Abstract
The genetic landscape and molecular features of collecting duct carcinoma (CDC) of the kidney remain largely unknown. Herein, we performed whole exome sequencing (WES) and transcriptome sequencing (RNASeq) on 7 CDC samples (CDC1 −7). Among the 7 samples, 4 samples with matched non-tumor tissue were used for copy number analysis by SNP array data. No recurrent somatic SNVs were observed except for MLL, which was found to be mutated (p.V297I and p.F407C) in 2 samples. We identified somatic SNVs in 14 other cancer census genes including: ATM, CREBBP, PRDM1, CBFB, FBXW7, IKZF1, KDR, KRAS, NACA, NF2, NUP98, SS18, TP53, and ZNF521. SNP array data identified a CDKN2A homozygous deletion in 3 samples and SNV analysis showed a non-sense mutation of the CDKN2A gene with unknown somatic status. To estimate the recurrent rate of CDKN2A abnormalities, we performed FISH screening of additional samples and confirmed the frequent loss (62.5%) of CDKN2A expression. Since cisplatin based therapy is the common treatment option for CDC, we investigated the expression of solute carrier (SLC) family transporters and found 45% alteration. In addition, SLC7A11 (cystine transporter, xCT), a cisplatin resistance associated gene, was found to be overexpressed in 4 out of 5 (80%) cases of CDC tumors tested, as compared to matched non-tumor tissue. In summary, our study provides a comprehensive genomic analysis of CDC and identifies potential pathways suitable for targeted therapies.
Keywords: collecting duct carcinoma, CDKN2A, solute carrier family genes
INTRODUCTION
Collecting duct renal carcinoma (CDC), also known as Bellini duct carcinoma, is a rare histological subtype (less than 2%) of renal cell carcinoma with unique clinical, histological, and pathological characteristics [1–3]. These tumors arise from the distal collecting ducts and are positioned in the renal pelvis with a gray or whitish appearance without considerable necrosis or hemorrhage [2, 3]. The clinical presentation of CDC is usually at advanced stage with symptomatic disease due to its aggressiveness, with 1-3 years disease specific survival. More than 60 percent of CDC patients manifest symptomatic disease at presentation and the common metastatic sites include lymph nodes, bone, lung, and liver [4, 5]. Epidemiological characterization of CDC in North America has revealed a prevalence of CDC in the African American male population [6, 4]. The systemic therapy offered to CDC patients is a cisplatin-based regimen, but the clinical benefit remains limited and the median survival is less than 12 months [4, 7, 8]. Treatment with targeted therapies, such as sunitinib, has also shown limited clinical benefit [9–11]. In addition, immunotherapies, including interferon alpha/gamma and interleukin, have not been shown to be significantly effective in CDC patients (n = 34) [5]. To determine the genetic alterations associated with chemo sensitivity, a preclinical study with human cell lines established from CDC patients revealed topoisomerase I (TOPI) expression to be associated with high in vitro sensitivity to TOPI and TOPII inhibitors, such as topotecan, doxorubicin, and epirubicin, suggesting TOP1 as a potential molecular target for CDC [12].
Comprehensive genomic and proteomic studies of CDC aimed at understanding the critical molecular architecture alterations associated with this tumor type have been limited. A recent report studying 17 locally advanced or metastatic CDC tumors detected 36 genomic alterations, the most common being NF2 (29%), SETD2 (24%), SMARCH1 (18%), and CDKN2A (12%), suggesting a potential role for mTOR inhibitors in patients with NF2 alterations [13]. A previous study of 29 CDC samples showed frequent DNA losses at 8p (9 out of 29), 16p (9 out of 29), 1p (7 out of 29), and 9p (7 out of 29); and high levels of amplifications at 13q (9 out of 29), suggesting CDC as a unique entity among kidney cancers [14].
To better understand the genomic profile of CDC tumors, we performed whole exome sequencing and RNASeq analysis of 7 CDC tumors and 4 matched non-tumor kidney tissues, as well as FISH analysis of CDKN2A on 16 CDC tumors. Our results revealed the frequent loss of CDKN2A in 62.5% (10 out of 16) and alteration of 45.3% (136 out of 300) of SLC family transporters in CDC tumors.
RESULTS
Genomic landscape of CDC
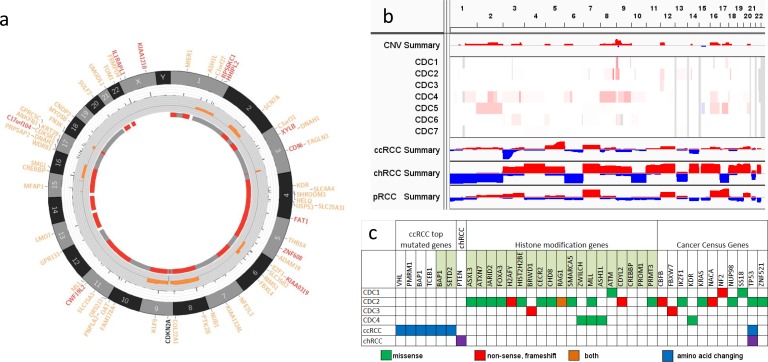
In our study, the overall somatic changes, including SNVs, INDELs, and CNVs, of 4 samples with matched non-tumor are shown in Figure 1. The analysis, performed as described [15–17], displays a significantly different landscape of genetic alterations in terms of somatic SNVs and INDELs (Figure 1a and Supplementary Table 1). SNP array data showed large scale somatic copy number alterations (SCNAs) and whole chromosome loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in all samples, with a small number of focal SCNAs (Supplementary Table 2). Whole exome sequencing (WES) of all 4 tumor samples identified 368 putative somatic SNVs and INDELs, including 325 missense mutations, 24 non-sense mutations, 17 frameshift indels, and 2 protein deletions.
Figure 1. Somatic alterations in kidney CDC.
a. A representative Circos plot of CDC samples. The plot shows (from outer to inner circle) genes with somatic amino acid changes (red genes are in Cancer Census Genes), chromosomes, allele frequencies of mutations, copy number aberration (orange for gain and blue for loss), and LOH (red means LOH and grey means no LOH). b. Somatic CNV in 7 CDC samples and summary of CNVs in CDC, ccRCC, chRCC, and pRCC. Red color represents copy number gain and blue copy number loss. c. Somatic SNVs in 4 CDC samples and significantly mutated genes in ccRCC and chRCC. Green means missense mutation, red means non-sense, frameshift mutations, and orange means both. TCGA data of ccRCC and pRCC, including clinical information, somatic mutations, SNP array CNV calls, and normalized RNASeqV2, were downloaded from the TCGA data portal. Alternation status of CDKN2A was determined by somatic mutation calls and CNV segmentation results. If a segment overlapped with CDKN2A and had a logR ratio less than −0.4, CDKN2A was considered a loss in this sample. For gene expression data, the RSEM quantified and normalized data were first log2 transferred, followed by significant test. All statistical tests were performed using R statistical program followed by a significance test.
Among the somatic mutated genes, several chromatin remodeling genes were found to be mutated, such as PRDM1, CREBBP, MLL, ASXL3, and CHD8. Somatic changes of epigenetic regulators represent a common theme in cancer genomes. In ccRCC studies, 3 chromatin remodeling genes, PBRM1, SETD2, and BAP1, are often reported as the top recurrently mutated genes [18–20]. In our study, MLL was the only recurrently mutated gene in 2 of the 4 samples. Fifteen somatically mutated genes in all 4 cases are in the Cancer Gene Consensus, including TP53, NF2, KRAS, and IKZF. However, none of the top mutated genes identified in ccRCC, including VHL, PBRM1, SETD2, KDM5C, BAP1, PTEN, MTOR, and PIK3CA, were found to be altered in our study, which could be due to either the small sample size or the unique mutation spectrum of our samples. SNP array data revealed 4 samples (CDC1, CDC2, CDC4, and CDC5) as having large copy number changes and most of those were copy number gains, except for a chr15 q12 to q21.3 loss found in sample CDC5. In addition, large scale LOH was more prevalent than copy number changes (Figure 1a) and all samples, except CDC7, had LOH in multiple whole chromosomes.
Loss of CDKN2A/p16 expression is common in CDC
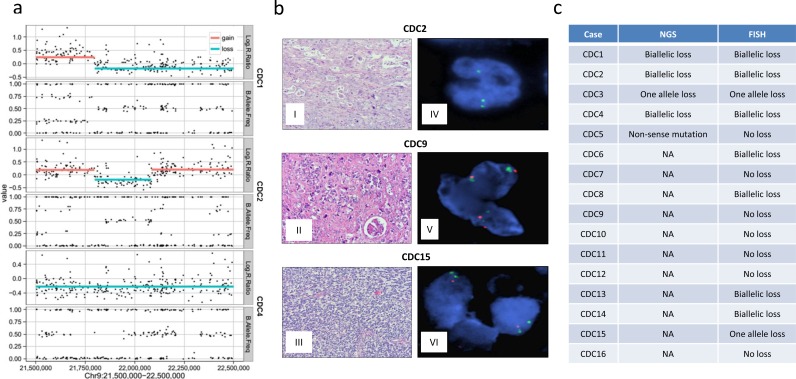
Focal homozygous deletions of chr 9 p-arm in all 3 samples (CDC1, CDC2, and CDC4) included CDKN2A. These deletions were homozygous with corresponding copy number losses (Figure 2a). To better estimate CDKN2A status and to validate findings in the SNP array, we performed fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) (Figure 2b) on the 7 sequenced samples and 9 additional FFPE samples (16 total samples). The FISH results validated the homozygous losses and further identified a homozygous loss in CDC6, which was not identified by SNP array, and a heterozygous loss in CDC3. Combined with 9 FFPE samples, we found 7 samples with biallelic loss and 2 samples with single copy loss of CDKN2A. In CDC5, a sample without matched non-tumor, SNV analysis identified a cytosine-to-adenine transversion (c.360C > A), encoding a p.E120* non-sense mutation for CDKN2A gene with unknown somatic status. This sample also showed LOH at CDKN2A loci, suggesting that this non-sense mutation could be biallelic. Figure 2c shows the comparative analysis of NGS and FISH data on the CDKN2A/P16INK4a status in CDC cases. Combining the results from SNP array, exome sequencing, and FISH, we identified 8 out of 16 (50%) homozygous losses and 2 heterozygous losses (12.5%) in all samples examined. A recent study showed similar results with genomic alteration of CDKN2A in 12% (2 out of 17) of CDC cases, one with homozygous gene deletion and another with truncation [13]. The CDKN2A gene encodes several proteins, including p16 (INK4a) and p14 (ARF), which are tumor suppressor genes that regulate the cell cycle and protect p53 [21, 22]. Loss of CDKN2A expression has been associated with the induction of CDK4/CDK6. Selective inhibitors for CDK4/CDK6 are currently in clinical development and, based on our findings, may represent a rational therapeutic strategy for CDC.
Figure 2. CDKN2A losses in CDC.
a. Copy number data show biallelic loss of CDKN2A in CDC1, CDC2, and CDC4 with negative log R ratios and normal like B allele frequencies. SNP array data log2 ratios were calculated by comparing the tumor sample signals with pooled non-tumor samples from Illumina. b. Representative tumor sample slides and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) results of normal, single copy loss, and biallelic loss of CDKN2A loci. I, II, III: H&Es of cases CDC2, CDC9, CDC15, respectively, with infiltrating pleomorphic collecting duct carcinoma. IV, CDC2, p16 FISH with no copies each of p16 and with preserved reference probe. V, CDC9, p16 FISH with two copies each of p16 and reference probe. VI, CDC15, p16 FISH with one copy of p16 and two copies of reference probe. c. Tabulation of p16 loss according to NGS and FISH data. Cases CDC6-CDC16 were not sequenced by NGS, noted as NA.
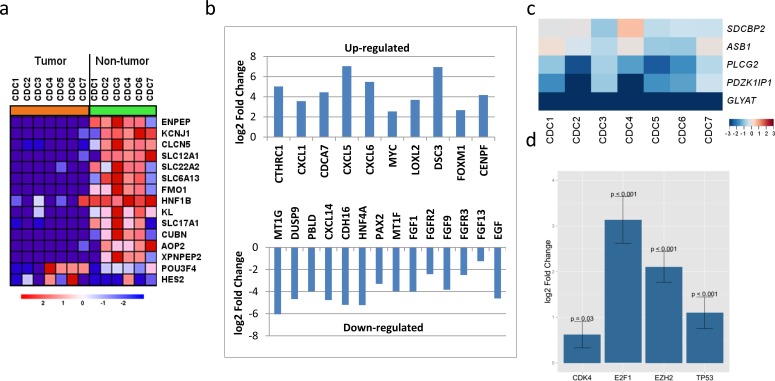
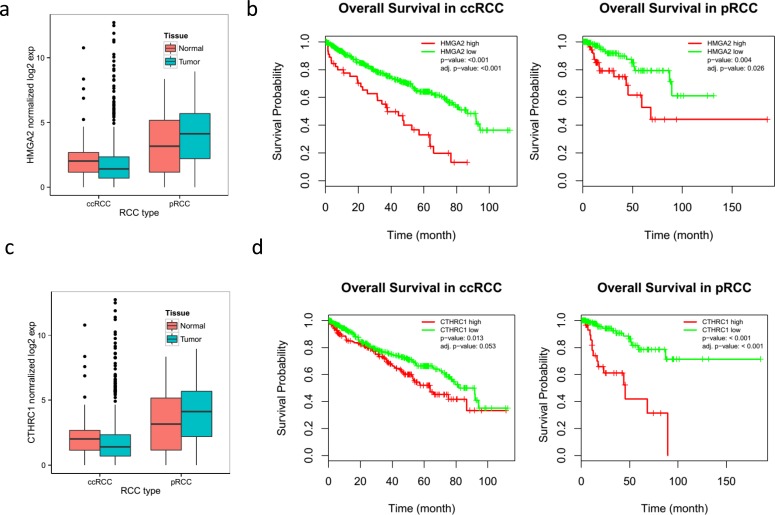
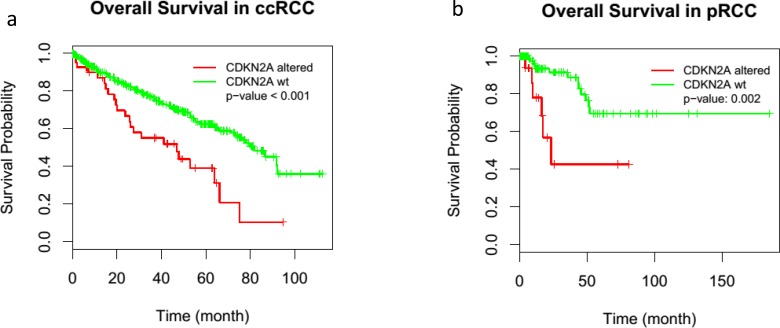
The paired analysis of RNASeq data revealed 2879 up-regulated and 1951 down-regulated genes in tumor samples, as compared with matched non-tumor samples. The principal component analysis (PCA) showed the separation of tumor and matched non-tumor samples at the first component and one tumor sample (CDC4) with a distinct expression profile at the second component. This was also seen in un-supervised clustering analysis. MYC amplification was identified in 1 sample (CDC2) and up-regulation in all 4 tumor samples analyzed (adjusted p-value < 0.001) (Figure 3b). The cell division cycle associated 7 (CDCA7) gene, one of the direct MYC targets, was also found to be up-regulated (Figure 3b). High-mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) and Collagen Triple Helix Repeat Containing 1 (CTHRC1), the top two up-regulated genes (according to our data) with log2 fold changes greater than 6, have been reported in the literature to be overly expressed in several cancer types and to be related to tumor prognosis [23–26]. A review of TCGA data showed HMGA2 to be overexpressed in ccRCC, but not in pRCC (Figure 7) and survival analysis showed significant poor outcome for the high HGMA2 expression group in both ccRCC and pRCC (log-rank test, p-value < 0.001 and 0.004, and adjusted p-value of < 0.001 and 0.026 for ccRCC and pRCC, respectively). Similarly, CTHRC1 was found to be significantly up-regulated in pRCC, but not in ccRCC, and the survival analysis showed significant poor overall survival for the high CTHRC1 expression group (log-rank test, p-value = 0.013 and 0.001, and adjusted p-value 0.053 and < 0.001 for ccRCC and pRCC, respectively). To support the significance of CDKN2A loss in renal cancer, we further analyzed the available TCGA data and found worst survival for ccRCC and pRCC patients with CDKN2A alteration, as compared to wild type (Figure 8). Based on these observations, up-regulation of HMGA2 and CTHRC1, together with loss of CDKN2A, may serve as prognosis markers in renal cell carcinoma.
Figure 3. RNASeq profiles of CDC gene expression.
a. Kidney specific genes were down-regulated in all CDC tumor samples. b. Selected top up- and down-regulated genes that have been associated with cancer prognosis. c. Gene expression changes (log2 fold changes) of a five-gene signature defined by a study of genomic alterations in non-clear cell RCC (http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/v47/n1/full/ng.3146.html) to classify non-ccRCCs. CDC shows a distinct pattern for those five genes compared with three subtypes of non-ccRCC. d. Four down-steam genes (CDK4, E2F1, EZH2, and TP53) of CDKN2A were all found to be significantly up-regulated by RNASeq analysis.
Figure 7. Overall poor survival in RCC patients with overexpression of HMGA2 and CTHRC1 which were found highly upregulated (top two genes) in CDC tumors.
The available TCGA data were downloaded and utilized to determine the survival probability in ccRCC patients in order to determine the significance of overexpression of these genes in CDC tumors. a. HMGA2 expression in ccRCC and pRCC. b. Overall survival probability of ccRCC and pRCC patients with high expression of HMGA2. c. CTHRC1 expression in ccRCC and pRCC. d. Overall survival probability of ccRCC and pRCC patients with high expression of CTHRC1.
Figure 8. Alteration of CDKN2A and renal cancer patients survival.
CDKN2A/p16INK4A alteration significantly decreased the survival in ccRCC a. and pRCC patients b.. TCGA data were used to evaluate the survival probability in renal cancer patients.
Alteration of the solute carrier (SLC) family members
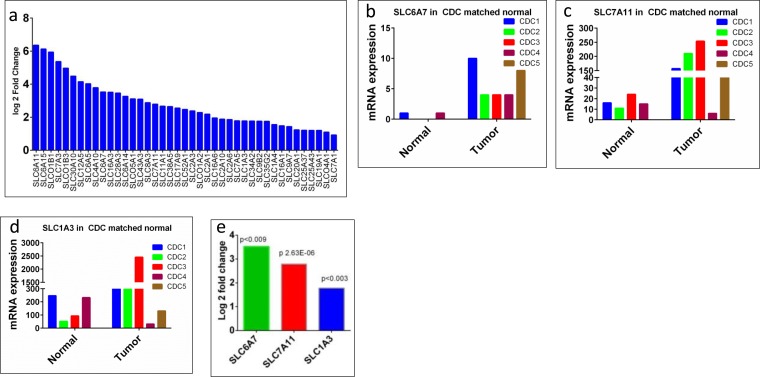
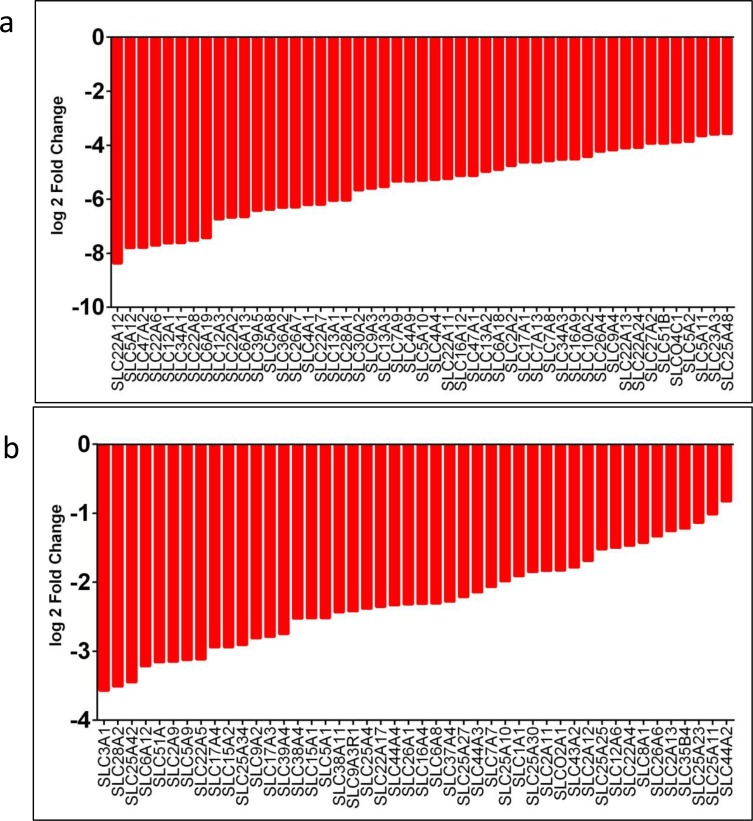
Since collecting ducts of the kidney are critical for transport, reabsorption, and excretion of several important electrolytes, we were interested in assessing the status of the membrane transporters, in particular, the solute carrier (SLC) family members, which play a critical role in transportation and absorption of electrolytes and drug resistance. Our RNASeq data analysis found 136 SLC family genes to be altered (41 up-regulated and 95 down-regulated; Figure 4a and Figure 9), which is 3.8 % (136 out of 4,830) of the total gene alterations and 45.3% (136 out of 300) of the SLC group of family members [27, 28], suggesting a potential role in CDC. The function of these altered transporters range from transport of amino acid, carbohydrates, metals, vitamins, and nucleotide sugars [27, 28]. The top 5 up-regulated genes (log2 fold change of 6.4 to 5.0) were SLC6A11, SLC6A15, SLCO1B1, SLC7A3, and SLCO1B3 (Figure 4a), which are involved in the transport of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), neutral amino acids (leucine, valine and methionine), organic anion update such as methotrexate, prostaglandin E2, cationic amino acids-arginine, lysine and ornithine, and organic anion methotrexate, respectively (Supplementary Table 3). The top down-regulated genes (log2 fold change of −8.4 to 7.6) were SLC22A12, SLC5A12, SLC47A2, SLC22A6, and SLC12A1 (Figure 9, Supplementary Table 4).
Figure 4. SLC family genes upregulated in CDC.
a. SLC family genes overexpressed in CDC tumors showed as log2 fold change. All the genes overexpressed were significantly different in CDC tumors, compared to matched non-tumor kidney. b. SLC6A7 mRNA expression in 4 matched non-tumor kidney and 5 CDC (1 non-matched) tumors. c. SLC7A11 mRNA expression in 4 matched non-tumor kidney and 5 CDC (1 non-matched) tumors. d. SLC1A3 mRNA expression in 4 matched normal kidney and 5 CDC (1 non-matched) tumors. e. Significant overexpression (log2 fold change) of drug resistance genes SLC6A7, SLC7A11, and SLC1A3 in CDC tumors.
Figure 9. SLC family genes downregulated in CDC tumors compared to non-tumor kidney.
SLC family genes downregulated in CDC tumors showed as log2 fold changes from 8.369 to 3.580 a. and 3.569 to 0.827 b.. All the genes listed are downregulated significantly in CDC tumors compared to matched non-tumor kidney. RNASeq data was used to identify SLC family gene expression levels in CDC tumors. The difference in the expression levels as a log2 fold change in expression levels was observed.
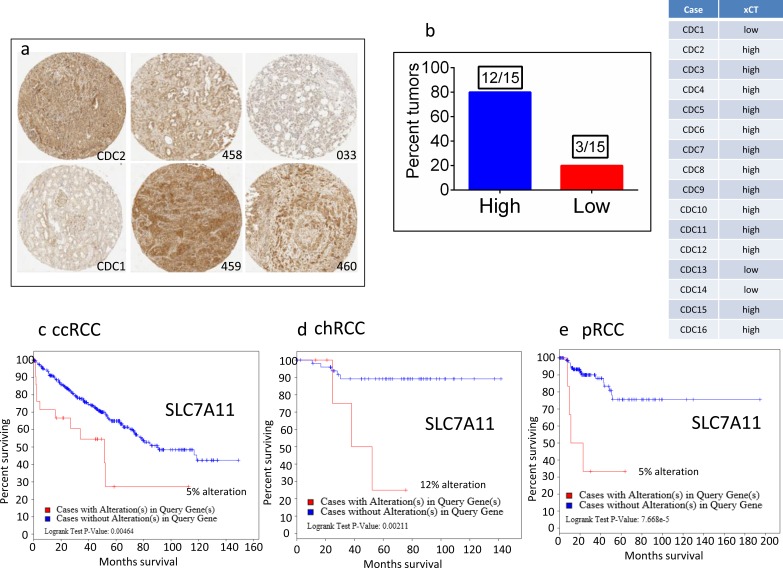
Thus, the critical analysis of individual amino acid transporters of SLC family genes from the up-regulated group led us to investigate three transporters: SLC7A11 (xCT, cystine transporter), SLC1A3 (GLAST, glutamate and aspartate transporter), and SLC6A7 (PROT, proline transporter) (Figure 4), which are known drug resistance markers [28–37]. Recent studies have reported xCT (SLC7A11), in particular, as a drug resistance maker and a novel target for therapeutic interventions in lung, breast, head & neck, and bladder cancers [35, 38–43]. Selective targeting of the glutamate and aspartate transporter, GLAST, has shown to reverse drug resistance in colorectal, ovarian, and breast cancer models [32, 44–46]. Recently, the proline transporter, PROT, was reported to have a significant role in the tumor microenvironment [29] and limiting of intracellular proline inhibits proliferation of renal cancer cells [47]. In accordance, our RNA sequence data showed the up-regulation of SLC7A11 (Figure 4c) and SLC1A3 (Figure 4d) mRNA in 80% of the cases (4 out of 5), with SLC6A7 (Figure 4b) up-regulated in 100% of the cases. In addition, immunohistochemical analysis of CDC tumors (n = 15) revealed the overexpression of xCT (SLC7A11) in 80% (12 out of 15) of the cases (Figure 5a, 5b). Taken together, our results demonstrate, for the first time, that overexpression of xCT, a cisplatin resistance associated marker, in CDC tumors, and suggest that xCT targeted combination therapies may be beneficial to CDC patients. In order to evaluate the SLC7A11 in other subtypes of kidney cancer, we have used the TCGA data [48, 49] and found that SLC7A11 significant upregulation in RCC subtypes ccRCC, chromophobe RCC (chRCC) and papillary RCC (pRCC) (Figure 6) and the upregulation was associated with significant poor survival of patients (Figure 5c, 5d, 5e). The other two transporters (SLC6A7 and SLC1A3) are not significantly upregulated (except SLC1A3 in ccRCC) in ccRCC, chRCC and pRCC and their association with the overall survival of RCC patients is not significant (Figure 6 and 11).
Figure 5. Overexpression of xCT in CDC tumors and the association of xCT (SLC7A11) overexpression with overall poor survival in ccRCC, chRCC and pRCC patients.
a.. Immunohistochemical detection of xCT was performed on CDC tumors using xCT antibody (5ug/ml, Abcam, MA). The numbers denoted in the figures are de-identified numbers of CDC tumors in the TMA. CDC1 and CDC2 tumors are included in the genomic profiling studies. Photmicrographs were captured using the Aperio Webscope Spectrum. b. Percent tumors (80%, 12 out of 15) express high levels of xCT. TCGA data analysis revealed the significant poor survival of RCC patients with xCT upregulation: c. ccRCC patients, Logrank Test P-value 0.00464; d. chRCC patients, Logrank Test P-value:0.00211, e. pRCC patients, Logrank Test P-value: 7.668e-5.
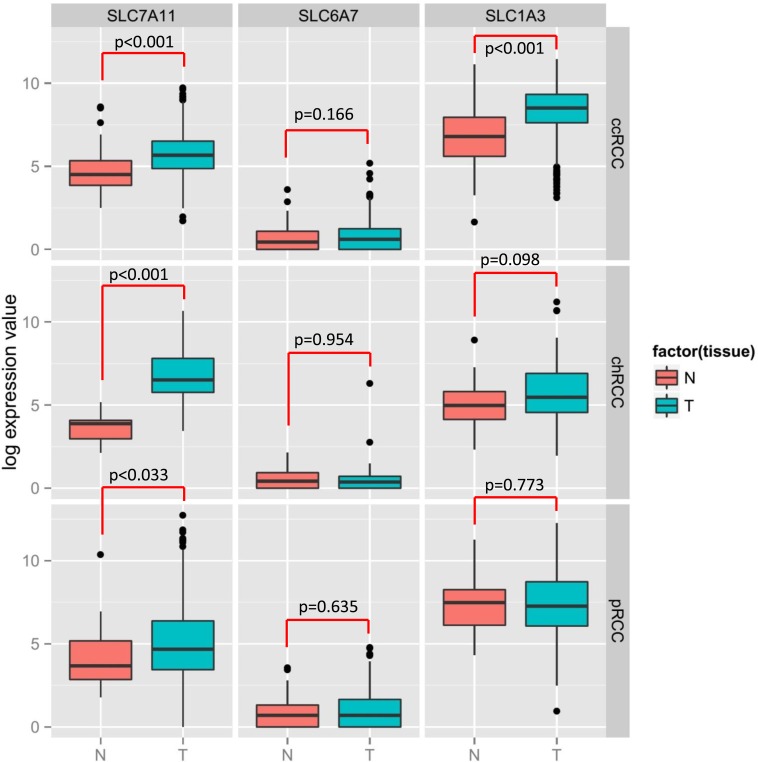
Figure 6. Significant upregulation of SLC7A11 in 3 subtypes of RCC (ccRCC, chRCC and pRCC) tumors compared to normal tissue.
TCGA data analysis revealed the differential expression of SLC7A11, SLC6A7 and SLC1A3 among the 3 subtypes of RCC tumors. Left panel showing the SLC7A11 expression in ccRCC, chRCC and pRCC; middle panel with SLC6A7, right panel with SLC1A3. N = Normal tissue, T = Tumor tissue
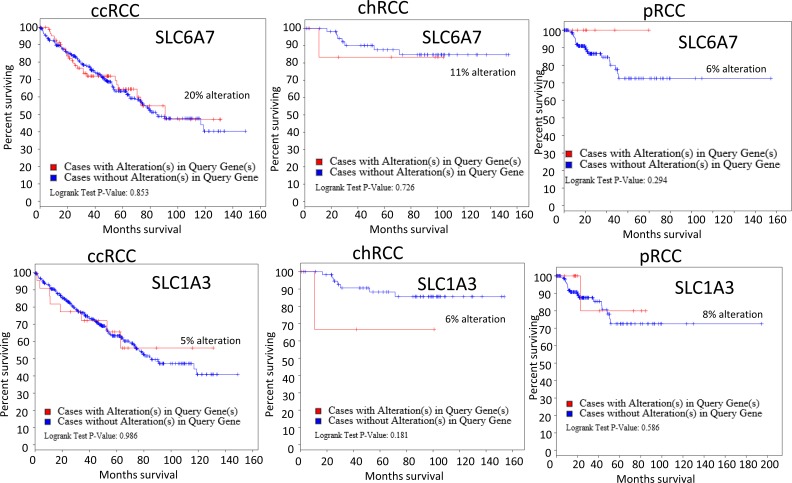
Figure 11. Alteration of SLC6A7 and SLC1A3 association with RCC patients survival.
Upper panel-TCGA data analysis of SLC6A7 alteration in 3 subtypes of RCC (ccRCC, chRCC and pRCC). Lower panel- SLC1A3 alteration and RCC patients’ survival.
DISCUSSION
Collecting renal cell carcinoma is a rare subtype of kidney cancer, aggressive in nature and in general resistant to chemotherapy and targeted therapies. One important limitation in the understanding the biology of CDC is the lack of relevant preclinical models. Clinical studies have proposed cisplatin based chemotherapy as standard of care for CDC. Further, triple combination of bevacizumab, gemcitabine and cisplatin/carboplatin has been reported to be effective in terms of progression-free survival and overall survival as compared to platinum-based chemotherapy [50]. Additionally, double HER2 blockade has been shown to have activity in disseminated CDC [51]. In the majority of CDC cases, surgical treatment did not result in cure [52]. A case report study on metastatic CDC revealed a favorable response to multikinase inhibitor sunitinib [53] suggested the role of targeted therapy in CDC. Several studies have provided genomic profiling and molecular targeted therapies for the most common types of kidney cancer, such as clear cell renal cell carcinoma, but very limited studies have been focused on CDC. A recent genomic profiling study [13] has suggested a potential therapeutic role for mTOR inhibitors in CDC with NF2 alterations. Additional studies are urgently needed to better understand the CDC molecular signature and to develop novel therapeutic agents and effective combination therapies.
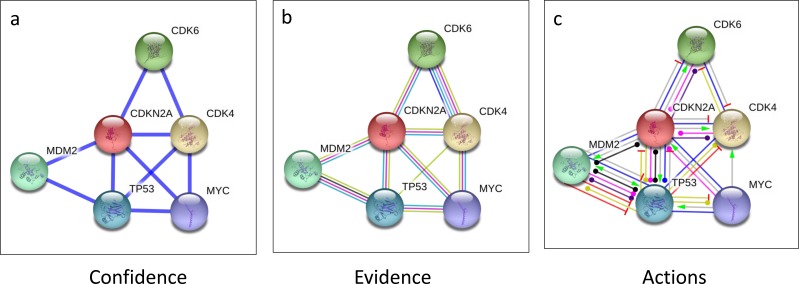
Since we observed that the CDKN2A was the most frequently altered gene in our CD samples, we assessed the p16 interacting proteins using the STRING10 biological database, a network which shows the known and predicted protein interactions. Our data suggest that p16 interacts with known oncogenic pathways CDK4, TP53, MYC, and MDM2 (Figure 10), and may play a biological role in CDC. Our RNASeq analysis confirmed the overexpression of CDK4, TP53, and MYC in the tumor samples, suggesting that indeed p16 deletion may play a critical role in the biology of CDC tumors by the overexpression of oncogenic signaling pathways. In particular, CDK4 upregulation in CDC tumors provides a potential target for therapeutic intervention since selective CDK4/CK6 inhibitors are now available for clinical testing.
Figure 10. CDKN2A interacting proteins.
To determine human CDKN2A interacting proteins, STRING10 (http://string-db.org/) database which provides known and predicted protein interactions was used. Interaction views of confidence a., evidence b. and actions c. are shown using parameters of highest confidence (0.900) and no more than 5 interactions. Protein interaction data show that CDKN2A interacts with CDK4 and TP53 (listed top 5), E2F1 and EZH2, (listed top 20, data not shown), which were found overexpressed by RNASeq analysis (Figure 3d), suggesting the functional significance of CDKN2A deletion in CDC tumors.
In our study we have also observed several SLC family genes upregulation including SLC7A11 (xCT) a marker associated with cisplatin resistance [34, 35, 37, 54]. To confirm the RNASeq data, we have evaluated the xCT expression in CDC tumors and found overexpression in 80% of cases (Figure 5a, 5b). Based on this observation we can speculate that upregulation of xCT may be responsible for the lack of CDC sensitivity to cisplatin, and targeted therapies aims to inhibit xCT may have a therapeutic benefit. In addition, we found upregulation of several genes such as HMGA2, CTHRC1 (top two genes) whose role in cancer progression and survival is well established (Figure 7). Recently, HMGA2 overexpression has been shown associated with cisplatin resistance in human non-small clear lung cancer [55] supports our findings to indicate that overexpressed genes contribute cisplatin based therapy resistance in CDC. Furthermore, its overexpression has been reported to associate with gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer [56], sunitinib in hepatocellular carcinoma [57]. Overexpression of CTHRC1 that encodes for a secretary protein involved in vascular remodeling through limiting collagen matrix deposition, has been associated with pancreatic cancer cells migration and metastasis [58], and melanoma invasiveness [59].
In summary, our study provides a comprehensive genomic analysis of CDC and identified the loss of CDKN2A expression and dysregulation of several transporters as frequent molecular alterations in this disease. We recognize the limited sample size of our report due to the rarity of CDC. Despite this limitation, we believe that our observations provide important findings which have a potential translational impact on the understanding of the well-known CDC chemotherapy resistance. These findings have immediate translational implications by suggesting rational combination strategies that may improve the clinical outcome for CDC patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patient samples
Frozen patient tumor samples and matched normal kidney tissues were obtained from the tissue bank at the participating institutions. These tissues were originally collected and processed according of the Institutional Review Board at each institution and were received at Roswell Park Cancer Institute as de-identified samples.
Exome sequencing read mapping and detection of somatic mutations
High quality paired-end reads passing Illumina RTA filter were aligned to the NCBI human reference genome (hg19) using BWA ([16]). PCR duplicated reads are marked and removed using Picard (http://picard.sourceforge.net/). Putative SNVs and indels were identified by running variation detection module of Bambino [15]. A putative mutation was further filtered based on the following criteria: (1) the alternative allele is absent in the paired non-tumor sample; (2) Fisher exact test p-value shows that number of reads with non-reference allele is significant higher in tumor sample; (3) mutant allele is present in both orientation; (4) absence of photopolymers at variant position. For putative indels, the filter process re-aligns all reads in both tumor and paired normal at the indel site with a template sequence generated by replacing reference allele with mutant one. After these two steps, germline variants are effectively removed. The putative variants were annotated using ANNOVAR [17] using NCBI RefSeq database.
Copy number analysis
Sample pairs (n = 5) with SNP array data, log2 ratios were calculated by comparing the tumor sample signals with pooled normal samples from Illumina. Then OncoSNP R package [60] was used to perform segmentation analysis on generating LOH and CNV segments. The segmentation results were further manually reviewed to identify missing focal copy number changes.
TCGA data analysis
TCGA data for ccRCC and pRCC including clinical information, somatic mutations, SNP array CNV calls, and normalized RNASeqV2 are downloaded from TCGA data portal. Alternation status of CDKN2A is determined by somatic mutation calls and CNV segmentation results. If a segment overlaps with CDKN2A has logR ratio less than −0.4, CDKN2A is considered loss in this sample. For gene expression data, the RSEM quantified and normalized data are first log2 transferred followed by significant test. All statistical tests are performed using R statistical program.
RNASeq data analysis
Raw reads passed quality filter was first pre-processed using tools FASTQC for quality control followed by sequence mapping using TopHat to the human reference genome and ENSEMBLE annotation database. HTSeq [61] was used to count number of reads mapped to each gene and transcript. Differentially expressed genes were identified using DESeq2 [62], a variance-analysis package developed to infer the statically significant difference in RNA-seq data. Multiple testing corrections will be performed in DESeq2. The list of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was analyzed for enriched pathway analysis using GSAA [63].
Immunohistochemical analysis
Immunohistochemical detection of xCT (encoded by SLC7A11 gene) in CDC tumors arranged in tissue microarray (TMA) available in Roswell Park Cancer Institute pathology core (RPCI_GUCa15) were used for detection of xCT. Triplicates tumor sections of each CDC tumor cores (1.0mm), de-identified numbers (CDC2, 458, 033, CDC1, 459 and 460) in TMA were utilized. CDC1 and CDC2 tumors were included in the current genomic profile studies. Additional cohort of 15 CDC tumors obtained from outside institute was also evaluated for the xCT expression. Rabbit polyclonal xCT antibody (Abcam, MA) was used at the dilution of 5 μg/ml to evaluate xCT using the protocol described [64]. Briefly, paraffin-embedded TMA sections were cut in 5 uM thickness sections, deparaffinized, rehydrated and subjected to heat mediated antigen unmasking in 10mM sodium citrate buffer (pH6.0). Quenching of endogenous peroxidases was done with 3% Hydrogen peroxide. Blocking was done with 1% bovine serum albumin in phosphate buffered saline for 1h followed by incubation with xCT primary antibody overnight. Sections were incubated with horseradish conjugated anti-Rabbit secondary antibody (Vector Laboratories, Burlington, CA) for 1hour and developed in diaminobezidine (Dako, Carpinteria, CA) and hematoxylin counterstain. Immunoscoring was performed by determining the intensity of staining level as low (2-20% positive cells) and high (80-100% positive cells).
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
To verify the CDKN2A NGS findings, we performed fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) on five sequenced CDC cases, followed by eleven additional cases obtained from outside institutions. CDKN2A enumeration by FISH was done using the commercially available combined CDKN2A/CEP9 probes (Vysis, Downers Grove, IL). Two hundred neoplastic cells were evaluated with the CDKN2A/CEP9 probe set for each of the collecting duct carcinoma cases. For each case, ratios were obtained by dividing the average number of CDKN2A probes per cell by the average number of CEP9 probes per cell. A ratio above 0.75 was considered “no loss of CDKN2A”. A ratio between 0.5 and 0.75 was considered a “heterozygous loss of CDKN2A”. A ratio below 0.5 was considered a “biallelic loss of CDKN2A”.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS TABLES
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Karoly Toth, Pathologist, for assessing the xCT IHC staining.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest.
GRANT SUPPORT
This research was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health (P30CA016056) (R.P.), a grant from the Roswell Park Cancer Institute Alliance Foundation (R.P.), and a donation from the Townson family (R.P.).
REFERENCES
- 1.Ciszewski S, Jakimow A, Smolska-Ciszewska B. Collecting (Bellini) duct carcinoma: A clinical study of a rare tumour and review of the literature. Can Urol Assoc J. 2015;9:E589–593. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gupta R, Billis A, Shah RB, Moch H, Osunkoya AO, Jochum W, Hes O, Bacchi CE, de Castro MG, Hansel DE, Zhou M, Vankalakunti M, Salles PG, Cabrera RA, Gown AM, Amin MB. Carcinoma of the collecting ducts of Bellini and renal medullary carcinoma: clinicopathologic analysis of 52 cases of rare aggressive subtypes of renal cell carcinoma with a focus on their interrelationship. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:1265–1278. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182635954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Srigley JR, Delahunt B. Uncommon and recently described renal carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 2009;22(Suppl 2):S2–S23. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dason S, Allard C, Sheridan-Jonah A, Gill J, Jamshaid H, Aziz T, Kajal B, Kapoor A. Management of renal collecting duct carcinoma: a systematic review and the McMaster experience. Curr Oncol. 2013;20:e223–232. doi: 10.3747/co.20.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tokuda N, Naito S, Matsuzaki O, Nagashima Y, Ozono S, Igarashi T, Japanese Society of Renal C. Collecting duct (Bellini duct) renal cell carcinoma: a nationwide survey in Japan. The Journal of urology. 2006;176:40–43. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(06)00502-7. discussion 43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wright JL, Risk MC, Hotaling J, Lin DW. Effect of collecting duct histology on renal cell cancer outcome. The Journal of urology. 2009;182:2595–2599. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kwon KA, Oh SY, Kim HY, Kim HS, Lee HY, Kim TM, Lim HY, Lee NR, Lee HJ, Hong SH, Rha SY. Clinical features and treatment of collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney from the korean cancer study group genitourinary and gynecology cancer committee. Cancer research and treatment. 2014;46:141–147. doi: 10.4143/crt.2014.46.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.May M, Ficarra V, Shariat SF, Zigeuner R, Chromecki T, Cindolo L, Burger M, Gunia S, Feciche B, Wenzl V, Aziz A, Chun F, Becker A, Pahernik S, Simeone C, Longo N, et al. Impact of clinical and histopathological parameters on disease specific survival in patients with collecting duct renal cell carcinoma: development of a disease specific risk model. The Journal of urology. 2013;190:458–463. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Procopio G, Testa I, Iacovelli R, Grassi P, Verzoni E, Garanzini E, Colecchia M, Torelli T, De Braud F. Treatment of collecting duct carcinoma: current status and future perspectives. Anticancer research. 2014;34:1027–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tannir NM, Plimack E, Ng C, Tamboli P, Bekele NB, Xiao L, Smith L, Lim Z, Pagliaro L, Araujo J, Aparicio A, Matin S, Wood CG, Jonasch E. A phase 2 trial of sunitinib in patients with advanced non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma. European urology. 2012;62:1013–1019. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.06.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhao RN, Nie LH, Gong R, Wang JZ, Wazir R, Liu LR, Song TR, Wei Q. Active targeted therapy for metastatic collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney: a case report and review of the literature. International urology and nephrology. 2013;45:1017–1021. doi: 10.1007/s11255-013-0468-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wu ZS, Lee JH, Kwon JA, Kim SH, Han SH, An JS, Lee JH, Lee ES, Park HR, Kim YS. Genetic alterations and chemosensitivity profile in newly established human renal collecting duct carcinoma cell lines. BJU international. 2009;103:1721–1728. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pal SK, Choueiri TK, Wang K, Khaira D, Karam JA, Van Allen E, Palma NA, Stein MN, Johnson A, Squillace R, Elvin JA, Chmielecki J, Yelensky R, Yakirevich E, Lipson D, Lin DI, et al. Characterization of Clinical Cases of Collecting Duct Carcinoma of the Kidney Assessed by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling. European urology. 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Becker F, Junker K, Parr M, Hartmann A, Fussel S, Toma M, Grobholz R, Pflugmann T, Wullich B, Strauss A, Behnes CL, Otto W, Stockle M, Jung V. Collecting duct carcinomas represent a unique tumor entity based on genetic alterations. PLoS One. 2013;8:e78137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Edmonson MN, Zhang J, Yan C, Finney RP, Meerzaman DM, Buetow KH. Bambino: a variant detector and alignment viewer for next-generation sequencing data in the SAM/BAM format. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:865–866. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dalgliesh GL, Furge K, Greenman C, Chen L, Bignell G, Butler A, Davies H, Edkins S, Hardy C, Latimer C, Teague J, Andrews J, Barthorpe S, Beare D, Buck G, Campbell PJ, et al. Systematic sequencing of renal carcinoma reveals inactivation of histone modifying genes. Nature. 2010;463:360–363. doi: 10.1038/nature08672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Varela I, Tarpey P, Raine K, Huang D, Ong CK, Stephens P, Davies H, Jones D, Lin ML, Teague J, Bignell G, Butler A, Cho J, Dalgliesh GL, Galappaththige D, Greenman C, et al. Exome sequencing identifies frequent mutation of the SWI/SNF complex gene PBRM1 in renal carcinoma. Nature. 2011;469:539–542. doi: 10.1038/nature09639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Farley MN, Schmidt LS, Mester JL, Pena-Llopis S, Pavia-Jimenez A, Christie A, Vocke CD, Ricketts CJ, Peterson J, Middelton L, Kinch L, Grishin N, Merino MJ, Metwalli AR, Xing C, Xie XJ, et al. A novel germline mutation in BAP1 predisposes to familial clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Molecular cancer research. 2013;11:1061–1071. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sherr CJ, McCormick F. The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer cell. 2002;2:103–112. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 2000;408:307–310. doi: 10.1038/35042675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.D'Angelo D, Esposito F, Fusco A. Epigenetic Mechanisms Leading to Overexpression of HMGA Proteins in Human Pituitary Adenomas. Front Med (Lausanne) 2015;2:39. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2015.00039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ke Z, He W, Lai Y, Guo X, Chen S, Li S, Wang Y, Wang L. Overexpression of collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 (CTHRC1) is associated with tumour aggressiveness and poor prognosis in human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5:9410–9424. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tang SC, Chen YC. Novel therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:10825–10844. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wu J, Wei JJ. HMGA2 and high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl) 2013;91:1155–1165. doi: 10.1007/s00109-013-1055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fujiwara R, Takenaka S, Hashimoto M, Narawa T, Itoh T. Expression of human solute carrier family transporters in skin: possible contributor to drug-induced skin disorders. Scientific reports. 2014;4:5251. doi: 10.1038/srep05251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lin L, Yee SW, Kim RB, Giacomini KM. SLC transporters as therapeutic targets: emerging opportunities. Nature reviews Drug discovery. 2015;14:543–560. doi: 10.1038/nrd4626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu W, Phang JM. MiRNA and Proline Metabolism in Cancer, Oncogene and Cancer - From Bench to Clinic. Siregar Yahwardiah., editor. InTech. 2013 doi: 10.5772/55139. http://www.intechopen.com/books/oncogene-and-cancer-from-bench-to-clinic/mirna-and-proline-metabolism-in-cancer Available from. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Saye M, Miranda MR, di Girolamo F, de los Milagros Camara M, Pereira CA. Proline modulates the Trypanosoma cruzi resistance to reactive oxygen species and drugs through a novel D, L-proline transporter. PLoS One. 2014;9:e92028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kanai Y, Clemencon B, Simonin A, Leuenberger M, Lochner M, Weisstanner M, Hediger MA. The SLC1 high-affinity glutamate and neutral amino acid transporter family. Mol Aspects Med. 2013;34:108–120. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2013.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pedraz-Cuesta E, Christensen S, Jensen AA, Jensen NF, Bunch L, Romer MU, Brunner N, Stenvang J, Pedersen SF. The glutamate transport inhibitor DL-Threo-beta-Benzyloxyaspartic acid (DL-TBOA) differentially affects SN38- and oxaliplatin-induced death of drug-resistant colorectal cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:411. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1405-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dai L, Noverr MC, Parsons C, Kaleeba JA, Qin Z. xCT, not just an amino-acid transporter: a multi-functional regulator of microbial infection and associated diseases. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:120. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Drayton RM, Catto JW. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2012;12:271–281. doi: 10.1586/era.11.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Drayton RM, Dudziec E, Peter S, Bertz S, Hartmann A, Bryant HE, Catto JW. Reduced expression of miRNA-27a modulates cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by targeting the cystine/glutamate exchanger SLC7A11. Clinical cancer research. 2014;20:1990–2000. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lewerenz J, Hewett SJ, Huang Y, Lambros M, Gout PW, Kalivas PW, Massie A, Smolders I, Methner A, Pergande M, Smith SB, Ganapathy V, Maher P. The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(−) in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:522–555. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Januchowski R, Zawierucha P, Andrzejewska M, Rucinski M, Zabel M. Microarray-based detection and expression analysis of ABC and SLC transporters in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy. 2013;67:240–245. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2012.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chintala S, Toth K, Yin MB, Bhattacharya A, Smith SB, Ola MS, Cao S, Durrani FA, Zinia TR, Dean R, Slocum HK, Rustum YM. Downregulation of cystine transporter xc by irinotecan in human head and neck cancer FaDu xenografts. Chemotherapy. 2010;56:223–233. doi: 10.1159/000316334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Guan J, Lo M, Dockery P, Mahon S, Karp CM, Buckley AR, Lam S, Gout PW, Wang YZ. The xc- cystine/glutamate antiporter as a potential therapeutic target for small-cell lung cancer: use of sulfasalazine. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology. 2009;64:463–472. doi: 10.1007/s00280-008-0894-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lu H, Samanta D, Xiang L, Zhang H, Hu H, Chen I, Bullen JW, Semenza GL. Chemotherapy triggers HIF-1-dependent glutathione synthesis and copper chelation that induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America; 2015; pp. E4600–4609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Timmerman LA, Holton T, Yuneva M, Louie RJ, Padro M, Daemen A, Hu M, Chan DA, Ethier SP, van ‘t Veer LJ, Polyak K, McCormick F, Gray JW. Glutamine sensitivity analysis identifies the xCT antiporter as a common triple-negative breast tumor therapeutic target. Cancer cell. 2013;24:450–465. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.08.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ye P, Mimura J, Okada T, Sato H, Liu T, Maruyama A, Ohyama C, Itoh K. Nrf2- and ATF4-dependent upregulation of xCT modulates the sensitivity of T24 bladder carcinoma cells to proteasome inhibition. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:3421–3434. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00221-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yoshikawa M, Tsuchihashi K, Ishimoto T, Yae T, Motohara T, Sugihara E, Onishi N, Masuko T, Yoshizawa K, Kawashiri S, Mukai M, Asoda S, Kawana H, Nakagawa T, Saya H, Nagano O. xCT inhibition depletes CD44v-expressing tumor cells that are resistant to EGFR-targeted therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer research. 2013;73:1855–1866. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3609-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sugiyama T, Sadzuka Y. Theanine and glutamate transporter inhibitors enhance the antitumor efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2003;1653:47–59. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(03)00031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fazzari J, Lin H, Murphy C, Ungard R, Singh G. Inhibitors of glutamate release from breast cancer cells; new targets for cancer-induced bone-pain. Scientific reports. 2015;5:8380. doi: 10.1038/srep08380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Christensen S, Jensen N, Stoeckel J, Belling K, Romer M, Gupta R, Brünner N, Pedersen S, Stenvang J. Colorectal cancer cell lines made resistant to SN38-and Oxaliplatin: Roles of altered ion transporter function in resistance? The FASEB Journal. 2013;27:lb452. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Loayza-Puch F, Rooijers K, Buil LC, Zijlstra J, Oude Vrielink JF, Lopes R, Ugalde AP, van Breugel P, Hofland I, Wesseling J, van Tellingen O, Bex A, Agami R. Tumour-specific proline vulnerability uncovered by differential ribosome codon reading. Nature. 2016;530:490–494. doi: 10.1038/nature16982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, Antipin Y, Reva B, Goldberg AP, Sander C, Schultz N. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:401–404. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, Cerami E, Sander C, Schultz N. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013;6:pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pecuchet N, Bigot F, Gachet J, Massard C, Albiges L, Teghom C, Allory Y, Mejean A, Escudier B, Oudard S. Triple combination of bevacizumab, gemcitabine and platinum salt in metastatic collecting duct carcinoma. Annals of oncology. 2013;24:2963–2967. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bronchud MH, Castillo S, Escriva de Romani S, Mourelo S, Fernandez A, Baena C, Murillo J, Julia JC, Esquius J, Romero R, Andreu X. HER2 blockade in metastatic collecting duct carcinoma (CDC) of the kidney: a case report. Onkologie. 2012;35:776–779. doi: 10.1159/000345041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sallami S, Tanguour M, Ben Rhouma S, Cherif K, Kchir N, Horchani A. Bellini renal cell carcinoma : diagnosis and treatment. A report of 7 cases [Article in French] La Tunisie medicale. 2011;89:792–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tazi EM, Essadi I, Tazi MF, Ahellal Y, M'Rabti H, Errihani H. Metastatic collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney treated with sunitinib. World journal of surgical oncology. 2011;9:73. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-9-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 54.Ma MZ, Chen G, Wang P, Lu WH, Zhu CF, Song M, Yang J, Wen S, Xu RH, Hu Y, Huang P. Xc- inhibitor sulfasalazine sensitizes colorectal cancer to cisplatin by a GSH-dependent mechanism. Cancer letters. 2015;368:88–96. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.07.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yang Y, Zhang P, Zhao Y, Yang J, Jiang G, Fan J. Decreased MicroRNA-26a expression causes cisplatin resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer biology & therapy. 2015:0. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1095405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Dangi-Garimella S, Krantz SB, Barron MR, Shields MA, Heiferman MJ, Grippo PJ, Bentrem DJ, Munshi HG. Three-dimensional collagen I promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer through MT1-MMP-mediated expression of HMGA2. Cancer research. 2011;71:1019–1028. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Marijon H, Dokmak S, Paradis V, Zappa M, Bieche I, Bouattour M, Raymond E, Faivre S. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and acquired resistance to sunitinib in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of hepatology. 2011;54:1073–1078. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Park EH, Kim S, Jo JY, Kim SJ, Hwang Y, Kim JM, Song SY, Lee DK, Koh SS. Collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by regulating migration and adhesion of tumor cells. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:694–702. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Tang L, Dai DL, Su M, Martinka M, Li G, Zhou Y. Aberrant expression of collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 in human solid cancers. Clinical cancer research. 2006;12:3716–3722. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yau C, Mouradov D, Jorissen RN, Colella S, Mirza G, Steers G, Harris A, Ragoussis J, Sieber O, Holmes CC. A statistical approach for detecting genomic aberrations in heterogeneous tumor samples from single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping data. Genome biology. 2010;11:R92. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-9-r92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:166–169. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome biology. 2014;15:550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Xiong Q, Mukherjee S, Furey TS. GSAASeqSP: a toolset for gene set association analysis of RNA-Seq data. Scientific reports. 2014;4:6347. doi: 10.1038/srep06347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ciamporcero E, Shen H, Ramakrishnan S, Yu Ku S, Chintala S, Shen L, Adelaiye R, Miles KM, Ullio C, Pizzimenti S, Daga M, Azabdaftari G, Attwood K, Johnson C, Zhang J, Barrera G, et al. YAP activation protects urothelial cell carcinoma from treatment-induced DNA damage. Oncogene. 2016;35:1541–53. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.