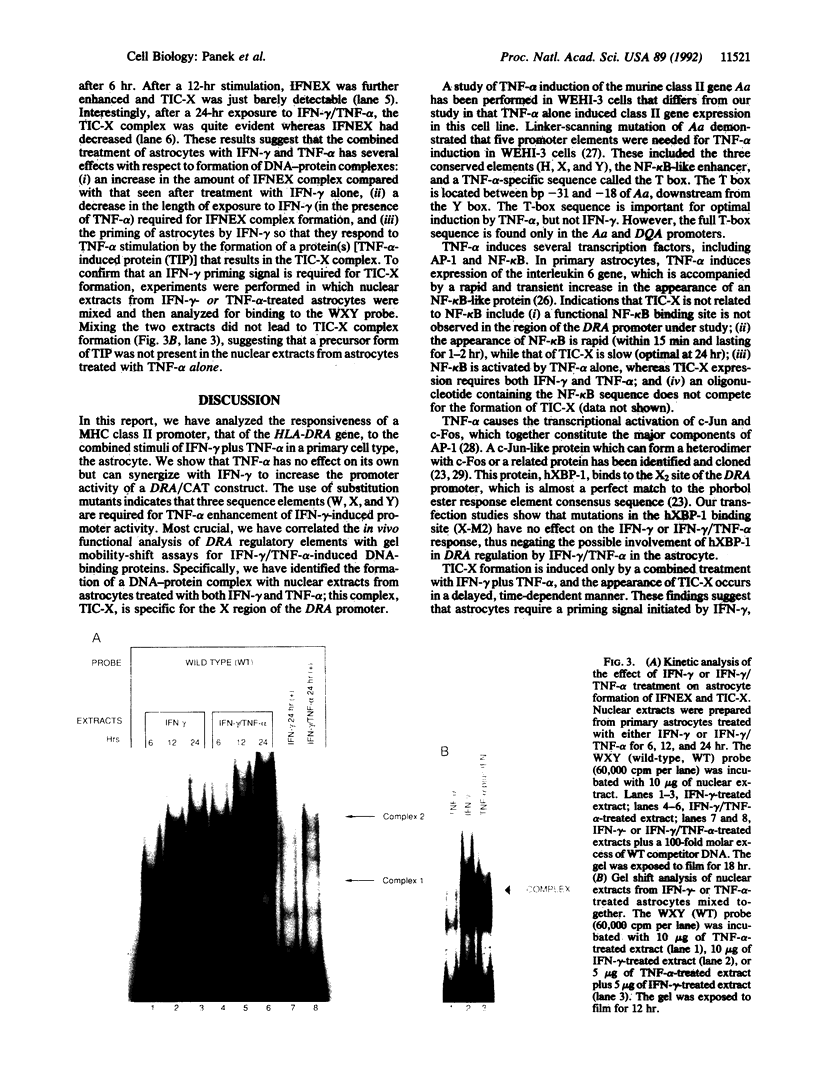
Abstract
The cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) alone does not induce class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) expression in most primary cells but can regulate ongoing class II expression in either a positive or negative fashion. The mechanism(s) by which TNF-alpha enhances interferon gamma (IFN-gamma)-induced class II expression was examined in a primary cell type, the astrocyte, by transient transfection of the HLA-DRA promoter linked to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene (DRA-CAT). We show that TNF-alpha, while having no effect on its own, can synergize with IFN-gamma to increase the level of promoter activity of a DRA-CAT construct. Three known sequences--W, X, and Y--are required for TNF-alpha enhancement of IFN-gamma-induced promoter activity. The corollary effect of TNF-alpha on DNA-binding proteins specific for these elements was examined. A previous report described a DNA-binding protein, IFN-gamma-enhanced factor X (IFNEX), which is upregulated by IFN-gamma in astrocytes and is specific for the X box of the DRA promoter. In this study, we found that TNF-alpha alone did not induce any nuclear proteins; however, combined treatment of astrocytes with both IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha induced a DNA-protein complex of slower electrophoretic mobility than IFNEX. The TNF-alpha-induced complex (TIC-X) has specificity for the X element of the DRA promoter. These results suggest a mechanism by which TNF-alpha enhances IFN-gamma-induced class II MHC expression via the formation of TIC-X.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Mogensen S. C., Vuillier F., Fiers W., Virelizier J. L. Autocrine secretion of tumor necrosis factor under the influence of interferon-gamma amplifies HLA-DR gene induction in human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6087–6091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Mathis D. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class-II genes: X, Y and other letters of the alphabet. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:681–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste E. N. Cytokines: influence on glial cell gene expression and function. Chem Immunol. 1992;52:106–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste E. N., Sparacio S. M., Bethea J. R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances interferon-gamma-mediated class II antigen expression on astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Dec;25(2-3):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90139-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Eng L. F., Dahl D., Uyeda C. T. Localization of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes by immunofluorescence. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung I. Y., Benveniste E. N. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by astrocytes. Induction by lipopolysaccharide, IFN-gamma, and IL-1 beta. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2999–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogswell J. P., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. X-box-binding proteins positively and negatively regulate transcription of the HLA-DRA gene through interaction with discrete upstream W and V elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7703–7707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogswell J. P., Zeleznik-Le N., Ting J. P. Transcriptional regulation of the HLA-DRA gene. Crit Rev Immunol. 1991;11(2):87–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierz W., Endler B., Reske K., Wekerle H., Fontana A. Astrocytes as antigen-presenting cells. I. Induction of Ia antigen expression on astrocytes by T cells via immune interferon and its effect on antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3785–3793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund Y. R., Dedrick R. L., Jones P. P. cis-acting sequences required for class II gene regulation by interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha in a murine macrophage cell line. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1283–1299. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Finn P. W., Davidon R., Nabavi N., Zeleznik-Le N. J., Ting J. P., Glimcher L. H. A new member of the leucine zipper class of proteins that binds to the HLA DR alpha promoter. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1581–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann J., Lo D., Naji A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Heber-Katz E. Antigen presenting function of class II MHC expressing pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):476–479. doi: 10.1038/336476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa P. T., ter Meulen V., Fontana A. Hyperinducibility of Ia antigen on astrocytes correlates with strain-specific susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4219–4223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H., Panek R. B., Benveniste E. N., Ting J. P. Usage of primary cells to delineate IFN-gamma-responsive DNA elements in the HLA-DRA promoter and to identify a novel IFN-gamma-enhanced nuclear factor. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3643–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H., Sasaki A., Ting J. P. Identification of an interferon-gamma-responsive element of a class II major histocompatibility gene in rat type 1 astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Mar;31(3):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90049-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. J., Liou H. C., Davidon R., Strominger J. L., Glimcher L. H. Human X-box-binding protein 1 is required for the transcription of a subset of human class II major histocompatibility genes and forms a heterodimer with c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4309–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Reiss C. S., Burakoff S. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A. Ia expression by vascular endothelium is inducible by activated T cells and by human gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1339–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Barras E., Satola S., Kobr M., Reinhart D., Sanchez C. H., Mach B. Cloning of the major histocompatibility complex class II promoter binding protein affected in a hereditary defect in class II gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4200–4204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servenius B., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Class II genes of the human major histocompatibility complex. The DO beta gene is a divergent member of the class II beta gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8759–8766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparacio S. M., Zhang Y., Vilcek J., Benveniste E. N. Cytokine regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression in astrocytes involves activation of an NF-kappa B-like nuclear protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Aug;39(3):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90257-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidovic M., Sparacio S. M., Elovitz M., Benveniste E. N. Induction and regulation of class II major histocompatibility complex mRNA expression in astrocytes by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Dec;30(2-3):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90103-T. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Jacob C. O. Regulation of MHC class II antigen expression. Opposing effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DR and Ia expression depends on the maturation and differentiation stage of the cell. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):899–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeleznik-Le N. J., Azizkhan J. C., Ting J. P. Affinity-purified CCAAT-box-binding protein (YEBP) functionally regulates expression of a human class II major histocompatibility complex gene and the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1873–1877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]