Abstract
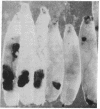
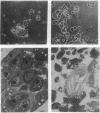
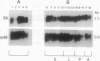
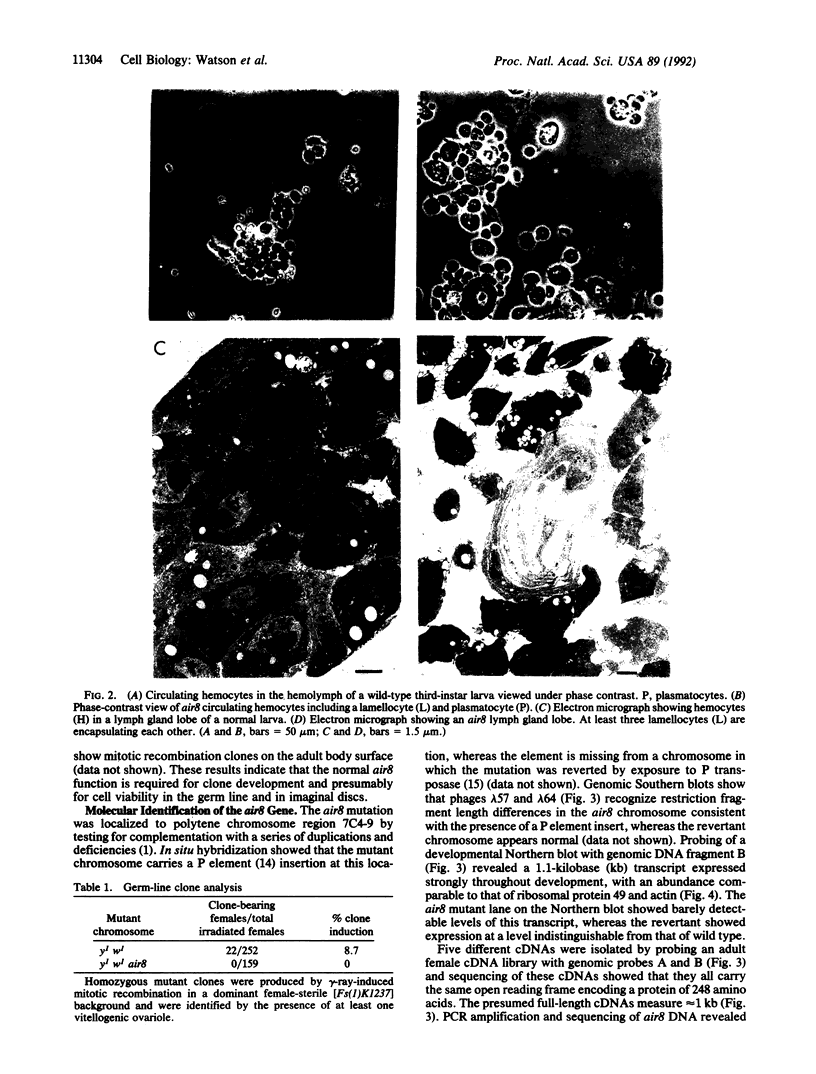
The tumor suppressor gene lethal(1)aberrant immune response 8 (air8) of Drosophila melanogaster encodes a homolog of the human S6 ribosomal protein. P element insertions that prevent expression of this gene cause overgrowth of the lymph glands (the hematopoietic organs), abnormal blood cell differentiation, and melanotic tumor formation. They also cause delayed development, inhibit growth of most of the larval organs, and lead to larval lethality. Mitotic recombination experiments indicate that the normal S6 gene is required for clone survival in the germ line and imaginal discs. The S6 gene produces a 1.1-kilobase transcript that is abundant throughout development in wild-type animals and in revertants derived from the insertional mutants but is barely detectable in the mutant larvae. cDNAs corresponding to this transcript show a 248-amino acid open reading frame with 75.4% identity and 94.8% similarity to both human and rat S6 ribosomal protein sequences. The results reveal a regulatory function of this ribosomal protein in the hematopoietic system of Drosophila that may be related to its developmentally regulated phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Lambertsson A. Characterization of a novel Minute-locus in Drosophila melanogaster: a putative ribosomal protein gene. Heredity (Edinb) 1990 Aug;65(Pt 1):51–57. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1990.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard G. F., Staniunas R. J., Bao S., Mafune K., Steele G. D., Jr, Gollan J. L., Chen L. B. Increased expression of human ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 messenger RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma and colon carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 1;52(11):3067–3072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellen H. J., O'Kane C. J., Wilson C., Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1288–1300. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. J., Sang J. H. Drosophila: lethal derangements of metamorphosis and modifications of gene expression caused by juvenile hormone mimics. Nature. 1968 Oct 26;220(5165):393–394. doi: 10.1038/220393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. J., Schmidt O. The genetic control of cell proliferation in Drosophila imaginal discs. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1990;13:169–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1990.supplement_13.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. J., Woods D. F. A major palmitoylated membrane protein of human erythrocytes shows homology to yeast guanylate kinase and to the product of a Drosophila tumor suppressor gene. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):621–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90136-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2891–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Bandi H. R., Hofsteenge J., Bussian B. M., Thomas G. Mitogen-activated 70K S6 kinase. Identification of in vitro 40 S ribosomal S6 phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22770–22775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotow H., Thomas G. Substrate recognition determinants of the mitogen-activated 70K S6 kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3074–3078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gateff E., Mechler B. M. Tumor-suppressor genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Crit Rev Oncog. 1989;1(2):221–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert L. I., Combest W. L., Smith W. A., Meller V. H., Rountree D. B. Neuropeptides, second messengers and insect molting. Bioessays. 1988 May;8(5):153–157. doi: 10.1002/bies.950080506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. Heat shock induces rapid dephosphorylation of a ribosomal protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross T., Nischt R., Gatermann K., Swida U., Käufer N. F. Primary structure of the ribosomal protein gene S6 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Genet. 1988;13(1):57–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00365757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinze H., Arnold H. H., Fischer D., Kruppa J. The primary structure of the human ribosomal protein S6 derived from a cloned cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4139–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Ueno K., Natori S. Counteraction by 20-hydroxyecdysone of the effect of juvenile hormone on phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 9;213(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Ueno K., Natori S. Identification of 30-kDa fat body protein of Sarcophaga peregrina larvae selectively phosphorylated in the presence of 20-hydroxyecdysone as ribosomal protein S6. J Biochem. 1986 Aug;100(2):493–498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. A., Jacobs-Lorena M. Selective translational regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression during early development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3583–3592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komitopoulou K., Gans M., Margaritis L. H., Kafatos F. C., Masson M. Isolation and Characterization of Sex-Linked Female-Sterile Mutants in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER with Special Attention to Eggshell Mutants. Genetics. 1983 Dec;105(4):897–920. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M., Glanville N., Mandel J. L., Gerlinger P., Palmiter R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: hormonal control of X and Y gene transcription and mRNA accumulation. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Molenaar C. M., Witsenboer H. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Yeast contains two functional genes coding for ribosomal protein S10. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5027–5039. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H. Control of ribosomal protein gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney P. A., Weber U., Onofrechuk P., Biessmann H., Bryant P. J., Goodman C. S. The fat tumor suppressor gene in Drosophila encodes a novel member of the cadherin gene superfamily. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):853–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechler B. M., Strand D., Kalmes A., Merz R., Schmidt M., Török I. Drosophila as a model system for molecular analysis of tumorigenesis. Environ Health Perspect. 1991 Jun;93:63–71. doi: 10.1289/ehp.919363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechler B. The fruit fly Drosophila and the fish Xiphophorus as model systems for cancer studies. Cancer Surv. 1990;9(3):505–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod J. J., Crippa M. Variations in the amount of polysomes in mature oocytes of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):586–592. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz R., Schmidt M., Török I., Protin U., Schuler G., Walther H. P., Krieg F., Gross M., Strand D., Mechler B. M. Molecular action of the l(2)gl tumor suppressor gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Aug;88:163–167. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9088163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N., Engstrom L., Mahowald A. P. Zygotic lethals with specific maternal effect phenotypes in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Loci on the X chromosome. Genetics. 1989 Feb;121(2):333–352. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Meyuhas O. Translational control of ribosomal protein production in mammalian cells. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):83–92. doi: 10.1159/000468749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Pendergast A. M. Regulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:195–230. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. L., Johnson T. K., Denell R. E. Lethal(1) aberrant immune response mutations leading to melanotic tumor formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genet. 1991;12(3):173–187. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Nick H. P., Lithgow T. Primary structure of mammalian ribosomal protein S6. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):170–177. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. F., Bryant P. J. The discs-large tumor suppressor gene of Drosophila encodes a guanylate kinase homolog localized at septate junctions. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):451–464. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]