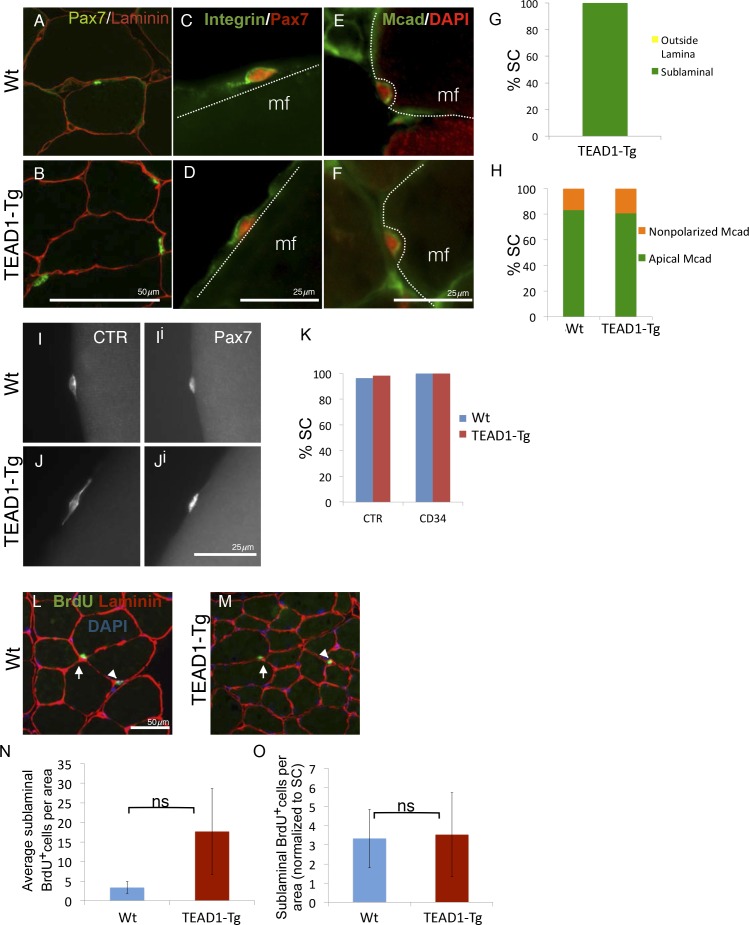
Figure 4. SC localization, marker expression, and long-term proliferation are no different in TEAD1-Tg compared to Wt mice.
(A–H) Localization of SC (Pax7, green) within the muscle fiber basal lamina (laminin, red) shown by IF of adult Wt (A) and TEAD1-Tg (B) TA sections and quantified for TEAD1-Tg TA sections (G). Polarized Integrin-β1 expression (Integrin, green) in SCs (Pax7, red) was assessed on TEAD1-Tg and Wt isolated EDL fibers (myofiber, mf) and found to be basally localized in all instances where the position of the SC on the fiber allowed for assessment (C,D). M-Cadherin (Mcad, green) polarization in SCs (Pax7, nuclei shown in red) was assessed in TA sections for apical localization (E,F), which is quantified in H. Non-polarized Mcad in Wt and TEAD1-Tg samples is likely due to imperfect SC orientation within the section. I–K) Assessment of quiescent marker (calcitonin receptor, CTR) expression in SCs (Pax7, Ii and Ji) on Wt (I) and TEAD1-Tg (J) isolated EDL fibers are represented by IF and quantified in K along with the general stem cell marker, CD34. L–N) Following a month-long BrdU treatment, Wt (L) and TEAD1-Tg (M) adult TA sections were assessed for long-term proliferation. Since myonuclei are non-proliferative and SC nuclei present the only other sublaminal nuclear species, this assay cumulatively captures any SC proliferation over the one-month long period. Very low numbers of BrdU nuclei were detected in both sublaminal and interstitial compartments of TA muscles from TEAD1-Tg and Wt mice. BrdU (green) labeled nuclei (blue) within the basal lamina (red) of the myofiber were quantified (N) and normalized to SC number (O). For G, H, and K n > 50 cells, while for N, 3 mice were quantified for each genotype.