Abstract
1H NMR spectroscopic and X-ray crystallographic investigations of a 1,3-bis(4-ethynyl-3-iodopyridinium)benzene scaffold with perrhenate reveal strong halogen bonding in solution, and bidentate association in the solid state. A nearly isostructural host molecule demonstrates significant C–H hydrogen bonding to perrhenate in the same phases.
With similar structural and electronic characteristics,1 perrhenate (ReO4−) is a tractable surrogate2 for the medically ubiquitous and environmentally pernicious3 oxoanion, pertechnetate (TcO4−).4 The metastable form of technetium5 and its long half-life6 decay product 99Tc are standards for radiolabeling7 and in situ radiotherapy. Considering the high mobility of 99TcO4−, its stability,8 and increasing production,9 the need for synthetic receptors to function as strong and selective chelating agents, liquid-liquid extractants,2 and ion-exchange stationary phases10 is pressing.
ReO4− and TcO4− are challenging targets due to their low hydration energies and diffuse charge densities.11 To combat these difficulties, a number of hydrogen bonding (HB) scaffolds and hosts have been developed.1, 11–12 Elegant HB examples include aza-cryptands with pH-tunable cavities,12a–c and charge neutral pyrrole-based macrocycles.12d–e In contrast, bidentate halogen bonding (XB) and unconventional C–H13 HB receptors for ReO4− or TcO4− have not been reported. XB14 in particular offers an exciting competitive15/cooperative16 alternative with the benefit of soft-soft HSAB complementarity.17 Herein, we report the first two receptors that exhibit strong XB and C–H HB with ReO4− in solution, and the first bidentate and tridentate structures of each in the solid state.
We have developed two bidentate receptor molecules based on a diethynyl benzene core (1 and 2, Scheme 1). 1 is designed to direct two XB donors towards one anionic guest in a planar conjugated conformation.19 Molecule 2—which lacks XB donors—was prepared to quantify C–H HB to ReO4−, and serve as a comparison. Both receptor scaffolds were synthesized by Sonogashira20 cross-coupling of 1,3-diethynyl benzene with either 3-bromo-4-iodopyridine or 4-bromopyridine hydrochloride. The XB donor iodines of 1 were installed by lithium halogen exchange followed by quenching with I2. Alkylation of the pyridines with octyl triflate activated the XB and HB donors of 1 and 2, respectively, and enhanced solubility in organic solvents. To minimize competitive intramolecular interactions, triflate counteranions were exchanged by metathesis for non-coordinating [BArF4]− anions.21 Methyl derivatives 1b and 2b were synthesized in a similar manner for X-ray diffraction studies.
Scheme 1.
a) 3-Bromo-4-iodopyridine, CuI, Pd(PPh3)2Cl2, DMF, DIPEA, rt, 24 h, 88%; b) n-BuLi, THF, −78°C, I2, 24 h, 41%; c) prepared according to literature procedure,18 22% d) octyl triflate or methyl triflate, DCM, rt, 24 h, 98%; e) vapor diffusion of ether into DCM solution of TBA+Cl−, 55–75%; Na+[BArF4]−, DCM, rt, 30 min, 59–75%.
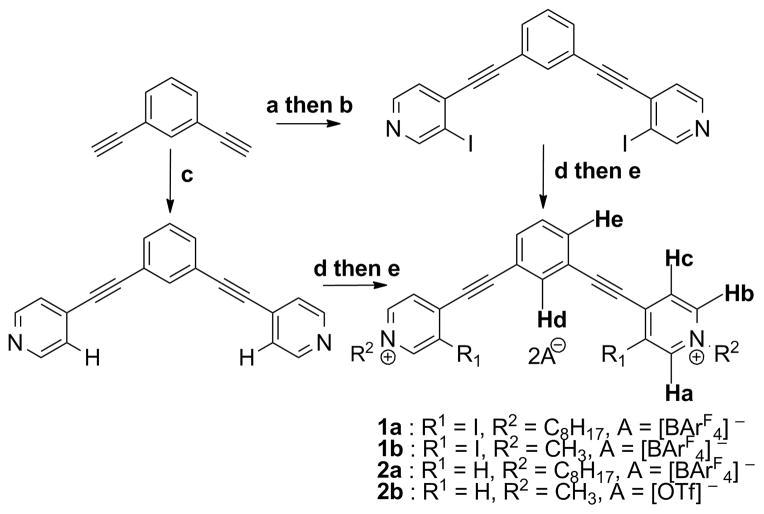
The crystal structure of 1b2+•2ReO4− represents the first bidentate XB22 to ReO4− in the solid state. Yellow single crystals of 1b2+•2ReO4− suitable for X-ray diffraction were grown by diffusing DCM into a DMF/MeOH solution of receptor 1b and tetra-n-butylammonium perrhenate (TBA+ReO4−).23 1b2+•2ReO4− crystallized in space group P21/c, forming bidentate XB to separate oxygens of a ReO4− anion (Figure 1, top). The C–I···O− distances 2.97 and 3.06 Å correspond to 84 and 86% of the Σ VdW radii, and corroborate strong XB interactions. To accommodate the size of ReO4−, both pyridinium rings rotate 11° from coplanarity. As a result, the observed C–I···O− bond angles of 175 and 168° also confirm strong XB interactions. Examination of the crystal packing reveals C–H HB and electrostatic contacts between ReO4− and five additional molecules of 1b (see ESI). The second ReO4− participates in seven C–H HB interactions, and two weak σ contacts with electron-deficient pyridinium rings.24 A head-to-tail π-stacking dimer (3.4 Å) is also observed.25 This arrangement produces columns of 1b with each ReO4− on alternating sides of the receptor.
Figure 1.
X-ray crystal structures of 1b2+•2ReO4− (top) highlighting bidentate XB to ReO4− in the solid state (red). Crystal structure of 2b2+•2ReO4− (bottom) illustrating tridentate C–H HB to ReO4− (black).
In contrast, the crystal structure of 2b2+•2ReO4− illustrates unique C–H HB to ReO4−. Colorless single crystals of 2b2+•2ReO4− were obtained by diffusing ether into a MeOH solution of receptor 2b and TBA+ReO4−.26 2b2+•2ReO4− crystallized in space group P21/n. Notably, tridentate C–H HB to ReO4− is formed using two Hc hydrogens and Hd (Figure 1, bottom), with C–H···O− distances of 2.64, 2.71 and 2.31 Å. In addition, four intermolecular C–H27 and two weak σ28 contacts with ReO4− are present. The second ReO4− is involved in nine C–H HB and two weak σ interactions. To enable tridentate binding to ReO4−, both pyridinium rings adjust 9° from coplanarity, and one ethynyl spacer deviates 8° from linearity. An off-centered head-to-tail π-stacking dimer (3.3 Å) is also noted (see ESI).25 Together, the crystal structures of 1b2+•2ReO4− and 2b2+•2ReO4− illustrate the importance of bidentate/tridentate XB and HB coordination to ReO4− in the solid state.
1H NMR spectroscopic titrations involving 1a and 2a were conducted to probe their corresponding XB and C–H HB capabilities in solution. Both 1a, 2a and TBA+ReO4− were independently soluble in CDCl3; however, precipitation of host-guest complexes necessitated a CDCl3/(CD3)2CO (3:2 v/v) mixed solvent. Titrating TBA+ReO4− produced noteworthy shifts for the pyridinium (Ha, Hb, and Hc) and phenyl (Hd) hydrogens for both 1a and 2a (Figure 2).29
Figure 2.
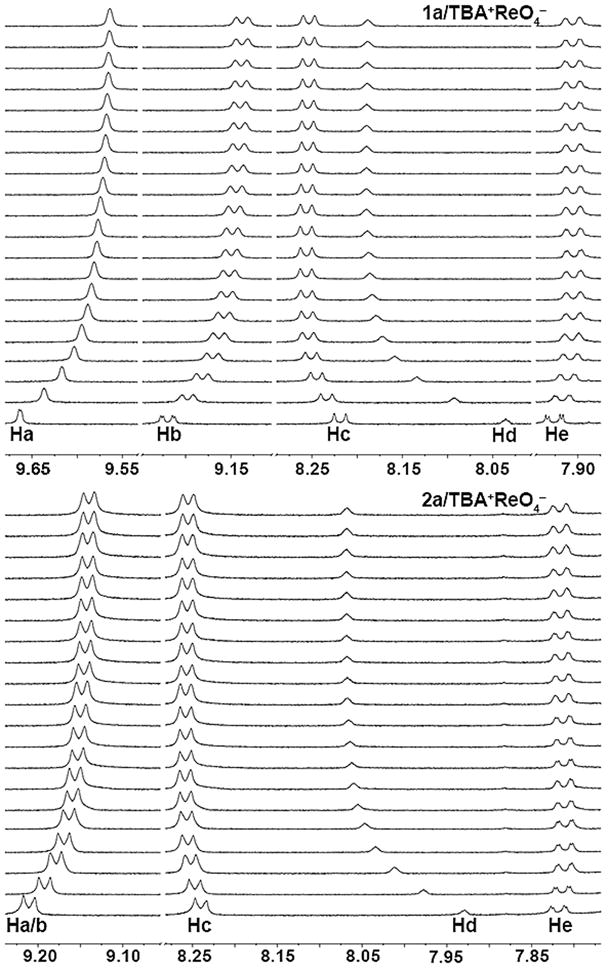
Partial 1H NMR spectra of 1a (top, 0–4.78 equiv) and 2a (bottom, 0–4.62 equiv) upon titrating TBA+ReO4− (equivalents from bottom to top).
The significant upfield shifting of Ha and Hb (Δδ = −0.099 and −0.082 ppm, respectively) on 1a is indicative of strong XB in solution.30 The dominant XB conformation as suggested by the crystal structure of 1b2+•2ReO4− is distinctly bidentate (Figure 1, top). Further evidence of XB in solution can be seen in the downfield 13C NMR shifting of 1a’s C–X carbons (Δδ = 0.150 ppm) upon titrating ReO4− (see ESI). Additionally, facile rotation of alkynyl-aromatic C–C bonds enables a second XB mode. Constructive bidentate XB-HB involving a single halogen and Hc/Hd is consistent with the downfield shifting of these hydrogens (Δδ = 0.038 and 0.154 ppm).31 Taken together, the greater upfield (Ha and Hb) and greater downfield (Hc and Hd) shifting of 1a is explained by strong bidentate XB in solution as well as XB-HB synergy.
For 2a, C–H HB and electrostatic contacts are the prevailing interactions in solution. Specifically, a tridentate binding site involving two Hc hydrogens and Hd proves the most active as evidenced by the crystal structure of 2b2+•2ReO4− and the downfield progression of these hydrogens (Δδ = 0.019 and 0.139 ppm, respectively). Upfield shifting of 2a’s Ha/b (Δδ = −0.071 ppm) is indicative of anion-HB augmentation of ring electron density.32
HypNMR 200833 was used to fit changes in shift to a stepwise association model:
| (1) |
| (2) |
Iterative and simultaneous refinement of multiple isotherms provided stability constants (Ka) for both 1a and 2a with ReO4−.34 For receptor 1a, the K1 of 8990 M−1 represents the first quantification of XB to ReO4− in solution, highlighting XB’s effectiveness at targeting this challenging oxoanion.35 Alternatively, 2a exhibits C–H HB and electrostatic interactions with ReO4−, which result in a K1 of 7390 M−1. Both 1a and 2a display modest K2 values of 172 and 145 M−1, respectively, that likely result from a combination of weak mono- and bidentate HB, and weak σ bonding.
The earliest quantification of XB and C–H HB to ReO4− in solution, and their corresponding bidentate/tridentate complexation in the solid state have been reported. The enhanced association of 1a to ReO4− when compared directly to a nearly isostructural and potent C–H HB molecule validates XB’s place alongside HB in an ongoing effort to design rational and selective receptors for ReO4− and TcO4−. Future work with 1a and 2a will include liquid-liquid extraction of ReO4− from aqueous phase, and exploration of XB and C–H HB with other anionic guests.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Peter Gans for his assistance with HypNMR 2008.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: synthesis and characterization of all novel compounds, 1H NMR titration methods and data, and X-ray crystallographic data and crystal packing.
Notes and references
- 1.Katayev EA, Kolesnikov GV, Sessler JL. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:1572. doi: 10.1039/b806468g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Clark JF, Clark DL, Whitener GD, Schroeder NC, Strauss SH. Environ Sci Technol. 1996;30:3124. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gu B, Brown GM, Bonnesen PV, Liang L, Moyer BA, Ober R, Alexandratos SD. Environ Sci Technol. 2000;34:1075. [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) Dilworth JR, Parrott SJ. Chem Soc Rev. 1998;27:43. [Google Scholar]; (b) Zuckier LS, Dohan O, Li Y, Chang CJ, Carrasco N, Dadachova E. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Finlay IG, Mason MD, Shelley M. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:392–400. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Jaubert F. Appl Radiat Isot. 2008;66:960. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2008.02.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.99mTC has an ideal half-life (6 h) and γ-ray emission energy (141 keV).
- 6.2.15 × 105 years.
- 7.(a) Koizumi K, Kobayashi K, Oba H, Umeda Y. Ann Nucl Med. 2001;15:439. doi: 10.1007/BF02988348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Kidokoro-Kunii Y, Emoto N, Cho K, Oikawa S. J Nippon Med Sch. 2006;73:10. doi: 10.1272/jnms.73.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Wakoff B, Nagy KL. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38:1765. doi: 10.1021/es0348795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Maksin D, Hercigonja R, Lazarević M, Žunić M, Nastasović A. Polym Bull. 2012;68:507. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Large scale production of 99Tc as a by-product of uranium-235 fission poses the biggest environmental concern. See: Schulte EH, Scoppa P. Sci Total Environ. 1987;64:163. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(87)90129-x.
- 10.Banerjee D, Rao MA, Joseph A, Manjrekar A, Singh I, Wattal PK. Desalin Water Treat. 2012;38:332. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Katayev EA, Boev NV, Khrustalev VN, Ustynyuk YA, Tananaev IG, Sessler JL. J Org Chem. 2007;72:2886. doi: 10.1021/jo0624849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.For examples of aza-cryptands, see: Farrell D, Gloe K, Gloe K, Goretzki G, McKee V, Nelson J, Nieuwenhuyzen M, Pal I, Stephan H, Town RM, Wichmann K. Dalton Trans. 2003:1961.McKee V, Nelson J, Town RM. Chem Soc Rev. 2003;32:309. doi: 10.1039/b200672n.Amendola V, Alberti G, Bergamaschi G, Biesuz R, Boiocchi M, Ferrito S, Schmidtchen FP. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2012;2012:3410.for pyrrole-based macrocycles, see: Kolesnikov GV, German KE, Kirakosyan G, Tananaev IG, Ustynyuk YA, Khrustalev VN, Katayev EA. Org Biomol Chem. 2011;9:7358. doi: 10.1039/c1ob05873h.Rambo BM, Sessler JL. Chem Eur J. 2011;17:4946. doi: 10.1002/chem.201100050.; for pH-controllable polycationic dendrimers, see: Stephan H, Spies H, Johannsen B, Kauffmann C, Vögtle F. Org Lett. 2000;2:2343. doi: 10.1021/ol006100r.; for noteworthy non-HB hydrophobic π-metalated cyclotriveratrylenes, see: Steed JW, Junk PC, Atwood JL, Barnes MJ, Raston CL, Burkhalter RS. J Am Chem Soc. 1994;116:10346.
- 13.2a solely employs C–H HB. Many receptors that utilize concerted N–H and C–H HB have been reported (see footnotes 1 and 11). For literature on unconventional C–H HB, see: Vargas R, Garza J, Dixon DA, Hay BP. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:4750.Juwarker H, Lenhardt JM, Pham DM, Craig SL. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:3740. doi: 10.1002/anie.200800548.Hua Y, Flood AH. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:1262. doi: 10.1039/b818033b.
- 14.(a) De Santis A, Forni A, Liantonio R, Metrangolo P, Pilati T, Resnati G. Chem Eur J. 2003;9:3974. doi: 10.1002/chem.200204655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Auffinger P, Hays FA, Westhof E, Ho PS. Proc of the Natl Acad of Sci, U S A. 2004;101:16789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407607101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Glaser R, Chen N, Wu H, Knotts N, Kaupp M. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:4412. doi: 10.1021/ja0383672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Rosokha SV, Neretin IS, Rosokha TY, Hecht J, Kochi JK. Heteroat Chem. 2006;17:449. [Google Scholar]; (e) Metrangolo P, Meyer F, Pilati T, Resnati G, Terraneo G. Chem Commun. 2008:1635. doi: 10.1039/b716879a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Cabot R, Hunter CA. Chem Commun. 2009;2005 doi: 10.1039/b822284c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Kilah NL, Wise MD, Serpell CJ, Thompson AL, White NG, Christensen KE, Beer PD. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:11893. doi: 10.1021/ja105263q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Legon AC. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2010;12:7736. doi: 10.1039/c002129f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Sarwar MG, Dragisic B, Sagoo S, Taylor MS. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:1674. doi: 10.1002/anie.200906488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Erdelyi M. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41:3547. doi: 10.1039/c2cs15292d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (i) Zapata F, Caballero A, White NG, Claridge TDW, Costa PJ, Félix Vt, Beer PD. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:11533. doi: 10.1021/ja302213r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (j) Beale TM, Chudzinski MG, Sarwar MG, Taylor MS. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:1667. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35213c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (k) Desiraju Gautam R, Ho PS, Kloo L, Legon Anthony C, Marquardt R, Metrangolo P, Politzer P, Resnati G, Rissanen K. Pure Appl Chem. 2013;85:1711. [Google Scholar]; (l) Kniep F, Jungbauer SH, Zhang Q, Walter SM, Schindler S, Schnapperelle I, Herdtweck E, Huber SM. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2013;52:7028. doi: 10.1002/anie.201301351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (m) Priimagi A, Cavallo G, Metrangolo P, Resnati G. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46:2686. doi: 10.1021/ar400103r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (n) Vargas Jentzsch A, Hennig A, Mareda J, Matile S. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46:2791. doi: 10.1021/ar400014r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (o) Mukherjee A, Tothadi S, Desiraju GR. Acc Chem Res. 2014;47:2514. doi: 10.1021/ar5001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(a) Corradi E, Meille SV, Messina MT, Metrangolo P, Resnati G. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2000;39:1782. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1521-3773(20000515)39:10<1782::aid-anie1782>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Aakeröy CB, Fasulo M, Schultheiss N, Desper J, Moore C. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:13772. doi: 10.1021/ja073201c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.(a) Voth AR, Khuu P, Oishi K, Ho PS. Nat Chem. 2009;1:74. doi: 10.1038/nchem.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Chudzinski MG, McClary CA, Taylor MS. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:10559. doi: 10.1021/ja202096f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.(a) Pinter B, Nagels N, Herrebout WA, De Proft F. Chem Eur J. 2013;19:519. doi: 10.1002/chem.201202567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b) Nagels N, Geboes Y, Pinter B, De Proft F, Herrebout WA. Chem Eur J. 2014;20:8433. doi: 10.1002/chem.201402116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kaae BH, Harpsøe K, Kvist T, Mathiesen JM, Mølck C, Gloriam D, Jimenez HN, Uberti MA, Nielsen SM, Nielsen B, Bräuner-Osborne H, Sauerberg P, Clausen RP, Madsen U. ChemMedChem. 2012;7:440. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Facile rotation of alkynyl-aromatic C–C bonds provides interconversion between mono- and bidentate receptor conformations.
- 20.Sonogashira K, Tohda Y, Hagihara N. Tetrahedron Lett. 1975;16:4467. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Reger DL, Wright TD, Little CA, Lamba JJS, Smith MD. Inorg Chem. 2001;40:3810. doi: 10.1021/ic0100121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.There are two known examples of solid-state XB to ReO4−. One is a serendipitous monodentate XB between CHCl3 and ReO4−, see: Cowley AR, Dilworth JR, Salichou M. Dalton Trans. 2007:1621. doi: 10.1039/b617549j.The other is a trifurcated monodentate XB to three 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene molecules, see: Abate A, Martí-Rujas J, Metrangolo P, Pilati T, Resnati G, Terraneo G. Cryst Growth Des. 2011;11:4220.
- 23.Crystal data for 1b C22H16I2N2O8Re2, M = 1062.57, monoclinic, P21/c, a = 6.9841(5), b = 34.338(3), c = 11.4497(9), β = 99.704(2), V = 2706.6(4), Z = 4, T = 150 K, μ(MoKα) = 11.265 mm−1, ρcalcd = 2.608 ml−1, 2θmax = 52.74°, 65752 reflections collected, 5485 unique (Rint = 0.0505, Rsigma = 0.0250) R1 = 0.0477 (I > 2σ(I)) and wR2 = 0.1108 (all data). CCDC 1028026 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
- 24.There is one weak σ and one anion-π interaction. Interestingly, the anion-π oxygen-centroid distance is 3.22 Å with an oxygen-centroid-nitrogen angle of 89°. For literature on weak σ and anion-π interactions, see: Berryman OB, Bryantsev VS, Stay DP, Johnson DW, Hay BP. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;129:48. doi: 10.1021/ja063460m.Berryman OB, Hof F, Hynes MJ, Johnson DW. Chem Commun. 2006:506. doi: 10.1039/b511570a.Berryman OB, Sather AC, Hay BP, Meisner JS, Johnson DW. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:10895. doi: 10.1021/ja8035652.; for additional reviews on this growing subject, see: Gamez P, Mooibroek TJ, Teat SJ, Reedijk J. Acc Chem Res. 2007;40:435. doi: 10.1021/ar7000099.Hay BP, Bryantsev VS. Chem Commun. 2008:2417. doi: 10.1039/b800055g.Schottel BL, Chifotides HT, Dunbar KR. Chem Soc Rev. 2008;37:68. doi: 10.1039/b614208g.
- 25.No solution dimer is observed in the current solvent system. See ESI for crystal packing.
- 26.Crystal Data for 2b C22H18N2O8Re2, M = 810.78, monoclinic, P21/n, a = 15.5756(10), b = 7.6106(5) c = 19.6042(13), β = 100.084(2), V = 2288.0(3), Z = 4, T = 100.0 K, μ(MoKα) = 10.623 mm−1, ρcalcd = 2.354 g ml−1, 2θmax = 56.56°, 40497 reflections collected, 5583 unique (Rint = 0.0706, Rsigma = 0.0467), R1 = 0.0286 (I > 2σ(I)), wR2 = 0.0604 (all data). CCDC 1028025 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
- 27.One interaction is bidentate (Hc and He). The C–H···O− distances of 2.53 and 2.55 Å correspond to weak HB interactions.
- 28.Both weak σ interactions occur over the same electron-deficient pyridinium ring (ortho and meta carbons; oxygen-carbon distances 3.18 and 2.92 Å, respectively), and involve separate oxygens of a ReO4− anion. For literature on weak σ and anion-π interactions, see footnote 24.
- 29.Hydrogens He and the sole phenyl core triplet were not followed due to limited shifting and/or residual solvent peak (CHCl3) obstruction.
- 30.Cametti M, Raatikainen K, Metrangolo P, Pilati T, Terraneo G, Resnati G. Org Biomol Chem. 2012;10:1329. doi: 10.1039/c1ob06524f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.An ancillary Hc and Hd binding mode may also contribute to solution stability. See the crystal structure of 2b2+•2ReO4−.
- 32.For examples in the literature of this spectroscopic phenomenon, see: Lee CH, Na HK, Yoon DW, Won DH, Cho WS, Lynch VM, Shevchuk SV, Sessler JL. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:7301. doi: 10.1021/ja029175u.Amendola V, Boiocchi M, Fabbrizzi L, Palchetti A. Chem Eur J. 2005;11:5648. doi: 10.1002/chem.200500351.Gomez DE, Fabbrizzi L, Licchelli M, Monzani E. Org Biomol Chem. 2005;3:1495. doi: 10.1039/b500123d.Shao J, Lin H, Yu M, Cai Z, Lin H. Talanta. 2008;75:551. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.11.048.Wang Y, Lin H, Shao J, Cai ZS, Lin HK. Talanta. 2008;74:1122. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.08.015.. Upfield shifting could also arise in part from weak σ interactions, see: Gil-Ramírez G, Escudero-Adán EC, Benet-Buchholz J, Ballester P. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:4114. doi: 10.1002/anie.200800636.Caballero A, Zapata F, Gonzalez L, Molina P, Alkorta I, Elguero J. Chem Commun. 2014;50:4680. doi: 10.1039/c4cc00169a.Giese M, Albrecht M, Repenko T, Sackmann J, Valkonen A, Rissanen K. Eur J Org Chem. 2014;2014:2435.
- 33.Frassineti C, Ghelli S, Gans P, Sabatini A, Moruzzi MS, Vacca A. Anal Biochem. 1995;231:374. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.9984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Reported Kas are the average of triplicate data sets. Errors are estimated at 10%. Full details of the titration experiments including σs, SDs, and model determination are contained in the ESI. Titrations were conducted at 290 K.
- 35.2a‘s tridentate C–H HB site is active regardless of conformational changes. By comparison, 1a can oscillate between bidentate, monodentate, and inactive XB modes. Given these differences, 1a‘s superior association to ReO4− establishes XB’s effectiveness at targeting charge diffuse anions.