Nature Communications 6: Article number: 766010.1038/ncomms8660 (2015); Published: July 16 2015; Updated: October 10 2016
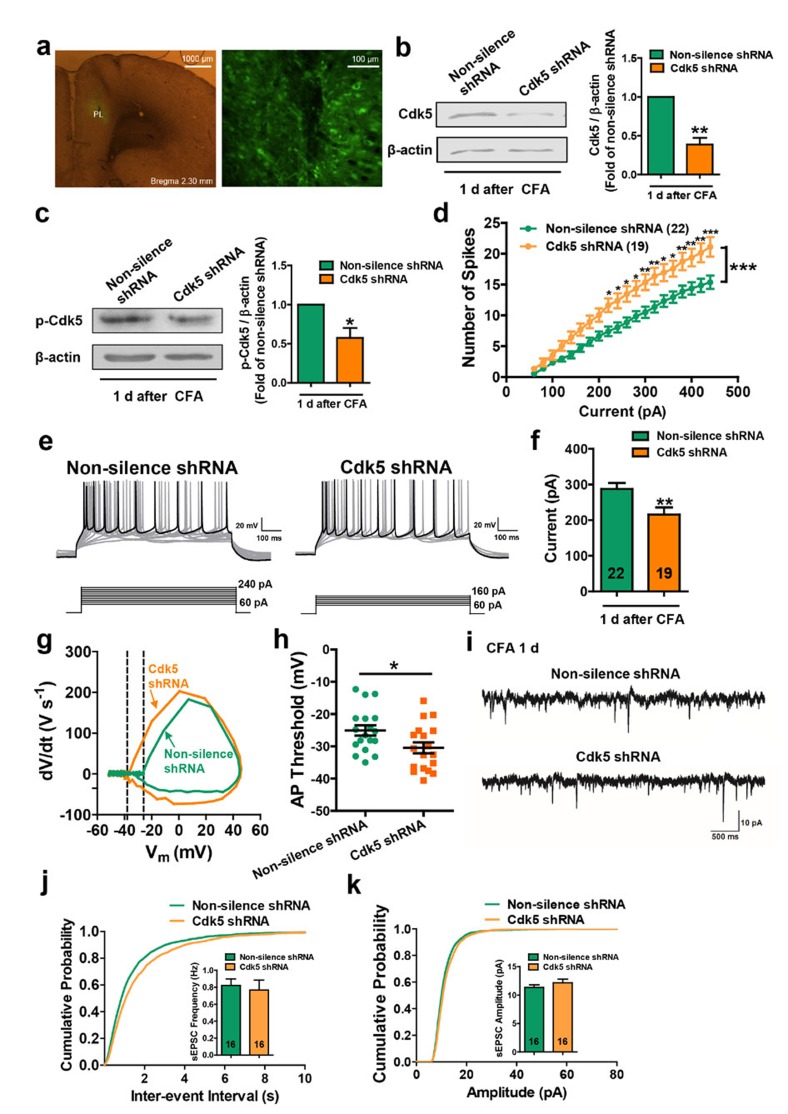
In Fig. 7i of this Article, a different section of the control trace was used to represent the Cdk5 shRNA trace. The correct version of Fig. 7, including a new representative Cdk5 shRNA trace in panel i, appears below as Fig. 1. The original conclusions are not affected by this change and the raw data files from which these traces were selected are now available as Supplementary Data 1 and 2.
Figure 1.
Supplementary Material
Non-silence shRNA-primary data
Cdk5 shRNA-primary data
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Non-silence shRNA-primary data
Cdk5 shRNA-primary data