Abstract
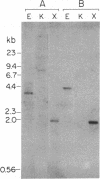
Diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI)/endozepine (EP)/acyl-CoA-binding protein (ACBP) is a small, highly conserved protein which has been independently isolated and characterized from different species using several different biological systems. To further investigate the structural and functional properties of this protein, we have cloned the homologous gene for DBI/EP/ACBP from the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The yeast gene contains no introns and encodes a polypeptide of 87 amino acids (including the initiating methionine), identical in length to the human gene product with 48% conservation of amino acid residues. The most highly conserved domain consists of 7 contiguous residues which are identical in all known protein species from yeast, birds, and mammals. This domain has previously been shown to constitute the hydrophobic binding site on DBI/EP/ACBP for acyl-CoA esters and is located within the second helical region of the molecule. Major and minor mRNA species of approximately 520 and 740 nucleotides, respectively, were detected in exponentially growing yeast. Sequences similar to those implicated in the regulation of fatty acid synthesis and beta-oxidation in yeast were detected in the promoter region of the gene. The presence of a highly conserved DBI/EP/ACBP gene in a primitive organism such as yeast provides support for the basic biological role of DBI/EP/ACBP as an acyl-CoA-binding protein and suggests that many of the biological functions attributed to it in higher organisms may result from its ability to interact with acyl-CoA. Hence, we have designated the yeast gene as ACB, for acyl-CoA-binding protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Costa E., Ferrero P., Fujimoto M., Cosenza-Murphy D., Guidotti A. Diazepam-binding inhibitor: a neuropeptide located in selected neuronal populations of rat brain. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):179–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3892688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsterdam A., Suh B. S. An inducible functional peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in mitochondria of steroidogenic granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1991 Jul;129(1):503–510. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-1-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen K. V., Ludvigsen S., Mandrup S., Knudsen J., Poulsen F. M. The secondary structure in solution of acyl-coenzyme A binding protein from bovine liver using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10654–10663. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besman M. J., Yanagibashi K., Lee T. D., Kawamura M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Identification of des-(Gly-Ile)-endozepine as an effector of corticotropin-dependent adrenal steroidogenesis: stimulation of cholesterol delivery is mediated by the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloem L. J., Yu L. A time-saving method for screening cDNA or genomic libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2830–2830. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Ferrero P., Guidotti A., Costa E. Neuropeptide modulation of GABA receptor C1- channels. Regul Pept Suppl. 1985;4:33–38. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronfman M., Morales M. N., Orellana A. Diacylglycerol activation of protein kinase C is modulated by long-chain acyl-CoA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):987–992. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. A yeast ARS-binding protein activates transcription synergistically in combination with other weak activating factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):887–897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. W., Agerberth B., Gell K., Andersson M., Mutt V., Ostenson C. G., Efendić S., Barros-Söderling J., Persson B., Jörnvall H. Isolation and characterization of porcine diazepam-binding inhibitor, a polypeptide not only of cerebral occurrence but also common in intestinal tissues and with effects on regulation of insulin release. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 1;174(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F. Sequence and structural features associated with translational initiator regions in yeast--a review. Gene. 1987;59(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., Doorenbosch M. M., Maurer C. T., de Winde J. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J., Grivell L. A. An ARS/silencer binding factor also activates two ribosomal protein genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4917–4923. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigel A., Feldmann H. Ty1 and delta elements occur adjacent to several tRNA genes in yeast. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1245–1250. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einerhand A. W., Voorn-Brouwer T. M., Erdmann R., Kunau W. H., Tabak H. F. Regulation of transcription of the gene coding for peroxisomal 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):113–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Zakian V. A. Position effect at S. cerevisiae telomeres: reversible repression of Pol II transcription. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):751–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90141-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Glaister D., Seeburg P. H., Guidotti A., Costa E. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human diazepam binding inhibitor, a natural ligand of an allosteric regulatory site of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hach M., Pedersen S. N., Börchers T., Højrup P., Knudsen J. Determination by photoaffinity labelling of the hydrophobic part of the binding site for acyl-CoA esters on acyl-CoA-binding protein from bovine liver. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):231–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2710231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter H., Müller U., Winnacker E. L., Gallwitz D. Isolation and DNA-binding characteristics of a protein involved in transcription activation of two divergently transcribed, essential yeast genes. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3029–3037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Cohen E. H. Sequences responsible for transcription termination on a gene segment in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W. UV crosslinking of RNA to nylon membrane enhances hybridization signals. Mol Biol Rep. 1986;11(2):107–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00364822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen J. Acyl-CoA-binding and transport, an alternative function for diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI), which is identical with acyl-CoA-binding protein. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Dec;30(12B):1405–1410. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(11)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen J. Acyl-CoA-binding protein (ACBP) and its relation to fatty acid-binding protein (FABP): an overview. 1990 Oct 15-Nov 8Mol Cell Biochem. 98(1-2):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00231387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q. L., Yamamoto N., Inoue A., Morisawa S. Fatty acyl-CoAs are potent inhibitors of the nuclear thyroid hormone receptor in vitro. J Biochem. 1990 May;107(5):699–702. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Shoyab M. Complete amino acid sequences of bovine and human endozepines. Homology with rat diazepam binding inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9727–9731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen J., Højrup P., Nielsen P. F., Roepstorff P., Knudsen J. Amino acid sequence of acyl-CoA-binding protein from cow liver. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):857–861. doi: 10.1042/bj2450857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen J., Knudsen J. Acyl-CoA-binding protein from cow. Binding characteristics and cellular and tissue distribution. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):709–714. doi: 10.1042/bj2480709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Einstein R., Brosius J. Putative diazepam binding inhibitor peptide: cDNA clones from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7221–7225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen I. B., Schulenberg H., Hansen H. O., Spener F., Knudsen J. A novel acyl-CoA-binding protein from bovine liver. Effect on fatty acid synthesis. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2410189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. P., Sinha A. K., Sikela J. M., Hahn W. E. Sequence and expression of the murine diazepam binding inhibitor. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Nov;6(2-3):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Hall B. D. Characterization of the yeast tRNA Ser genomic organization and DNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):921–934. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Mukhin A. G., Costa E., Krueger K. E. The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor is functionally linked to Leydig cell steroidogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3772–3779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Glick B. S., Arden S. R., Rothman J. E. Fatty acylation promotes fusion of transport vesicles with Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):955–961. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plesofsky-Vig N., Brambl R. Pantothenic acid and coenzyme A in cellular modification of proteins. Annu Rev Nutr. 1988;8:461–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.08.070188.002333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Vischer S., Glennon M. C., Regazzi R., Deeney J. T., Corkey B. E. Malonyl-CoA and long chain acyl-CoA esters as metabolic coupling factors in nutrient-induced insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5802–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. T., Börchers T., Knudsen J. Comparison of the binding affinities of acyl-CoA-binding protein and fatty-acid-binding protein for long-chain acyl-CoA esters. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):849–855. doi: 10.1042/bj2650849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüller H. J., Hahn A., Tröster F., Schütz A., Schweizer E. Coordinate genetic control of yeast fatty acid synthase genes FAS1 and FAS2 by an upstream activation site common to genes involved in membrane lipid biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):107–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05033.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Gentry L. E., Marquardt H., Todaro G. J. Isolation and characterization of a putative endogenous benzodiazepineoid (endozepine) from bovine and human brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11968–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA polymerase I promoters and transcription factors. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):189–190. doi: 10.1038/310189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Rose T. M., Shoyab M. Human DBI (endozepine): relationship to a homologous membrane associated protein (MA-DBI). Neuropharmacology. 1991 Dec;30(12B):1373–1380. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(11)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waku K. Origins and fates of fatty acyl-CoA esters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 4;1124(2):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90085-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb N. R., Rose T. M., Malik N., Marquardt H., Shoyab M., Todaro G. J., Lee D. C. Bovine and human cDNA sequences encoding a putative benzodiazepine receptor ligand. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):71–79. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]