Figure 2.
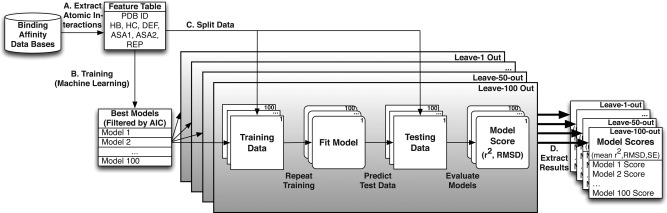
Replicated cross‐validation evaluates expected model accuracy. We used multiple different hierarchical, replicated cross‐validation analyses to evaluate the accuracy with which statistical models could predict molecular binding affinities from structural information (see Methods). A: Atomic interactions (see Fig. 1) were extracted from the atomic coordinates of each protein−ligand complex. B: Statistical models were fit to different portions of these data, with the best‐fit models selected by AIC (see Methods). C: Each data set was randomly partitioned into training and testing data, using 5 different leave‐out strategies (see Methods). Each model was fit to the training data, and accuracy was evaluated on the set‐aside testing data by calculating Pearson's correlation (r 2) and the root mean squared deviation (RMSD) between predicted and experimentally determined binding affinities (see Methods). D. The entire cross‐validation procedure was repeated 100 times, and we report the mean and standard error in r2 and RMSD across the 100 cross‐validation replicates.
