Abstract
Tight-seal whole-cell recording and Ca2+ imaging were simultaneously performed on cell clusters or individual acinar cells of rat lacrimal glands during application of the secretagogue acetylcholine. Activation of Ca(2+)-dependent K+ and Cl- currents was selectively followed as a function of time by placing the cell potential near the equilibrium potential for Cl- or for K+ ion, respectively. Upon acetylcholine application to cell clusters, K(+)- and Cl(-)-selective currents displayed a distinctive initial rise ("hump"). At this time, there was only a small elevation of Ca2+ concentration, [Ca2+]i, that was restricted to the luminal end of acinar cells. A quantitative analysis of Ca2+ and current signals during the hump suggested that the luminal membrane contained high densities of K(+)- and Cl(-)-selective channels, roughly 10 times higher than those found in the basolateral domain. Distinct luminal and basolateral membrane domains were preserved in isolated cells, but with less contrasted densities than in cell clusters. The results suggest that Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels are implicated not only in the transfer of salt from the blood compartment to the interior of acinar cells, as commonly accepted, but also in the electrolyte secretion from the cell interior to the acinar lumen.
Full text
PDF
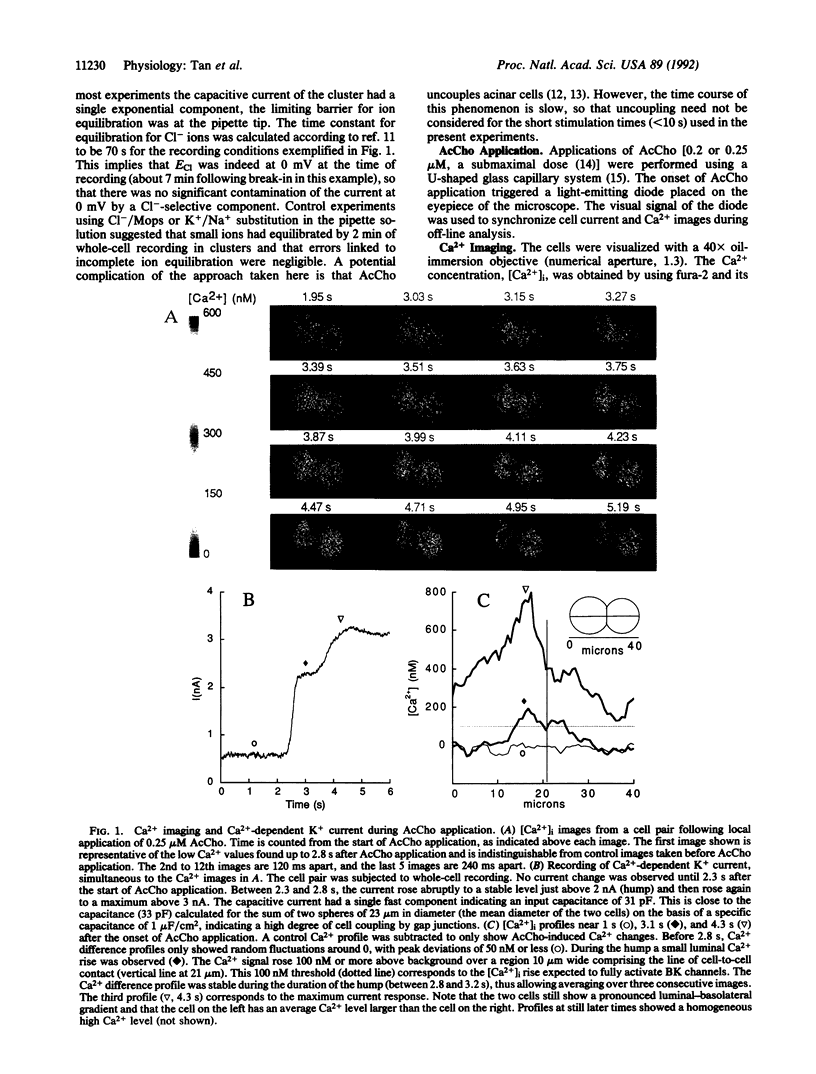
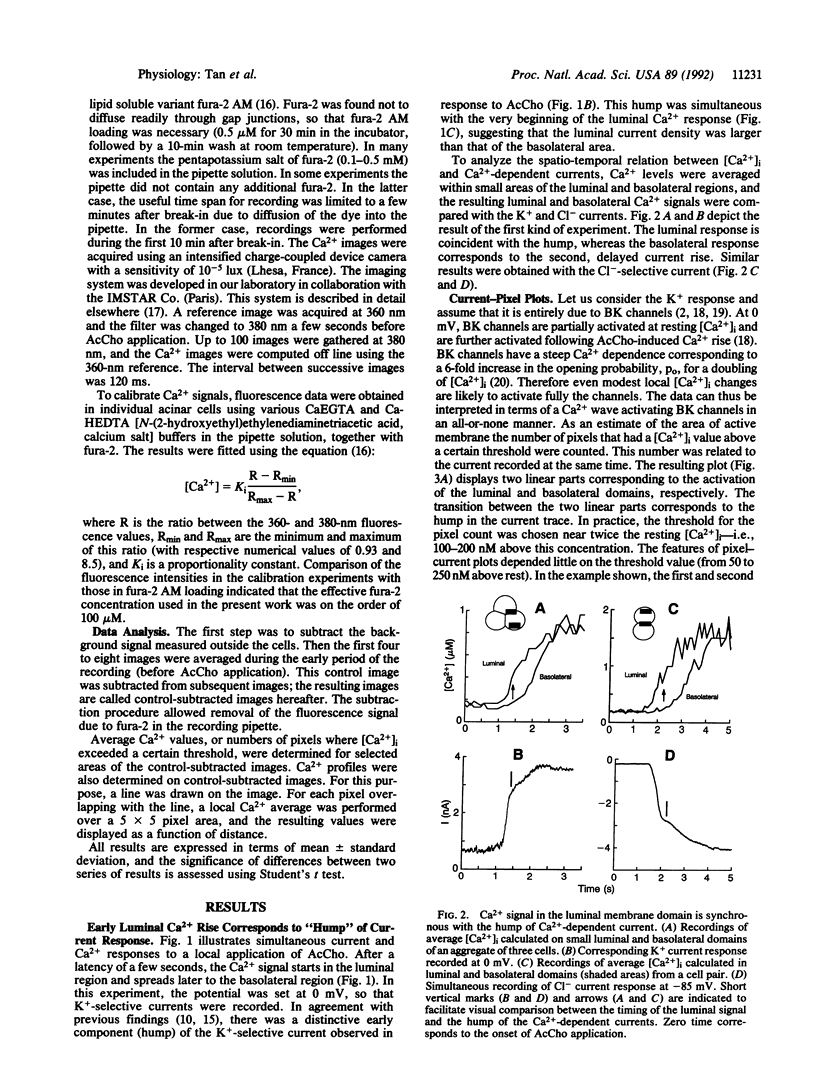
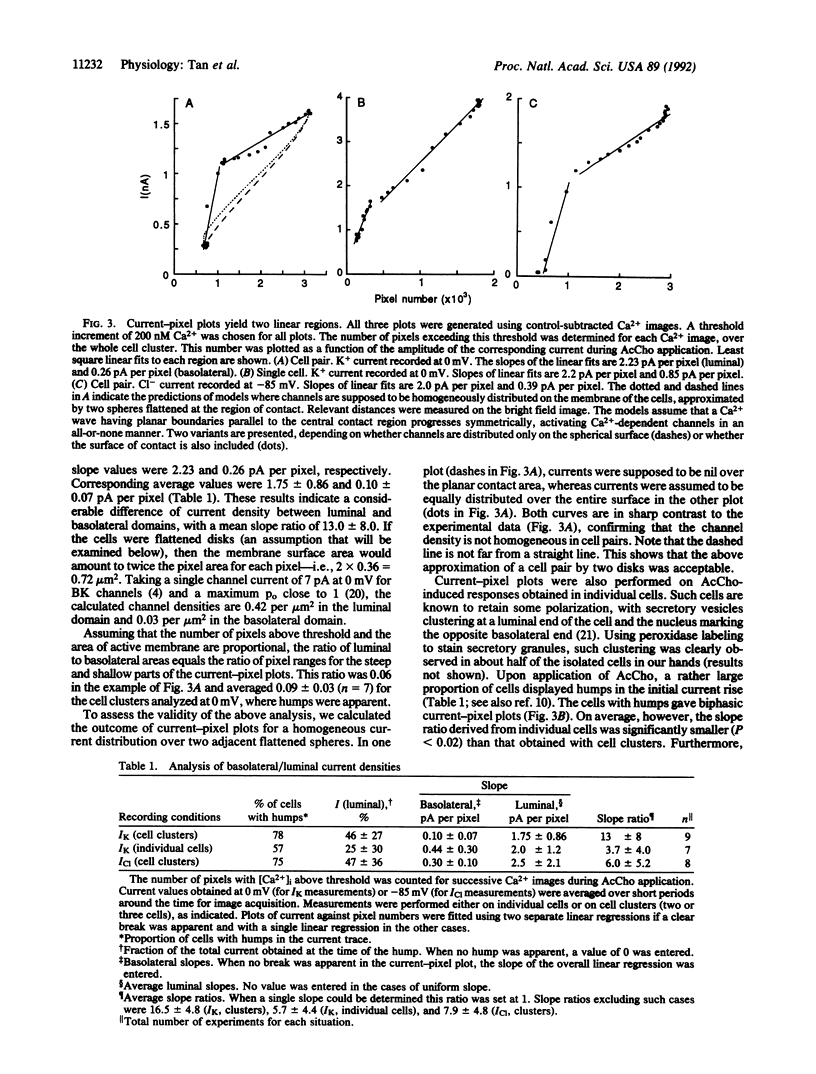

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., Carraway C. A. Membrane-cytoskeleton interactions in animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):147–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnadieu E., Cefai D., Tan Y. P., Paresys G., Bismuth G., Trautmann A. Imaging early steps of human T cell activation by antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1992 May 1;148(9):2643–2653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:179–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foskett J. K., Gunter-Smith P. J., Melvin J. E., Turner R. J. Physiological localization of an agonist-sensitive pool of Ca2+ in parotid acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog V., Sies H., Miller F. Exocytosis in secretory cells of rat lacrimal gland. Peroxidase release from lobules and isolated cells upon cholinergic stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):692–706. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: acetylcholine-evoked electrical uncoupling and its ionic dependency. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:81–06. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Augustine G. J. Cytosolic Ca2+ gradients triggering unidirectional fluid secretion from exocrine pancreas. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):735–738. doi: 10.1038/348735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. A receptor for protons in the nerve cell membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2325–2327. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Evans M. G., Tan Y. P., Trautmann A. Muscarinic response in rat lacrimal glands. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:15–32. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P. The initiation of calcium release following muscarinic stimulation in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:665–687. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P., Trautmann A. Three types of calcium-dependent channel in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:293–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Peterson O. H. Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):159–161. doi: 10.1038/299159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Trautmann A. Acetylcholine modulation of the conductance of intercellular junctions between rat lacrimal cells. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:283–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H. Stimulus-secretion coupling: cytoplasmic calcium signals and the control of ion channels in exocrine acinar cells. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:1–51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randriamampita C., Chanson M., Trautmann A. Calcium and secretagogues-induced conductances in rat exocrine pancreas. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jan;411(1):53–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00581646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Petersen O. H. The effect of Na+ and Cl- removal and of loop diuretics on acetylcholine-evoked membrane potential changes in mouse lacrimal acinar cells. Q J Exp Physiol. 1985 Jul;70(3):437–445. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1985.sp002927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann A., Marty A. Activation of Ca-dependent K channels by carbamoylcholine in rat lacrimal glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):611–615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]