Abstract
Recoverin, a recently discovered member of the EF-hand superfamily of Ca(2+)-binding proteins, serves as a Ca2+ sensor in vision. The amino terminus of the protein from retinal rod cells contains a covalently attached myristoyl or related N-acyl group. We report here studies of unmyristoylated and myristoylated recombinant recoverin designed to delineate the biological role of this hydrophobic unit. Ca2+ induces the binding of both the unmyristoylated and myristoylated proteins to phenyl-agarose, a hydrophobic support. Binding was half-maximal at 1.1 and 1.0 microM Ca2+, respectively. The Hill coefficients of 1.8 and 1.7, respectively, indicate that binding was cooperative. In contrast, Ca2+ induced the binding of myristoylated but not of unmyristoylated recoverin to rod outer segment membranes. Binding to these membranes was half-maximal at 2.1 microM Ca2+, and the Hill coefficient was 2.4. Likewise, myristoylated but not unmyristoylated recoverin exhibited Ca(2+)-induced binding to phosphatidylcholine vesicles. These findings suggest that the binding of Ca2+ to recoverin has two effects: (i) hydrophobic surfaces are exposed, allowing the protein to interact with complementary nonpolar sites, such as the aromatic rings of phenyl-agarose; and (ii) the myristoyl group is extruded, enabling recoverin to insert into a lipid bilayer membrane. The myristoyl group is likely to be an active participant in Ca2+ signaling by recoverin and related EF-hand proteins such as visinin and neurocalcin.
Full text
PDF
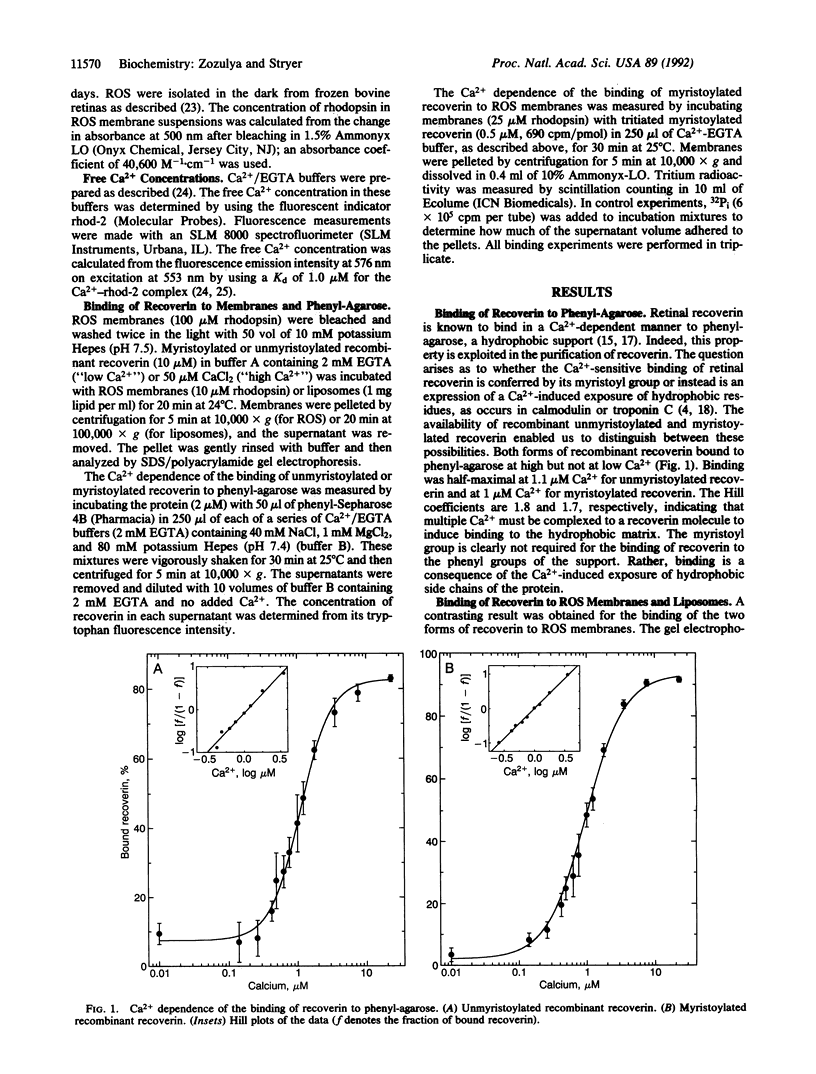
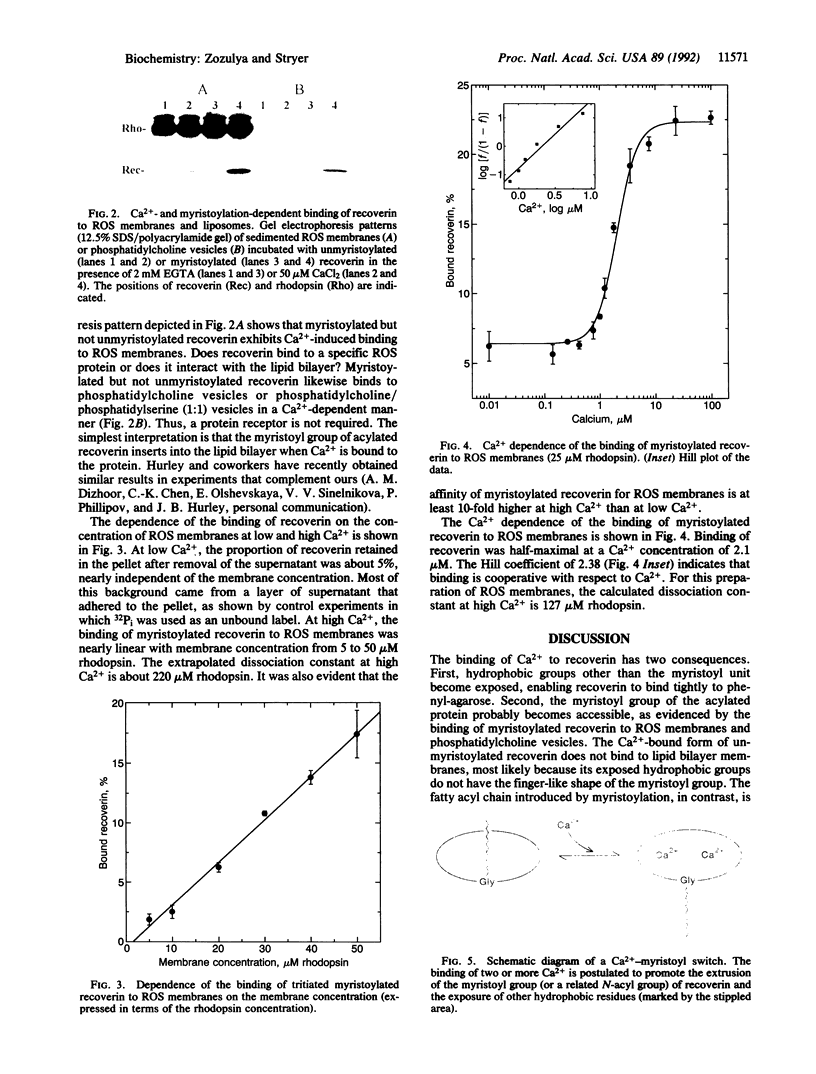
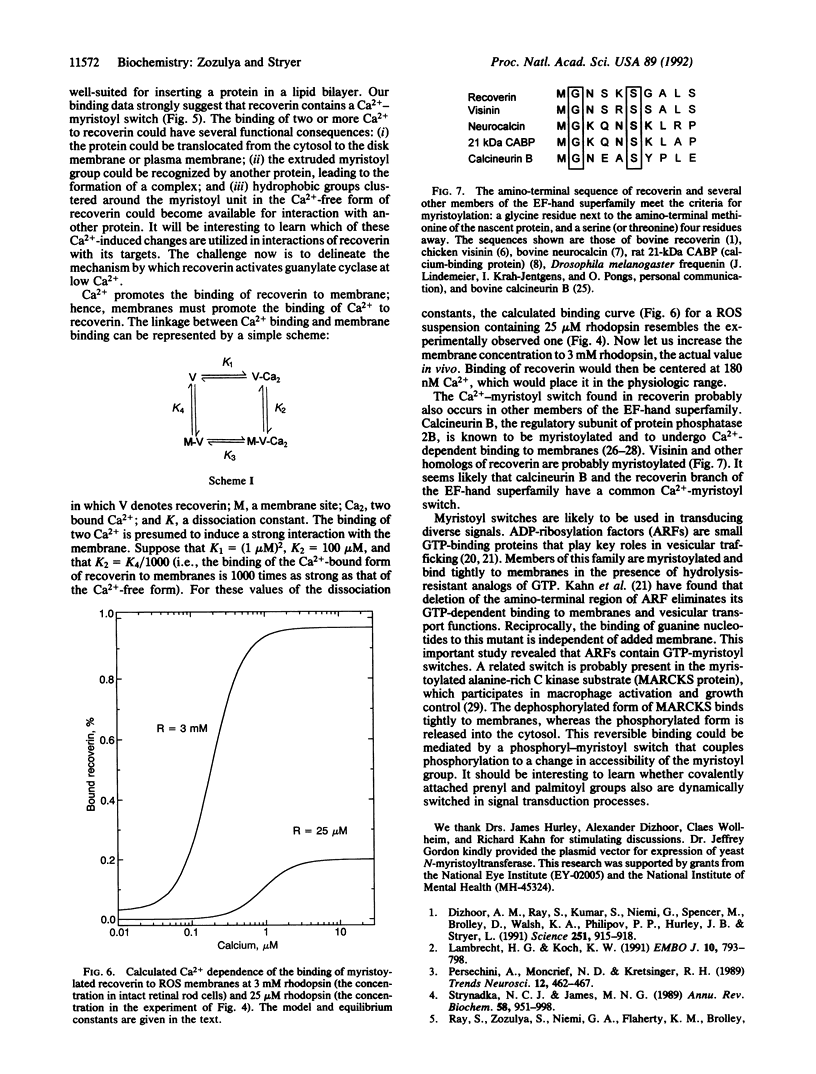

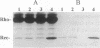
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Klee C. B., Cohen P. The structure of the B subunit of calcineurin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 15;139(3):663–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Kunisawa R., Kaim D., Thorner J. Yeast has homologs (CNA1 and CNA2 gene products) of mammalian calcineurin, a calmodulin-regulated phosphoprotein phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7376–7380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes R. J., Resh M. D., Broach J. R. Acylation and prenylation of proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;2(6):1108–1113. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizhoor A. M., Ericsson L. H., Johnson R. S., Kumar S., Olshevskaya E., Zozulya S., Neubert T. A., Stryer L., Hurley J. B., Walsh K. A. The NH2 terminus of retinal recoverin is acylated by a small family of fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16033–16036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizhoor A. M., Ray S., Kumar S., Niemi G., Spencer M., Brolley D., Walsh K. A., Philipov P. P., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Recoverin: a calcium sensitive activator of retinal rod guanylate cyclase. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):915–918. doi: 10.1126/science.1672047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio R. J., Jackson-Machelski E., Heuckeroth R. O., Olins P. O., Devine C. S., Yonemoto W., Slice L. W., Taylor S. S., Gordon J. I. Protein N-myristoylation in Escherichia coli: reconstitution of a eukaryotic protein modification in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Ca2+-induced hydrophobic site on calmodulin: application for purification of calmodulin by phenyl-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Duronio R. J., Rudnick D. A., Adams S. P., Gokel G. W. Protein N-myristoylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8647–8650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A. Quantitation and purification of ADP-ribosylation factor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:233–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95169-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Randazzo P., Serafini T., Weiss O., Rulka C., Clark J., Amherdt M., Roller P., Orci L., Rothman J. E. The amino terminus of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) is a critical determinant of ARF activities and is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein transport. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13039–13046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura S., Murakami M. Calcium-dependent regulation of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase by a protein from frog retinal rods. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):420–423. doi: 10.1038/349420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura S., Takamatsu K., Kitamura K. Purification and characterization of S-modulin, a calcium-dependent regulator on cGMP phosphodiesterase in frog rod photoreceptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):411–417. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80823-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B. Ca2+-dependent phospholipid- (and membrane-) binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6645–6653. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Kajimoto Y., Hashimoto T., Mukai H., Shirai Y., Saheki S., Tanaka C. cDNA cloning of a neural visinin-like Ca(2+)-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1219–1225. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok-Keung Fung B., Stryer L. Photolyzed rhodopsin catalyzes the exchange of GTP for bound GDP in retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2500–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht H. G., Koch K. W. A 26 kd calcium binding protein from bovine rod outer segments as modulator of photoreceptor guanylate cyclase. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):793–798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic calcium based on rhodamine and fluorescein chromophores. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8171–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano A., Terasawa M., Watanabe M., Usuda N., Morita T., Hidaka H. Neurocalcin, a novel calcium binding protein with three EF-hand domains, expressed in retinal amacrine cells and ganglion cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1207–1211. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81534-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Watanabe M., Ando Y., Hagiwara M., Terasawa M., Hidaka H. Full sequence of neurocalcin, a novel calcium-binding protein abundant in central nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80968-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini A., Moncrief N. D., Kretsinger R. H. The EF-hand family of calcium-modulated proteins. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):462–467. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polans A. S., Buczyłko J., Crabb J., Palczewski K. A photoreceptor calcium binding protein is recognized by autoantibodies obtained from patients with cancer-associated retinopathy. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):981–989. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politino M., King M. M. Calcineurin-phospholipid interactions. Identification of the phospholipid-binding subunit and analyses of a two-stage binding process. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7619–7622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S., Zozulya S., Niemi G. A., Flaherty K. M., Brolley D., Dizhoor A. M., McKay D. B., Hurley J., Stryer L. Cloning, expression, and crystallization of recoverin, a calcium sensor in vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5705–5709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., James M. N. Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:951–998. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamatsu K., Kitamura K., Noguchi T. Isolation and characterization of recoverin-like Ca(2+)-binding protein from rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91635-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Rosen A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Regulation by phosphorylation of reversible association of a myristoylated protein kinase C substrate with the plasma membrane. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):320–322. doi: 10.1038/351320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R., Pozzan T. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ with quin2. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:230–262. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata K., Goto K., Kuo C. H., Kondo H., Miki N. Visinin: a novel calcium binding protein expressed in retinal cone cells. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90059-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]