Abstract
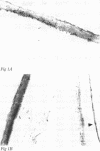
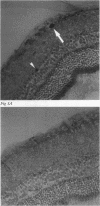
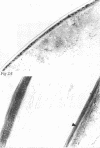
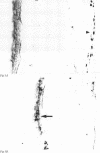
AIMS--Immunohistochemical techniques were used to investigate c-Fos and c-Jun proto-oncogene expression in the cornea, lens, and retina after ultraviolet irradiation of the rat eye. METHODS--Eyes of anaesthetised rats were exposed to 1.5 J/cm2 of ultraviolet radiation (280-380 nm). Animals were perfused 1, 6, or 24 hours after irradiation and tissue sections were incubated with specific antiserum to c-Fos and c-Jun, respectively. RESULTS--Non-irradiated contralateral eyes displayed no c-Fos and c-Jun immunoreactivity. One and 6 hours after ultraviolet exposure numerous c-Fos and c-Jun immunopositive nuclei were observed mainly in the epithelial cell layers of the cornea and the lens epithelium. Scattered labelled nuclei were detectable in the retinal ganglion cell layer and the inner nuclear layer. Twenty four hours after irradiation c-Fos and c-Jun protein expression returned to near control levels. Histological signs of ultraviolet damage (for example, chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation) were first recognisable in the corneal epithelium 6 hours after irradiation and became more apparent at later times. CONCLUSION--Thus, the rapid and sustained activation of c-Fos and c-Jun expression in the eye after single ultraviolet exposure may represent the molecular mechanism underlying ultraviolet induced photodamage and initiation of cell death. Furthermore, topical application of a c-fos antisense oligodeoxynucleotide to the ultraviolet exposed rat eye inhibited the increase in c-Fos expression in the cornea, suggesting therapeutic activity of antisense drugs in corneal malignant and infectious diseases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andley U. P., Lewis R. M., Reddan J. R., Kochevar I. E. Action spectrum for cytotoxicity in the UVA- and UVB-wavelength region in cultured lens epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994 Feb;35(2):367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan H. E., Tao Y., Bazan N. G. Platelet-activating factor induces collagenase expression in corneal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8678–8682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuerman R. W., Thompson H. W. Molecular and cellular responses of the corneal epithelium to wound healing. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl. 1992;(202):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1992.tb02161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craner S. L., Hoffman G. E., Lund J. S., Humphrey A. L., Lund R. D. cFos labeling in rat superior colliculus: activation by normal retinal pathways and pathways from intracranial retinal transplants. Exp Neurol. 1992 Sep;117(3):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(92)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danno K., Horio T. Formation of UV-induced apoptosis relates to the cell cycle. Br J Dermatol. 1982 Oct;107(4):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1982.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon J. The photophysics and photobiology of the eye. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1991 Jul;10(1-2):23–40. doi: 10.1016/1011-1344(91)80209-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garmyn M., Yaar M., Holbrook N., Gilchrest B. A. Immediate and delayed molecular response of human keratinocytes to solar-simulated irradiation. Lab Invest. 1991 Oct;65(4):471–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillardon F., Eschenfelder C., Uhlmann E., Hartschuh W., Zimmermann M. Differential regulation of c-fos, fosB, c-jun, junB, bcl-2 and bax expression in rat skin following single or chronic ultraviolet irradiation and in vivo modulation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotide superfusion. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3219–3225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorgels T. G., van Norren D. Spectral transmittance of the rat lens. Vision Res. 1992 Aug;32(8):1509–1512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(92)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassilli E., Carcereri de Prati A., Monti D., Troiano L., Menegazzi M., Barbieri D., Franceschi C., Suzuki H. Studies of the relationship between cell proliferation and cell death. II. Early gene expression during concanavalin A-induced proliferation or dexamethasone-induced apoptosis of rat thymocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 16;188(3):1261–1266. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91367-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R. Primary response genes induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:281–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower K., McCready J. Mechanisms involved in cataract development following near-ultraviolet radiation of cultured lenses. Curr Eye Res. 1992 Jul;11(7):679–689. doi: 10.3109/02713689209000741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Fornace A. J., Jr Response to adversity: molecular control of gene activation following genotoxic stress. New Biol. 1991 Sep;3(9):825–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jose J. G. Posterior cataract induction by UV-B radiation in albino mice. Exp Eye Res. 1986 Jan;42(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(86)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman N. J., Wang R. R., Spector A. Ultraviolet light induced DNA damage and repair in bovine lens epithelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 1990 Dec;9(12):1185–1193. doi: 10.3109/02713689009003475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovary K., Bravo R. Expression of different Jun and Fos proteins during the G0-to-G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts: in vitro and in vivo associations. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2451–2459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., Lee M. M., Scotto J. Xeroderma pigmentosum. Cutaneous, ocular, and neurologic abnormalities in 830 published cases. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Feb;123(2):241–250. doi: 10.1001/archderm.123.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. L., Tso M. O., Jampol L. M., Miller S. A., Waxler M. Retinal injury induced by near-ultraviolet radiation in aphakic and pseudophakic monkey eyes. A preliminary report. Retina. 1990;10(4):301–314. doi: 10.1097/00006982-199010000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Cotter T. G. Ultraviolet B irradiation of human leukaemia HL-60 cells in vitro induces apoptosis. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Apr;59(4):1001–1016. doi: 10.1080/09553009114550891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milam A. H. Strategies for rescue of retinal photoreceptor cells. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Oct;3(5):797–804. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90156-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringvold A., Davanger M. Changes in the rabbit corneal stroma caused by UV-radiation. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1985 Oct;63(5):601–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1985.tb05253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein O. D. Phototoxicity and the cornea. J Natl Med Assoc. 1992 Jul;84(7):579–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G., Ghosh R., Amstad P. A., Cerutti P. A. Mechanism of induction of c-fos by ultraviolet B (290-320 nm) in mouse JB6 epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):38–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Vendrell M., Hayward M., Baker S. J., Miao G. G., Schilling K., Robertson L. M., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Continuous c-fos expression precedes programmed cell death in vivo. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):166–169. doi: 10.1038/363166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Rahmsdorf H. J., Steffen A., Litfin M., Herrlich P. UV-induced DNA damage is an intermediate step in UV-induced expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, collagenase, c-fos, and metallothionein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5169–5181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Kawamura K., Imaki J. Differential expression of c-fos mRNA in rat retinal cells: regulation by light/dark cycle. Neuron. 1993 Jun;10(6):1049–1054. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90053-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigman S., Vaughan T. Near-ultraviolet light effects on the lenses and retinas of mice. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Jun;13(6):462–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zrenner E. Lichtinduzierte Schäden am Auge. Fortschr Ophthalmol. 1990;87 (Suppl):S41–S51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]