Abstract
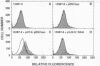
Mutations of the human interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) receptor intracellular domain have permitted us to define a restricted region of that domain as necessary for both induction of class I major histocompatibility complex antigen by IFN-gamma and protection against encephalomyocarditis virus. This region consists of five amino acids (YDKPH), all of which are conserved in the human and murine receptors. Tyr-457 and His-461 are essential for activity. Approximately 80% of the amino acids of the intracellular domain of the receptor is not required for major histocompatibility complex class I antigen induction or for antiviral protection against encephalomyocarditis virus. The observation that there was no protection by IFN-gamma against vesiculostomatitis virus indicates that other factors, in addition to chromosome 21 accessory factor(s), are required to generate the full complement of transduction signals from the human IFN-gamma receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Dembić Z., Merlin G. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M. The interferon-gamma receptor: a comparison with other cytokine receptors. J Interferon Res. 1990 Dec;10(6):551–558. doi: 10.1089/jir.1990.10.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Schreiber R. D. Internalization and degradation of receptor-bound interferon-gamma by murine macrophages. Demonstration of receptor recycling. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Familletti P. C., Rubinstein S., Pestka S. A convenient and rapid cytopathic effect inhibition assay for interferon. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Fernandez-Luna J., Schreiber R. D. Identification of two regions within the cytoplasmic domain of the human interferon-gamma receptor required for function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19626–19635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores I., Mariano T. M., Pestka S. Human interferon omega (omega) binds to the alpha/beta receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19875–19877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariglio M., Franco A., Cavallo G., Landolfo S. Evidence for a GTP-binding protein involved in interferon-gamma transduction signal. J Interferon Res. 1988 Aug;8(4):463–472. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs V. C., Williams S. R., Gray P. W., Schreiber R. D., Pennica D., Rice G., Goeddel D. V. The extracellular domain of the human interferon gamma receptor interacts with a species-specific signal transducer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5860–5866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Becton D. L., Somers S. D., Gray P. W., Adams D. O. Interferon-gamma modulates protein kinase C activity in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1378–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey G. K., McCourt D. W., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Dependence on the presence of a functionally active receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17868–17875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino Y., Kumar C. S., Mariano T. M., Lai D. H., Pestka S. Chimeric interferon-gamma receptors demonstrate that an accessory factor required for activity interacts with the extracellular domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3741–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino Y., Mariano T. M., Kumar C. S., Kozak C. A., Pestka S. Expression and reconstitution of a biologically active mouse interferon gamma receptor in hamster cells. Chromosomal location of an accessory factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6948–6951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Jones C., Kumar C. S., Stefanos S., O'Connell S., Pestka S. Expression and reconstitution of a biologically active human interferon-gamma receptor in hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1827–1830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Jones C., Rashidbaigi A., Geyer D. D., Morse H. G., Wright R. B., Pestka S. Chromosome mapping of biological pathways by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and cell fusion: human interferon gamma receptor as a model system. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):583–592. doi: 10.1007/BF01535312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Pestka S. B., Pestka S. Efficient cloning of PCR generated DNA containing terminal restriction endonuclease recognition sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6156–6156. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Rashidbaigi A., Jones C., Tischfield J. A., Shows T. B., Pestka S. Human chromosomes 6 and 21 are required for sensitivity to human interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4151–4155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C. S., Muthukumaran G., Frost L. J., Noe M., Ahn Y. H., Mariano T. M., Pestka S. Molecular characterization of the murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17939–17946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Bekesi E. Phosphorylation of human immune interferon (IFN-gamma). Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:296–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Pestka S. Interferon receptors. Immunol Today. 1988 Dec;9(12):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C., Merlin G., Ballotti R., Metzler M., Aguet M. Rapid increase of the human IFN-gamma receptor phosphorylation in response to human IFN-gamma and phorbol myristate acetate. Involvement of different serine/threonine kinases. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4257–4264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata Y., Rosen O. M., Makman M. H., Bloom B. R. Biochemical analysis of mutants of a macrophage cell line resistant to the growth-inhibitory activity of interferon. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1342–1347. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic V., Yu S. F., Figueiredo F., Hollenbach P. W., Gawdi G., Herman B., Uhing R. J., Adams D. O. Role of Na+/H+ exchange by interferon-gamma in enhanced expression of JE and I-A beta genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):469–471. doi: 10.1126/science.2541500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Langer J. A., Jung V., Jones C., Morse H. G., Tischfield J. A., Trill J. J., Kung H. F., Pestka S. The gene for the human immune interferon receptor is located on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):384–388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehberg E., Kelder B., Hoal E. G., Pestka S. Specific molecular activities of recombinant and hybrid leukocyte interferons. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11497–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Roberts W. K., Kerr I. M. 2-5A accumulates to high levels in interferon-treated, vaccinia virus-infected cells in the absence of any inhibition of virus replication. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):220–228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.220-228.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Orchansky P. The interferon receptors. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(3):249–275. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Mechanisms of the antiviral action of interferons. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:27–72. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Schmidt H., Lengyel P., Reddy E. S., Morgan W. R., Weissman S. M. Transcripts of human HLA gene fragments lacking the 5'-terminal region in transfected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):649–653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]