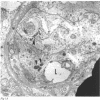
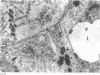
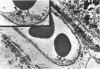
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Tubuloreticular structures (TRS) are subcellular inclusions that are most commonly found in endothelial cells and lymphocytes of patients with autoimmune or collagen vascular disorders. In AIDS, TRS have been described in various tissues throughout the body including the lung, kidney, liver, muscle, and skin. METHODS: Ocular tissues from 23 patients with AIDS were examined by electron microscopy. These included 17 postmortem eyes in addition to three chorioretinal and three conjunctival biopsy specimens. RESULTS: The overall prevalence of TRS in the ocular and conjunctival endothelial cells was found to be 83% (19/23). CONCLUSIONS: This is the first documented study of the prevalence of these structures in the ocular structures of patients with AIDS. Given the high frequency of their occurrence in AIDS, it is recommended that the presence of TRS in ocular or conjunctival tissues be an indication for obtaining an HIV antibody titre. Additionally, a rheumatological examination for HIV seronegative patients is suggested.
Full text
PDF
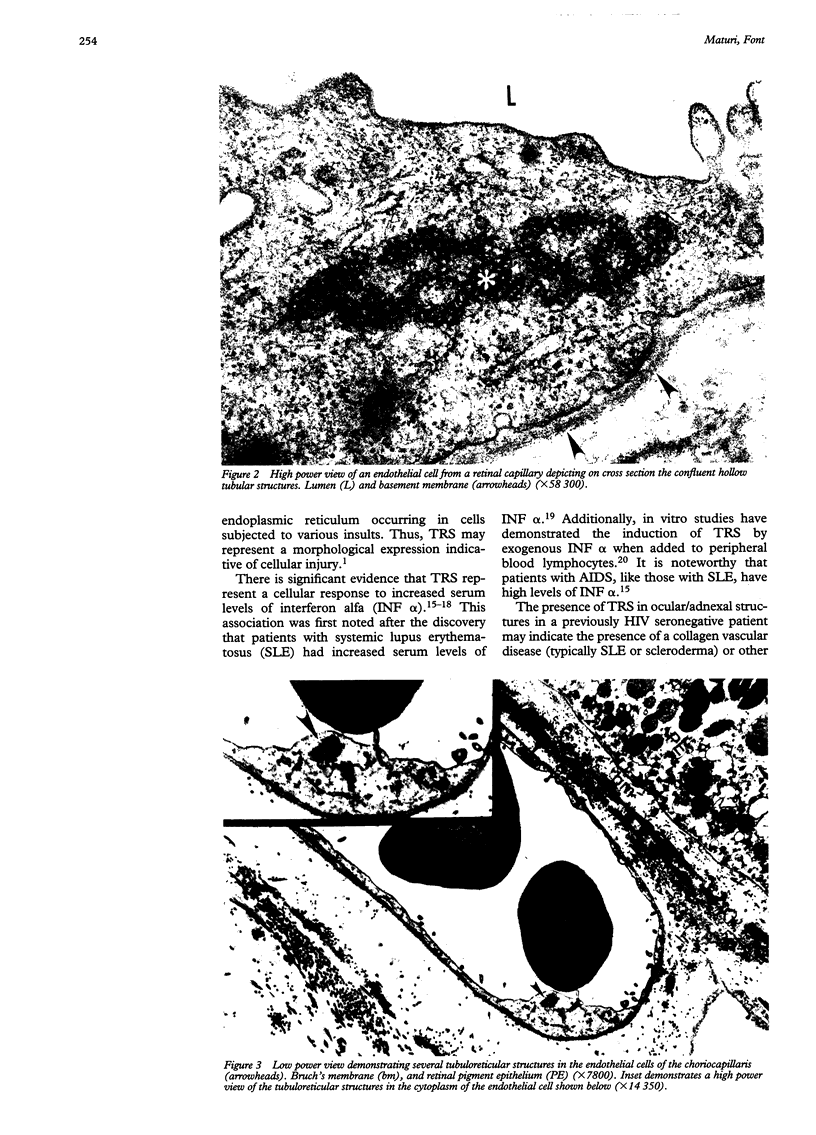
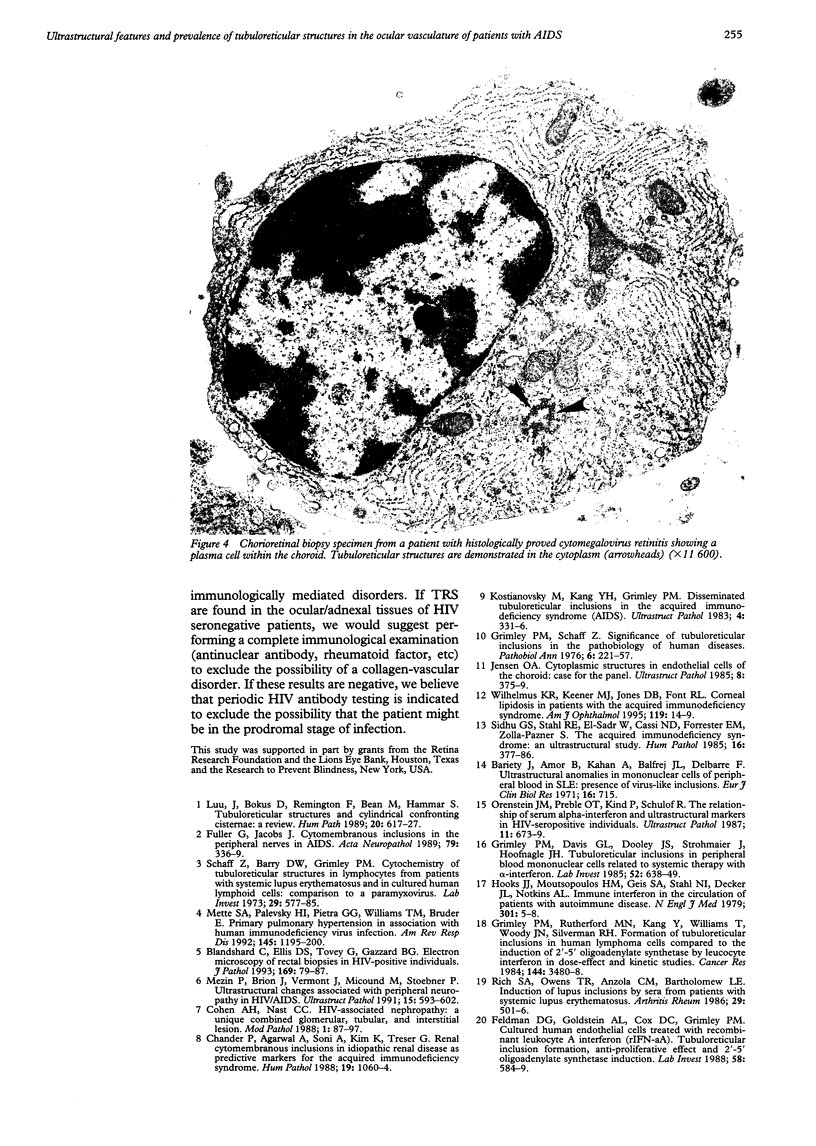
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanshard C., Ellis D. S., Tovey G., Gazzard B. G. Electron microscopy of rectal biopsies in HIV-positive individuals. J Pathol. 1993 Jan;169(1):79–87. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chander P., Agarwal A., Soni A., Kim K., Treser G. Renal cytomembranous inclusions in idiopathic renal disease as predictive markers for the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1988 Sep;19(9):1060–1064. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. H., Nast C. C. HIV-associated nephropathy. A unique combined glomerular, tubular, and interstitial lesion. Mod Pathol. 1988 Mar;1(2):87–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., Goldstein A. L., Cox D. C., Grimley P. M. Cultured human endothelial cells treated with recombinant leukocyte A interferon. Tubuloreticular inclusion formation, antiproliferative effect, and 2',5' oligoadenylate synthetase induction. Lab Invest. 1988 May;58(5):584–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller G. N., Jacobs J. M. Cytomembranous inclusions in the peripheral nerves in AIDS. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;79(3):336–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00294672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Davis G. L., Kang Y. H., Dooley J. S., Strohmaier J., Hoofnagle J. H. Tubuloreticular inclusions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells related to systemic therapy with alpha-interferon. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):638–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Rutherford M. N., Kang Y. H., Williams T., Woody J. N., Silverman R. H. Formation of tubuloreticular inclusions in human lymphoma cells compared to the induction of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase by leucocyte interferon in dose-effect and kinetic studies. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3480–3488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Schaff Z. Significance of tubuloreticular inclusions in the pathobiology of human diseases. Pathobiol Annu. 1976;6:221–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen O. A. Cytoplasmic structures in endothelial cells of the choroid. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1985;8(4):375–379. doi: 10.3109/01913128509141527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostianovsky M., Kang Y. H., Grimley P. M. Disseminated tubuloreticular inclusions in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Ultrastruct Pathol. 1983 Jun;4(4):331–336. doi: 10.3109/01913128309140585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luu J. Y., Bockus D., Remington F., Bean M. A., Hammar S. P. Tubuloreticular structures and cylindrical confronting cisternae: a review. Hum Pathol. 1989 Jul;20(7):617–627. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezin P., Brion J. P., Vermont J., Micoud M., Stoebner P. Ultrastructural changes associated with peripheral neuropathy in HIV/AIDS. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1991 Nov-Dec;15(6):593–602. doi: 10.3109/01913129109023189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M., Preble O. T., Kind P., Schulof R. The relationship of serum alpha-interferon and ultrastructural markers in HIV-seropositive individuals. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1987;11(5-6):673–679. doi: 10.3109/01913128709048453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. A., Owens T. R., Anzola M. C., Bartholomew L. E. Induction of lupus inclusions by sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):501–507. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaff Z., Barry D. W., Grimley P. M. Cytochemistry of tubuloreticular structures in lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and in cultured human lymphoid cells: comparison to a paramyxovirus. Lab Invest. 1973 Dec;29(6):577–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu G. S., Stahl R. E., el-Sadr W., Cassai N. D., Forrester E. M., Zolla-Pazner S. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: an ultrastructural study. Hum Pathol. 1985 Apr;16(4):377–386. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmus K. R., Keener M. J., Jones D. B., Font R. L. Corneal lipidosis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995 Jan;119(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73808-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]