Abstract
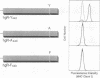
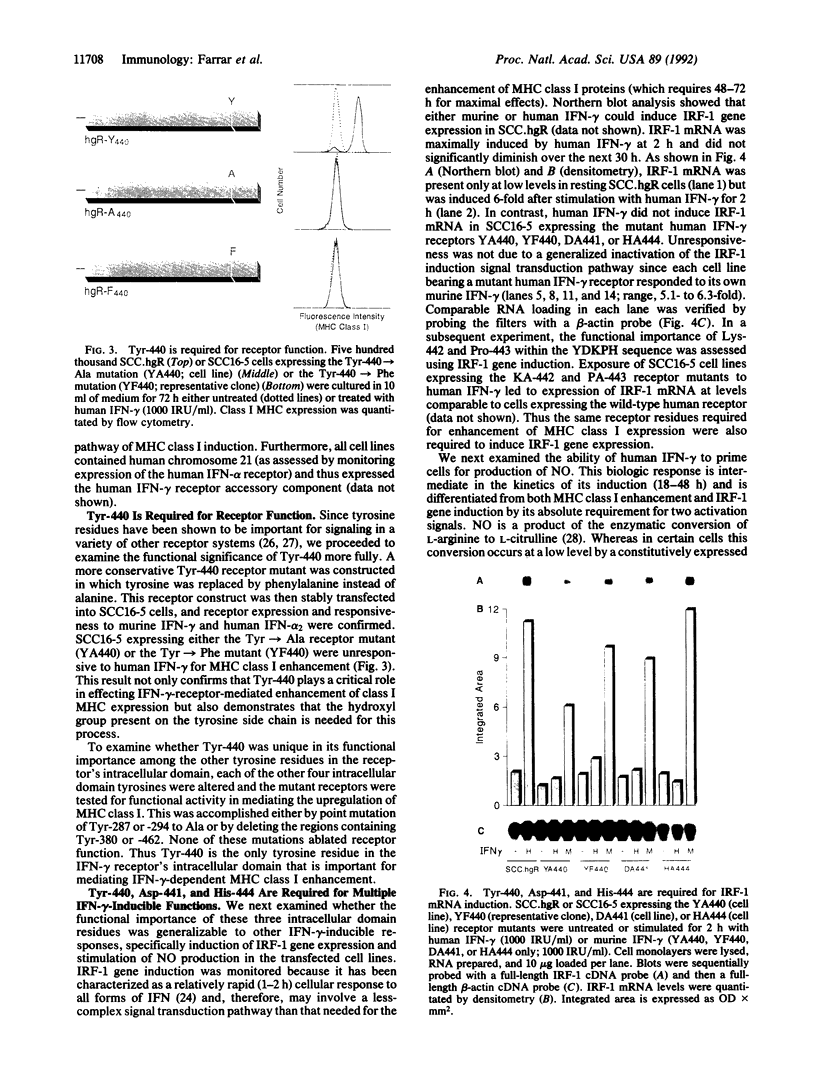
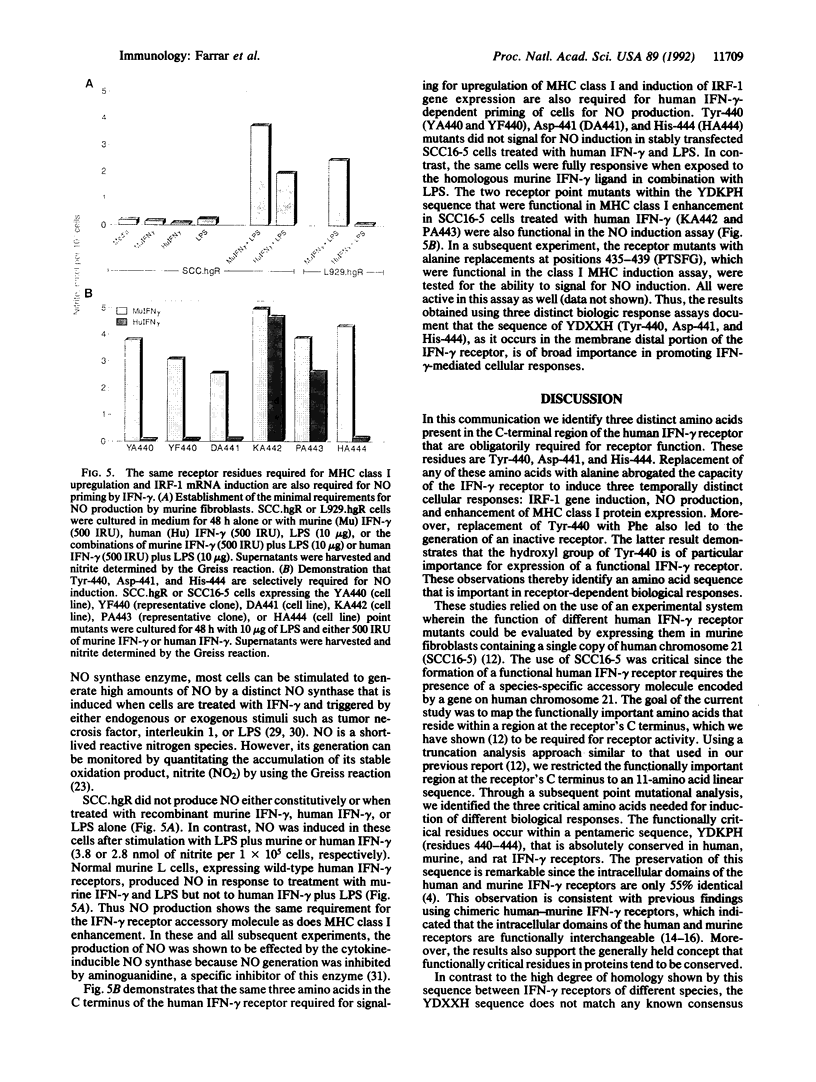
We have previously shown that the intracellular domain of the interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) receptor plays an obligate role in receptor-mediated signal transduction. Moreover, we have specifically identified two regions within the human IFN-gamma receptor's intracellular domain required for functional activity: the membrane-proximal 48 amino acids required for both functional activity and receptor-mediated ligand internalization and the C-terminal 39 amino acids required exclusively for biologic response induction. Herein we report the identification of the 3 amino acids within the C-terminal region of the receptor that are obligatorily required for receptor function. By using a set of overlapping truncation mutants, the minimal functional sequence within the C-terminal region was localized to residues 434-444 (APTSFGYD-KPH). By mutating each individual residue within this sequence to alanine, three residues (Tyr-440, Asp-441, and His-444) were identified as being critical for IFN-gamma-dependent (i) upregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I proteins, (ii) activation of the IFN regulatory factor 1 gene, and (iii) stimulation of cells to produce nitric oxide. The more conservative Tyr-440-->Phe substitution also resulted in a nonfunctional receptor. Subsequent mutational analysis of all five of the IFN-gamma receptor's intracellular tyrosine residues revealed that Tyr-440 was the sole tyrosine required for receptor activity. These results thus identify a unique sequence in the IFN-gamma receptor that is required for initiation of IFN-gamma-dependent biologic responses and highlight the importance of the hydroxyl side chain of Tyr-440 in this process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Dembić Z., Merlin G. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrus J. L., Jr, Chesky L., Stephany D., McFarland P., Mostowski H., Fauci A. S. Functional studies examining the subpopulation of human B lymphocytes responding to high molecular weight B cell growth factor. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):3949–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Structural design and molecular evolution of a cytokine receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6934–6938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cofano F., Moore S. K., Tanaka S., Yuhki N., Landolfo S., Appella E. Affinity purification, peptide analysis, and cDNA sequence of the mouse interferon gamma receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4064–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Sweetland M. A., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin-1 beta-induced formation of EPR-detectable iron-nitrosyl complexes in islets of Langerhans. Role of nitric oxide in interleukin-1 beta-induced inhibition of insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21351–21354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. A., Tilton R. G., Chang K., Hasan K. S., Ido Y., Wang J. L., Sweetland M. A., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Williamson J. R., McDaniel M. L. Aminoguanidine, a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide formation, prevents diabetic vascular dysfunction. Diabetes. 1992 Apr;41(4):552–556. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T., Rehm A., Aguet M., Pfizenmaier K. Human chromosome 21 is necessary and sufficient to confer human IFN gamma responsiveness to somatic cell hybrids expressing the cloned human IFN gamma receptor gene. Cytokine. 1990 May;2(3):157–161. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90010-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs V. C., Williams S. R., Gray P. W., Schreiber R. D., Pennica D., Rice G., Goeddel D. V. The extracellular domain of the human interferon gamma receptor interacts with a species-specific signal transducer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5860–5866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leong S., Fennie E. H., Farrar M. A., Pingel J. T., Fernandez-Luna J., Schreiber R. D. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for the murine interferon gamma receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8497–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmi S., Merlin G., Aguet M. Functional characterization of a hybrid human-mouse interferon gamma receptor: evidence for species-specific interaction of the extracellular receptor domain with a putative signal transducer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmi S., Peghini P., Metzler M., Merlin G., Dembic Z., Aguet M. Cloning of murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA: expression in human cells mediates high-affinity binding but is not sufficient to confer sensitivity to murine interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9901–9905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey G. K., McCourt D. W., Schreiber R. D. Ligand-induced phosphorylation of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Dependence on the presence of a functionally active receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17868–17875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey G. K., Schreiber R. D. Biosynthetic analysis of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Identification of N-linked glycosylation intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11981–11988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino Y., Kumar C. S., Mariano T. M., Lai D. H., Pestka S. Chimeric interferon-gamma receptors demonstrate that an accessory factor required for activity interacts with the extracellular domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3741–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibino Y., Mariano T. M., Kumar C. S., Kozak C. A., Pestka S. Expression and reconstitution of a biologically active mouse interferon gamma receptor in hamster cells. Chromosomal location of an accessory factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6948–6951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Collard J. G., Tulp A., Cox D., Millington-Ward A., Pearson P. Construction and analysis of an EMBL-3 phage library containing partially digested human chromosome 21-specific DNA inserts (15-20 kb). Cytometry. 1986 Sep;7(5):411–417. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Jones C., Kumar C. S., Stefanos S., O'Connell S., Pestka S. Expression and reconstitution of a biologically active human interferon-gamma receptor in hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1827–1830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Rashidbaigi A., Jones C., Tischfield J. A., Shows T. B., Pestka S. Human chromosomes 6 and 21 are required for sensitivity to human interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4151–4155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C. S., Muthukumaran G., Frost L. J., Noe M., Ahn Y. H., Mariano T. M., Pestka S. Molecular characterization of the murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17939–17946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Kitamura T., Harada N., Yokota T., Arai K. Cytokine receptors and signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:295–331. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Maniatis T. Expression cloning of the murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9248–9252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolini R., Jouvin M. H., Kinet J. P. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E immediately after receptor engagement and disengagement. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):855–858. doi: 10.1038/353855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Calderon J., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the human IFN-gamma receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4231–4237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]