Abstract
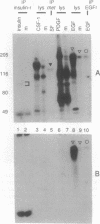
Rabbits were immunized with a synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to a major autophosphorylation site of p185neu/erbB2 to determine the feasibility of producing tyrosine-phosphopeptide-specific antibodies. A series of adsorption and affinity chromatography steps were used to select antibodies with the desired reactivity. Immunoblot experiments showed that the resulting serum is highly specific for tyrosine-phosphorylated forms of p185 and the related epidermal growth factor receptor. The serum recognized these two receptors selectively when compared to five other receptor tyrosine kinases and several phosphorylated substrates. The serum is compatible with tissue-based assays since it detected tyrosine phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in immunofluorescence experiments on permeabilized cells. The generality of the procedures used means that similar anti-tyrosine phosphopeptide sera can be produced that recognize other tyrosine kinases and substrates. Such sera will have numerous applications in research and clinical settings.
Full text
PDF



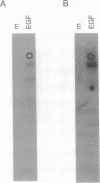
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anbazhagan R., Gelber R. D., Bettelheim R., Goldhirsch A., Gusterson B. A. Association of c-erbB-2 expression and S-phase fraction in the prognosis of node positive breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 1991 Jan;2(1):47–53. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a057824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. M., McGuire W. L. Follow-up study of HER-2/neu amplification in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):944–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernik A. J., Girault J. A., Nairn A. C., Chen J., Snyder G., Kebabian J., Greengard P. Production of phosphorylation state-specific antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:264–283. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01025-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Emilia J., Bulovas K., D'Ercole K., Wolf B., Steele G., Jr, Summerhayes I. C. Expression of the c-erbB-2 gene product (p185) at different stages of neoplastic progression in the colon. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1233–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Riveros J. R., Sibley E., Kastelic T., Lane M. D. Substrate phosphorylation catalyzed by the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Kinetic correlation to autophosphorylation of specific sites in the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21557–21572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Eisen H. N. Characterization and use of monoclonal antibodies for isolation of phosphotyrosyl proteins from retrovirus-transformed cells and growth factor-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1343–1352. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funasaka Y., Boulton T., Cobb M., Yarden Y., Fan B., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E., Anderson D. M., Zakut R., Mishima Y. c-Kit-kinase induces a cascade of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in normal human melanocytes in response to mast cell growth factor and stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase but is down-regulated in melanomas. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Feb;3(2):197–209. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I., Rubin G. M. Making a difference: the role of cell-cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90470-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan R., Margolis B., Dombalagian M., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. Identification of autophosphorylation sites of HER2/neu. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Jan;1(1):3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Rosen O. M. Antibodies to deduced sequences of the insulin receptor distinguish conserved and nonconserved regions in the IGF-I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2489–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. E., Sliwkowski M. X., Akita R. W., Henzel W. J., Lee J., Park J. W., Yansura D., Abadi N., Raab H., Lewis G. D. Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Sato J. D., Le A., Polikoff J., Sato G. H., Mendelsohn J. Growth stimulation of A431 cells by epidermal growth factor: identification of high-affinity receptors for epidermal growth factor by an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1337–1341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Sim S. S., Kim U. H., Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Carpenter G., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine residues in bovine phospholipase C-gamma phosphorylated by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3940–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Borrello I., Bellot F., Comoglio P., Schlessinger J. Egf binding to its receptor triggers a rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of the erbB-2 protein in the mammary tumor cell line SK-BR-3. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1647–1651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Issing W., Miki T., Popescu N. C., Aaronson S. A. Isolation and characterization of ERBB3, a third member of the ERBB/epidermal growth factor receptor family: evidence for overexpression in a subset of human mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., King C. R. Overexpression of the EGF receptor-related proto-oncogene erbB-2 in human mammary tumor cell lines by different molecular mechanisms. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):605–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupu R., Colomer R., Kannan B., Lippman M. E. Characterization of a growth factor that binds exclusively to the erbB-2 receptor and induces cellular responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann A., Dervan P. A., Johnston P. A., Gullick W. J., Carney D. N. c-erbB-2 oncoprotein expression in primary human tumors. Cancer. 1990 Jan 1;65(1):88–92. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900101)65:1<88::aid-cncr2820650119>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merwin J. R., Anderson J. M., Kocher O., Van Itallie C. M., Madri J. A. Transforming growth factor beta 1 modulates extracellular matrix organization and cell-cell junctional complex formation during in vitro angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jan;142(1):117–128. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhy L. C., Shih C., Cowing D., Finkelstein R., Weinberg R. A. Identification of a phosphoprotein specifically induced by the transforming DNA of rat neuroblastomas. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik S., Hazan R., Fisher E. R., Sass R. E., Fisher B., Redmond C., Schlessinger J., Lippman M. E., King C. R. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project: prognostic significance of erbB-2 protein overexpression in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1990 Jan;8(1):103–112. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. B., Rhim J. S., Park S. C., Kimm S. W., Kraus M. H. Amplification, overexpression, and rearrangement of the erbB-2 protooncogene in primary human stomach carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6605–6609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Nilson L. A., DiMaio D. Activation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor by the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):845–855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R., Rothwell V. M., Nicola N. A. Transformation of murine fibroblasts by a retrovirus encoding the murine c-fms proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1989 Aug;4(8):1015–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. M., Goldberg I. D., Liu D., Setter E., Donovan M. A., Bhargava M., Reiss M., Kacinski B. M. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates epithelial tumor cell motility. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5315–5321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. H., Baltimore D., Eisen H. N. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins isolated by affinity chromatography with antibodies to a synthetic hapten. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):654–656. doi: 10.1038/294654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Godolphin W., Jones L. A., Holt J. A., Wong S. G., Keith D. E., Levin W. J., Stuart S. G., Udove J., Ullrich A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):707–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2470152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F. Antiphosphotyrosine antibodies in oncogene and receptor research. Methods Enzymol. 1991;198:494–501. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)98048-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Heffernan P. A., Weinberg R. A. p185, a product of the neu proto-oncogene, is a receptorlike protein associated with tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1729–1740. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kamps M. P., Cao H. Oncogenic activation of p185neu stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3969–3973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kamps M. P. EGF-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of p185neu: a potential model for receptor interactions. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):995–1001. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P., Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A., Rohrschneider L. R. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of c-fms proteins expressed in FDC-P1 and BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2528–2538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Gunsalus J. R., Nemenoff R. A., Frackelton A. R., Pierce M. W., Avruch J. Identification of the insulin receptor tyrosine residues undergoing insulin-stimulated phosphorylation in intact rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):350–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Peles E., Cupples R., Suggs S. V., Bacus S. S., Luo Y., Trail G., Hu S., Silbiger S. M., Levy R. B. Neu differentiation factor: a transmembrane glycoprotein containing an EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90456-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildenhain Y., Pawson T., Blackstein M. E., Andrulis I. L. p185neu is phosphorylated on tyrosine in human primary breast tumors which overexpress neu/erbB-2. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):879–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M. J., Peterse J. L., Mooi W. J., Wisman P., Lomans J., Dalesio O., Nusse R. Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer. Association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 10;319(19):1239–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811103191902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]