Abstract
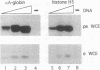
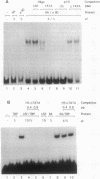
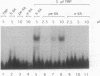
Avian histone H5 and alpha A-globin genes are transcribed much more efficiently in whole cell extracts derived from immature polychromatic erythrocytes than in extracts from mature duck erythrocytes. We found that these differential activities are detectable only if assayed with promoters containing a functional TATA box. The addition of either highly purified human or recombinant yeast transcription factor IIA (TFIIA) to extracts from mature erythrocytes resulted in a significant increase in transcription from TATA-containing promoters, whereas transcription from TATA-less promoters remained unaffected. Moreover, the activity of TFIIA was found to be reduced in extracts from mature erythrocytes. These data support the proposition that inactivation of TFIIA may contribute to a general repression of gene activity in avian erythrocytes, and only those genes with alternative mechanisms of initiation complex formation continue to be expressed in these cells. In the case of the histone H5 gene, such an alternative mechanism could be mediated via the interaction between duck erythrocyte upstream stimulating factor and TFIID.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Côté J., Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Regulation of histone and beta A-globin gene expression during differentiation of chicken erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3663–3672. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bungert J., Kober I., Düring F., Seifart K. H. Transcription factor eUSF is an essential component of isolated transcription complexes on the duck histone H5 gene and it mediates the interaction of TFIID with a TATA-deficient promoter. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):885–898. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90250-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification and analysis of transcription factor IIA and identification of transcription factor IIJ. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):413–421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Tönjes R. Conserved dyad symmetry structures at the 3' end of H5 histone genes. Analysis of the duck H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düring F., Gerhold H., Seifart K. H. Transcription factor USF from duck erythrocytes transactivates expression of the histone H5 gene in vitro by interacting with an intragenic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1225–1231. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Cuadrado A., Rousseau S., Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Repression of the H5 histone gene by a factor from erythrocytes that binds to the region of transcription initiation. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1857–1866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. The Zta trans-activator protein stabilizes TFIID association with promoter DNA by direct protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2441–2454. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Ha I., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Green M. R. Binding of general transcription factor TFIIB to an acidic activating region. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):569–571. doi: 10.1038/353569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription: whole-cell extract. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. Family of proteins that interact with TFIID and regulate promoter activity. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90530-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranish J. A., Lane W. S., Hahn S. Isolation of two genes that encode subunits of the yeast transcription factor IIA. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.1546313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. The complexities of eukaryotic transcription initiation: regulation of preinitiation complex assembly. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90164-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Purification and characterization of a specific RNA polymerase II transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2003–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. M., Wiaderkiewicz R., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Histone H5 in the control of DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):68–71. doi: 10.1126/science.2740916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Engel J. D. Transcription of the chicken histone H5 gene is mediated by distinct tissue-specific elements within the promoter and the 3' enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2228–2232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Stamler S. J., Engel J. D. Erythroid-specific transcription of the chicken histone H5 gene is directed by a 3' enhancer. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):827–830. doi: 10.1038/328827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usuda Y., Kubota A., Berk A. J., Handa H. Affinity purification of transcription factor IIA from HeLa cell nuclear extracts. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2305–2310. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07767.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Seifart K. H. TFIIA is required for in vitro transcription of mammalian U6 genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16359–16364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Wanandi I., Seifart K. H. Identification of transcription factors required for the expression of mammalian U6 genes in vitro. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2595–2603. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingart S., Sommer U., Gerhold H., Seifart K. H. Transcription of the alpha A-globin gene of the duck. Development of a homologous in vitro system and identification of trans-acting factors. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 15;183(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]