Abstract
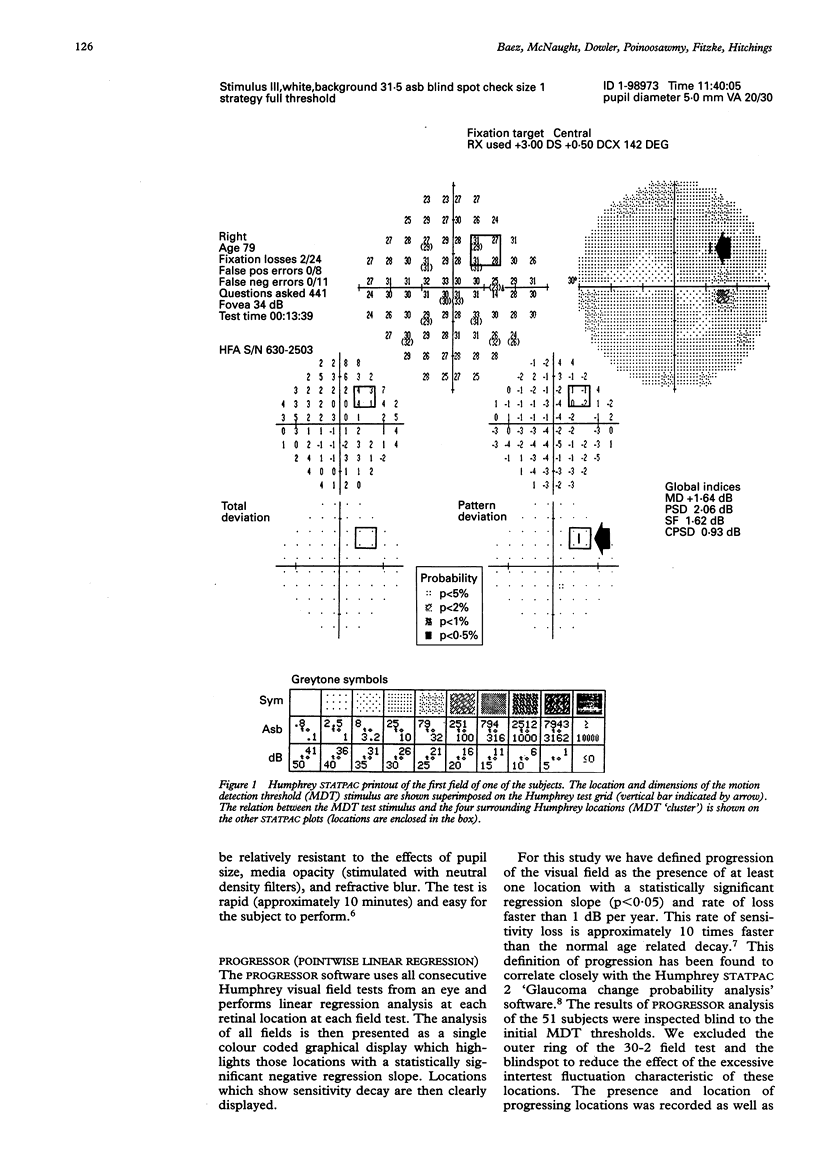
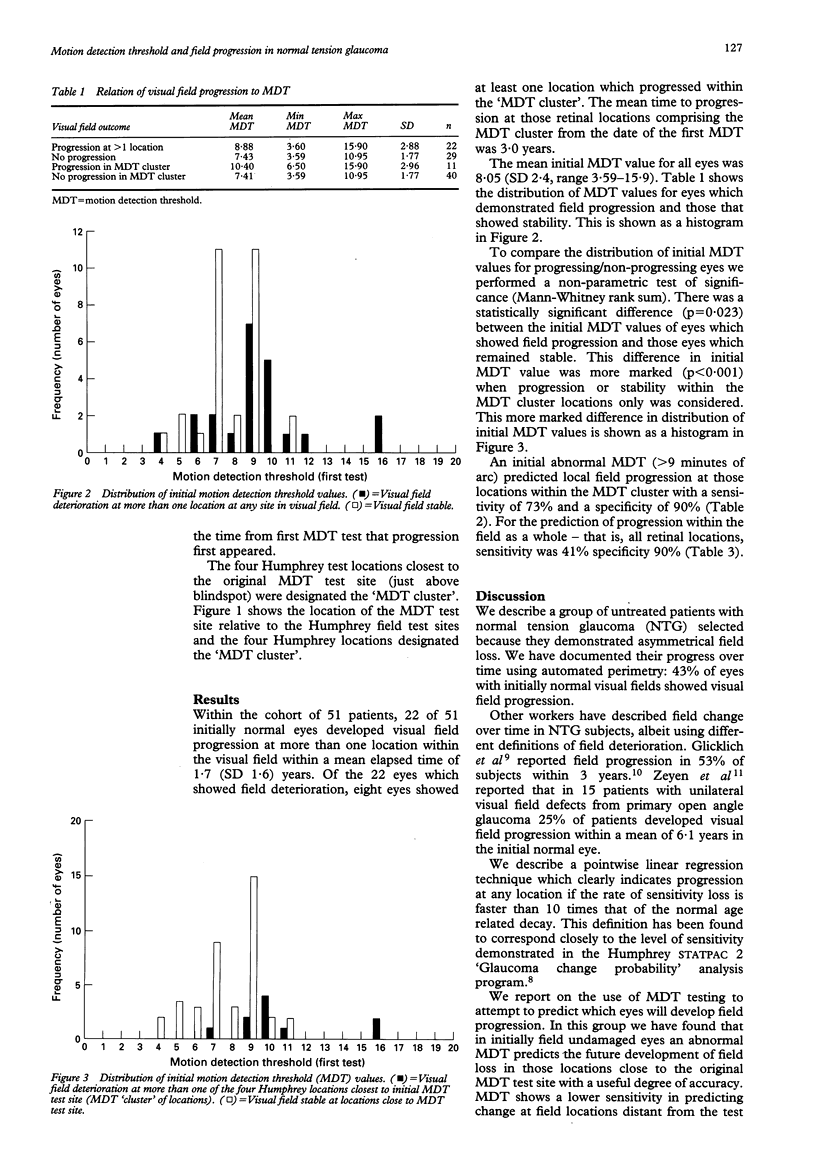
Psychophysical tests may demonstrate abnormalities of visual function before the appearance of conventional visual field loss in glaucoma. Motion detection thresholds (MDT) were measured in the normal fellow eye of 51 patients with confirmed normal tension glaucoma and initially unilateral field loss. Humphrey visual fields from the initially normal eye covering a mean follow up of 3.4 years were assessed using pointwise linear regression analysis. In 22 of the 51 eyes with normal visual fields at presentation, field deterioration occurred at one or more Humphrey locations within a mean of 1.7 (SD 1.6) years. An initially abnormal MDT test showed a sensitivity of 73% and a specificity of 90% in predicting field deterioration within the cluster of four Humphrey locations closest to the original MDT test site. Sensitivity was lower (40%) in predicting progression at retinal locations distant from the MDT test site, though specificity remained high (90%).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gliklich R. E., Steinmann W. C., Spaeth G. L. Visual field change in low-tension glaucoma over a five-year follow-up. Ophthalmology. 1989 Mar;96(3):316–320. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)33070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijl A., Lindgren G., Olsson J. Normal variability of static perimetric threshold values across the central visual field. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 Nov;105(11):1544–1549. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060110090039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchings R. A., Anderton S. A. A comparative study of visual field defects seen in patients with low-tension glaucoma and chronic simple glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983 Dec;67(12):818–821. doi: 10.1136/bjo.67.12.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal A. G., Rodieck R. W., Dreher B. Retinal ganglion cell classes in the Old World monkey: morphology and central projections. Science. 1981 Sep 4;213(4512):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.7268423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone M. S., Hubel D. H. Psychophysical evidence for separate channels for the perception of form, color, movement, and depth. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3416–3468. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03416.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Dunkelberger G. R., Green W. R. Chronic human glaucoma causing selectively greater loss of large optic nerve fibers. Ophthalmology. 1988 Mar;95(3):357–363. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(88)33176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyen T. G., Caprioli J. Progression of disc and field damage in early glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993 Jan;111(1):62–65. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1993.01090010066028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


