-lamp in one eye of 39 patients, 32 with refractive errors within 3 dioptres of emmetropia. The disc was measured by projecting a slit beam of known height onto the image of the disc. A magnification factor for the contact lens was calculated from first principles and disc height recalculated. These measurements were compared with those obtained by photographic methods using the corrections suggested by Bengtsson and Krakau. In the analysis on the 32 eyes within 3 dioptres of emmetropia the best correlation with clinical measurements was obtained with correction 3 using spectacle refraction and keratometry (r = 0.8614). The contact lens measurement was within plus or minus 0.1 mm of the photographic measurement in 67% of cases and plus or minus 0.2 mm in all cases. This simple method is advocated for the routine assessment of optic disc size.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold J. V., Gates J. W., Taylor K. M. Possible errors in the measurement of retinal lesions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993 Jul;34(8):2576–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazsi A. G., Drance S. M., Schulzer M., Douglas G. R. Neuroretinal rim area in suspected glaucoma and early chronic open-angle glaucoma. Correlation with parameters of visual function. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984 Jul;102(7):1011–1014. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030813022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach P., Rassow B., Wesemann W. Absolute ocular fundus dimensions measured by multiple-beam interference fringes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Nov;30(11):2314–2319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B., Krakau C. E. Correction of optic disc measurements on fundus photographs. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1992;230(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00166758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B., Krakau C. E. Some essential optical features of the Zeiss fundus camera. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1977 Feb;55(1):123–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1977.tb06101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B. The variation and covariation of cup and disc diameters. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1976 Dec;54(6):804–818. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1976.tb01801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuchat L., Safran A. B. Optic nerve hypoplasia: papillary diameter and clinical correlation. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1985 Dec;5(4):249–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli J., Klingbeil U., Sears M., Pope B. Reproducibility of optic disc measurements with computerized analysis of stereoscopic video images. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Jul;104(7):1035–1039. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050190093046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cioffi G. A., Robin A. L., Eastman R. D., Perell H. F., Sarfarazi F. A., Kelman S. E. Confocal laser scanning ophthalmoscope. Reproducibility of optic nerve head topographic measurements with the confocal laser scanning ophthalmoscope. Ophthalmology. 1993 Jan;100(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandona L., Quigley H. A., Jampel H. D. Variability of depth measurements of the optic nerve head and peripapillary retina with computerized image analysis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 Dec;107(12):1786–1792. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1989.01070020868029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCESCHETTI A., BOCK R. H. Megalopapilla; a new congenital anomaly. Am J Ophthalmol. 1950 Feb;33(2):227-35, illust. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(50)90841-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Gusek G. C., Guggenmoos-Holzmann I., Naumann G. O. Variability of the real dimensions of normal human optic discs. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988;226(4):332–336. doi: 10.1007/BF02172962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Gusek G. C., Naumann G. O. Optic disc morphometry in chronic primary open-angle glaucoma. I. Morphometric intrapapillary characteristics. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988;226(6):522–530. doi: 10.1007/BF02169199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. B., Gusek G. C., Naumann G. O. Optic disc, cup and neuroretinal rim size, configuration and correlations in normal eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Jul;29(7):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. J., Schwartz B., Takamoto T., Eu J. K. Interference fringe scale for absolute ocular fundus measurement. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1983 Feb;24(2):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littmann H. Zur Bestimmung der wahren Grösse eines Objektes auf dem Hintergrund des lebenden Auges. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1982 Apr;180(4):286–289. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1055068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotmar W. Dependence of magnification upon the camera-to-eye distance in the Zeiss fundus camera. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1984 Feb;62(1):131–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1984.tb06766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A. M. Measuring fundus landmarks. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990 Jan;31(1):41–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikelberg F. S., Douglas G. R., Schulzer M., Airaksinen P. J., Wijsman K., Mawson D. The correlation between cup-disk ratio, neuroretinal rim area, and optic disk area measured by the video-ophthalmograph (Rodenstock analyzer) and clinical measurement. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986 Jan 15;101(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(86)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery D. M. Clinical disc biometry in early glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1993 Jan;100(1):52–56. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(13)31713-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery D. M. Measurement of optic disc and neuroretinal rim areas in normal and glaucomatous eyes. A new clinical method. Ophthalmology. 1991 Jan;98(1):50–59. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(91)32342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pach J., Pennell D. O., Romano P. E. Optic disc photogrammetry: magnification factors for eye position, centration, and ametropias, refractive and axial; and their application in the diagnosis of optic nerve hypoplasia. Ann Ophthalmol. 1989 Dec;21(12):454–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portney G. L. Photogrammetric analysis of volume asymmetry of the optic nerve head cup in normal, hypertensive, and glaucomatous eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975 Jul;80(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(75)90868-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyott A. A., Montgomery D. M. Inter-observer variation in clinical optic disc biometry. Eye (Lond) 1993;7(Pt 3):452–456. doi: 10.1038/eye.1993.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Brown A. E., Morrison J. D., Drance S. M. The size and shape of the optic disc in normal human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Jan;108(1):51–57. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070030057028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. New techniques for the examination of the optic disc and their clinical application. Trans Sect Ophthalmol Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1976 Mar-Apr;81(2):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamoto T., Schwartz B. Reproducibility of photogrammetric optic disc cup measurements. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985 Jun;26(6):814–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



