Abstract
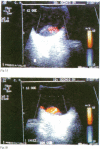
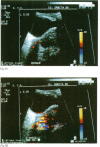
The intravenous injection of an ultrasound contrast agent can enhance signals from blood flow. Broad toxicological and pharmaceutical studies in animals confirmed the safety and efficacy of an ultrasound contrast agent made of microparticles of galactose with stabilised microbubbles in watery suspension (SH U 508 A). In this paper 10 patients with different malignant orbital and ocular tumours have been evaluated with an echo colour Doppler machine before and after the injection of SH U 508 A. An enhancement of the Doppler signals in the lesions in different degrees has been detected. This echographic contrast agent seems to be very important not only in the evaluation of vascular lesions, but also in evaluating the effectiveness of radiotherapy in malignant tumours and could spread the echographic indications in several other ophthalmic fields.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atta H. R., Byrne S. F. The findings of standardized echography for choroidal folds. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Sep;106(9):1234–1241. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060140394040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns P. N. Principles of Doppler and color flow. Radiol Med. 1993 May;85(5 Suppl 1):3–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne S. R., Glaser J. S. Orbital tissue differentiation with standardized echography. Ophthalmology. 1983 Sep;90(9):1071–1090. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(83)80050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramiak R., Shah P. M. Echocardiography of the aortic root. Invest Radiol. 1968 Sep-Oct;3(5):356–366. doi: 10.1097/00004424-196809000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthoff R., Winkler P., Helmke K., Berger R. Diagnosis and treatment control of choroidal melanomas--the role of B-scan and Doppler-technique. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl. 1992;(204):59–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1992.tb04926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R., Sawhney S., Berry M. Real-time sonography of orbital tumours, Colour Doppler characterization: initial experience. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl. 1992;(204):46–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1992.tb04923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ophir J., Parker K. J. Contrast agents in diagnostic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1989;15(4):319–333. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(89)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossoinig K. C. Standardized echography: basic principles, clinical applications, and results. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1979 Winter;19(4):127–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlief R. Ultrasound contrast agents. Curr Opin Radiol. 1991 Apr;3(2):198–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Elion J. L., McClure R. R., Kwan O. L., DeMaria A. N. Left heart opacification with peripheral venous injection of a new saccharide echo contrast agent in dogs. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989 Jun;13(7):1622–1628. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff-Korman P. G., Kormann B. A., Hasenfratz G. C., Spengel F. A. Duplex and color Doppler ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of choroidal tumors. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl. 1992;(204):66–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1992.tb04928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]