Abstract
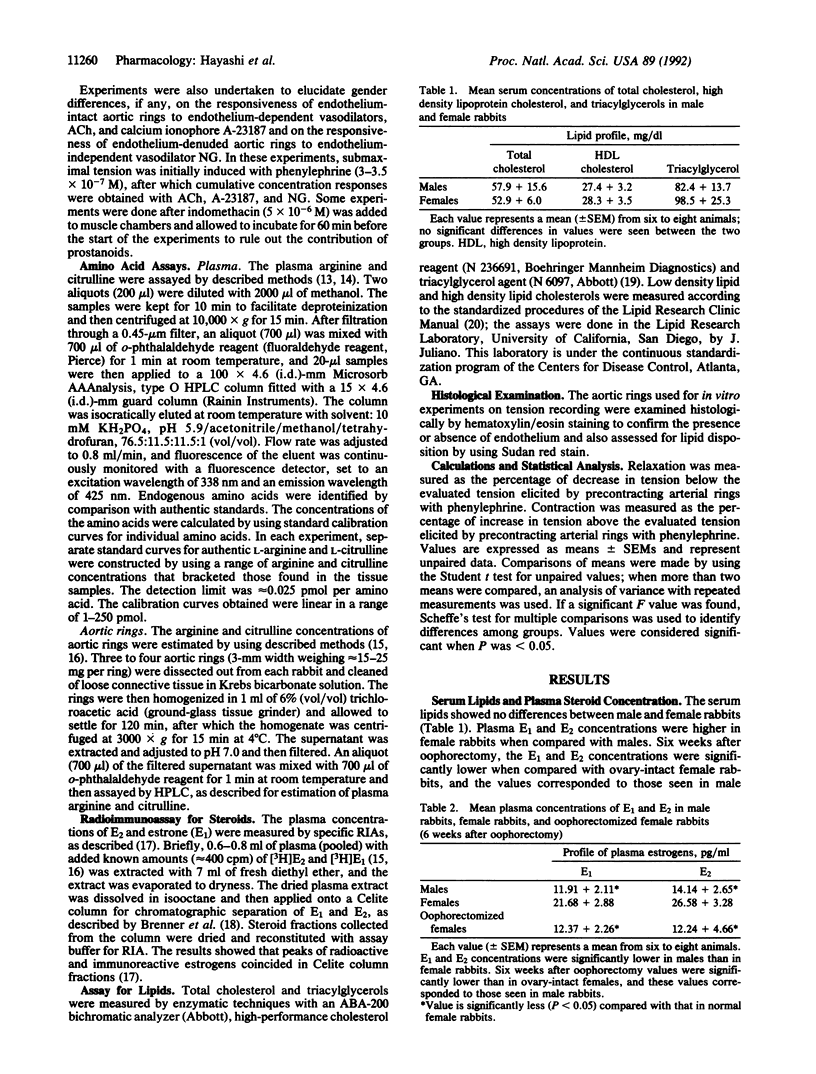
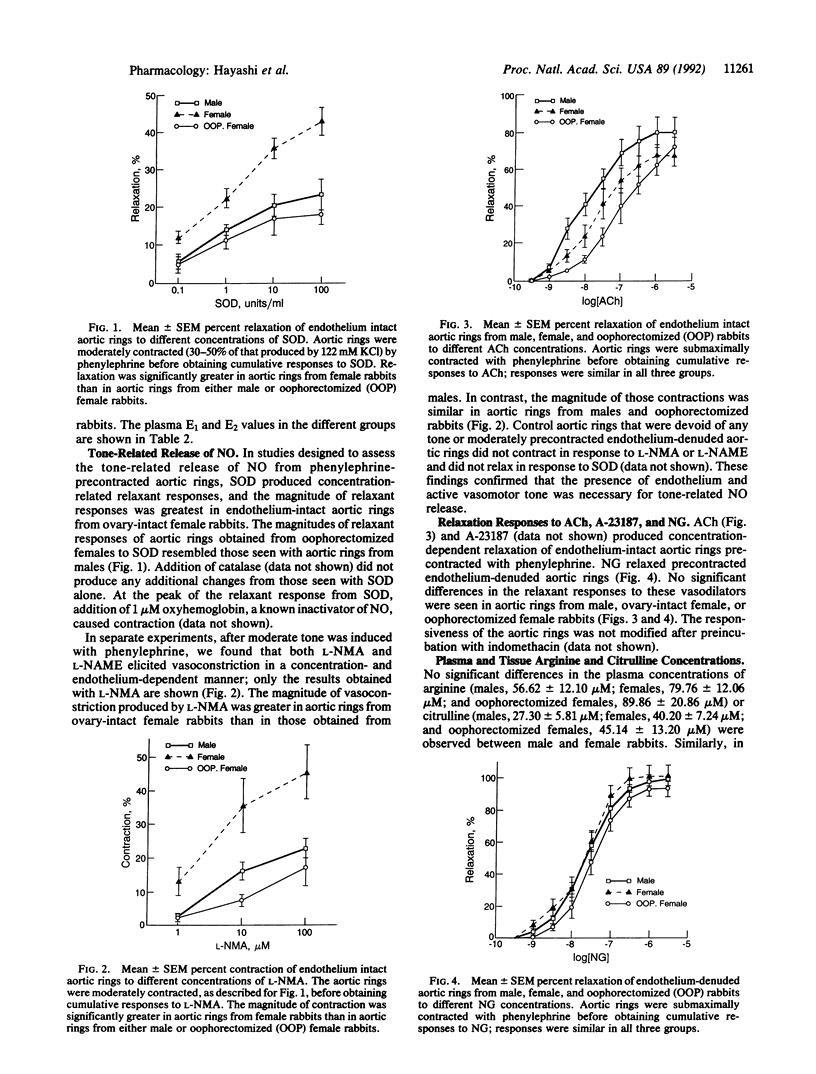
Estradiol is known to exert a protective effect against the development of atherosclerosis, but the mechanism of this hormonal action is unknown. One of the early events in the development of atherosclerosis is the adhesion of macrophages to endothelial cells, and nitric oxide (NO) inhibits this process. We show that basal release of NO is greater with endothelium-intact aortic rings from female rabbits than those from males. Oophorectomy diminishes both circulating estradiol concentration and basal release of NO to levels seen in male rabbits. These data establish that basal NO release from endothelium-intact aortic rings depends on circulating estradiol concentration and offer an explanation for the protective effect of estradiol against the development of atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. R., Kaplan J. R., Manuck S. B., Koritnik D. R., Parks J. S., Wolfe M. S., Clarkson T. B. Inhibition of coronary artery atherosclerosis by 17-beta estradiol in ovariectomized monkeys. Lack of an effect of added progesterone. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Nov-Dec;10(6):1051–1057. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisaka K., Gross S. S., Griffith O. W., Levi R. L-arginine availability determines the duration of acetylcholine-induced systemic vasodilation in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisaka K., Gross S. S., Griffith O. W., Levi R. NG-methylarginine, an inhibitor of endothelium-derived nitric oxide synthesis, is a potent pressor agent in the guinea pig: does nitric oxide regulate blood pressure in vivo? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):881–886. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bath P. M., Hassall D. G., Gladwin A. M., Palmer R. M., Martin J. F. Nitric oxide and prostacyclin. Divergence of inhibitory effects on monocyte chemotaxis and adhesion to endothelium in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Mar-Apr;11(2):254–260. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner P. F., Guerrero R., Cekan Z., Diczfalusy E. Radioimmunoassay method for six steroids in human plasma. Steroids. 1973 Dec;22(6):775–794. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(73)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush T. L., Barrett-Connor E., Cowan L. D., Criqui M. H., Wallace R. B., Suchindran C. M., Tyroler H. A., Rifkind B. M. Cardiovascular mortality and noncontraceptive use of estrogen in women: results from the Lipid Research Clinics Program Follow-up Study. Circulation. 1987 Jun;75(6):1102–1109. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.6.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom M. H., Fernstrom J. D. Rapid measurement of free amino acids in serum and CSF using high-performance liquid chromatography. Life Sci. 1981 Nov 16;29(20):2119–2130. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90669-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. The role of endothelium in the responses of vascular smooth muscle to drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:175–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Mügge A., Alheid U., Haverich A., Frölich J. C. Selective attenuation of endothelium-mediated vasodilation in atherosclerotic human coronary arteries. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):185–190. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Calmodulin-dependent endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase activity is present in the particulate and cytosolic fractions of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1788–1792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galle J., Busse R., Bassenge E. Hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis change vascular reactivity in rabbits by different mechanisms. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Nov-Dec;11(6):1712–1718. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.6.1712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galle J., Busse R., Bassenge E. Hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis change vascular reactivity in rabbits by different mechanisms. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Nov-Dec;11(6):1712–1718. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.6.1712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: I. Transition of blood-borne monocytes into foam cells in fatty lesions. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisclard V., Miller V. M., Vanhoutte P. M. Effect of 17 beta-estradiol on endothelium-dependent responses in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jan;244(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. E., Bush P. A., Ignarro L. J. Depletion of arterial L-arginine causes reversible tolerance to endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):714–721. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Moncada S., Palmer R. M. Bioassay of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) from porcine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):685–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Mitchell J. A., Harris H. J., Katsura M., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Endothelial cells metabolize NG-monomethyl-L-arginine to L-citrulline and subsequently to L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90627-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Adams J. B., Horwitz P. M., Wood K. S. Activation of soluble guanylate cyclase by NO-hemoproteins involves NO-heme exchange. Comparison of heme-containing and heme-deficient enzyme forms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4997–5002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Buga G. M., Wood K. S., Byrns R. E., Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9265–9269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lippton H., Edwards J. C., Baricos W. H., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J., Gruetter C. A. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Hjortland M. C., McNamara P. M., Gordon T. Menopause and risk of cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Oct;85(4):447–452. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-4-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati L., Chow F. P., Woollard M. L., Hutton R. A., Dandona P. Prostacyclin-like activity in the female rat thoracic aorta and the inferior vena cava after ethinyloestradiol and norethisterone. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Nov;59(5):369–372. doi: 10.1042/cs0590369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki S., Arnold W., Mittal C., Murad F. Stimulation of guanylate cyclase by sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin and nitric oxide in various tissue preparations and comparison to the effects of sodium azide and hydroxylamine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977 Feb;3(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J. K., Gilman D. P., Meldrum D. R., Judd H. L., Sawyer C. H. Relationship between circulating estrogens and the central mechanisms by which ovarian steroids stimulate luteinizing hormone secretion in aged and young female rats. Endocrinology. 1981 Mar;108(3):836–841. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-3-836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. S., Read M. A., Dusting G. J. Synergistic inhibition of platelet aggregation by endothelium-derived relaxing factor and prostacyclin. Thromb Res. 1988 Mar 1;49(5):437–449. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(98)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F., Mittal C. K., Arnold W. P., Katsuki S., Kimura H. Guanylate cyclase: activation by azide, nitro compounds, nitric oxide, and hydroxyl radical and inhibition by hemoglobin and myoglobin. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy A., Bajusz S., Patthy L. Preparation and characterization of Ng-mono-, di- and trimethylated arginines. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1977;12(3):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach M. J., Singer H. A., Loeb A. L. Mechanisms of endothelium-dependent vascular smooth muscle relaxation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jun 1;34(11):1867–1874. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Comparative pharmacology of endothelium-derived relaxing factor, nitric oxide and prostacyclin in platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits human platelet adhesion to vascular endothelium. Lancet. 1987 Nov 7;2(8567):1057–1058. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91481-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. The anti-aggregating properties of vascular endothelium: interactions between prostacyclin and nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;92(3):639–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma I., Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Nathan C., Levi R. Identification of arginine as a precursor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8664–8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer V. G., Woodson B. T., Mawhinney T. D., Rarey K. E., Bauman M. J., Raymer S. L., Peterson E. Free amino acid analysis of guinea pig perilymph: a possible clinical assay for the PLF enigma? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1990 Dec;103(6):981–985. doi: 10.1177/019459989010300616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M. J., Willett W. C., Colditz G. A., Rosner B., Speizer F. E., Hennekens C. H. A prospective study of postmenopausal estrogen therapy and coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 24;313(17):1044–1049. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510243131703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. K., Adams M. R., Klopfenstein H. S. Estrogen modulates responses of atherosclerotic coronary arteries. Circulation. 1990 May;81(5):1680–1687. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.5.1680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Simmons D., Steinberg D., Beltz W. F., Weinreb R., Young S. G., Lester P., Kelly N., Juliano J. Intensive combination drug therapy of familial hypercholesterolemia with lovastatin, probucol, and colestipol hydrochloride. Circulation. 1989 Jan;79(1):16–28. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



