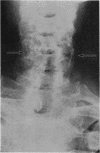
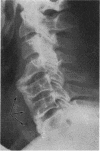
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHATTERJEE B. M. Horner's syndrome following phrenic crush. Am J Ophthalmol. 1956 Dec;42(6):920–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES C. L., HENDERSON J. W. Horner's syndrome: an analysis of 216 cases. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;46(3 Pt 1):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILDING D. A., TACHDJIAN M. O. Dysphagia and hypertrophic spurring of the cervical spine. N Engl J Med. 1960 Jul 7;263:11–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196007072630103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANNING E. L. Solitary neurofibroma presenting in pharynx and neck with Horner's syndrome. AMA Arch Otolaryngol. 1953 Dec;58(6):740–741. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1953.00710040767014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON J. F. Horner's syndrome due to an osteochondroma of the first rib. Can Med Assoc J. 1948 Aug;59(2):152–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH G. W., ROBINSON R. A. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958 Jun;40-A(3):607–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]