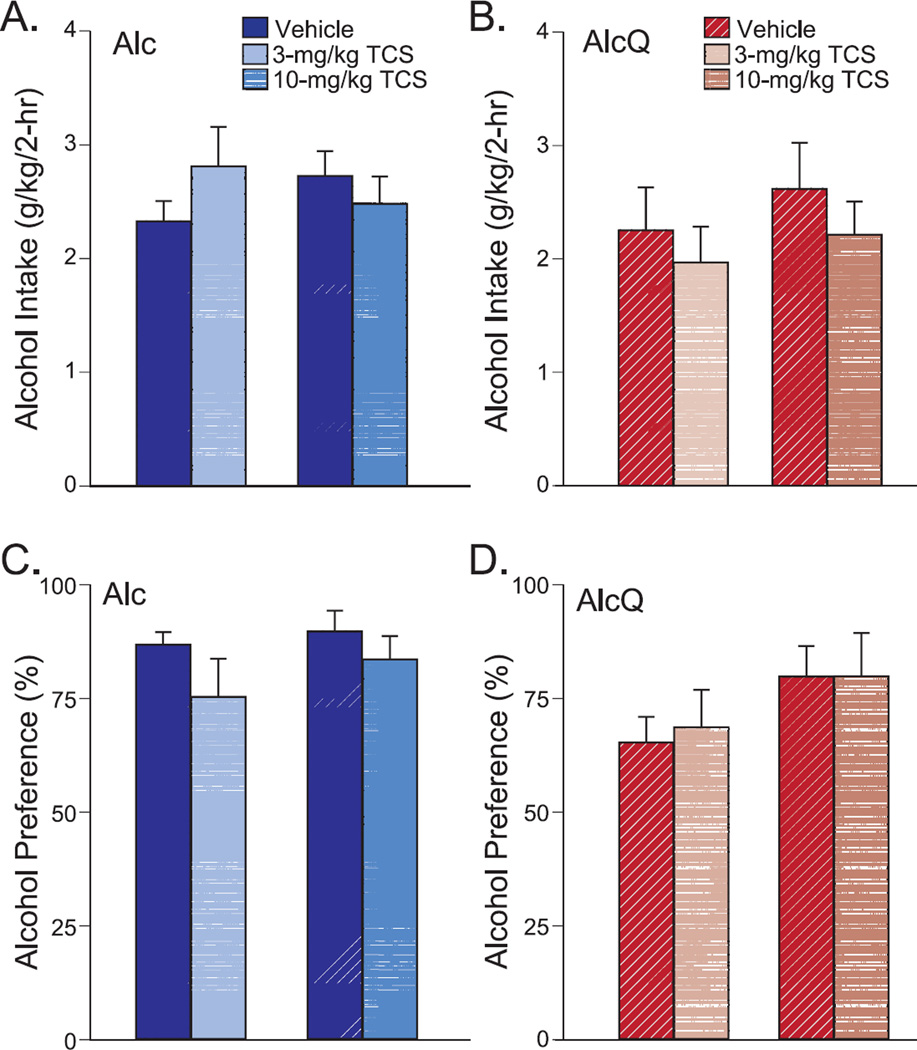
Figure 6. Systemic OX2R blockade had no effect on alcohol drinking.
The 3 or 10-mg/kg TCS-OX2-29 were compared to their respective vehicle groups by a two-way ANONA with repeated measures which showed that TCS did not change (A) alcohol-only (interaction: F(1,23)=2.62, p=0.12; drug: F(1,23)=0.28, p=0.6; cohort: F(1,23)=0.01, p=0.91) or (B) alcohol-quinine (interaction: F(1,23)=0.03, p=0.86; drug: F(1,23)=1.08, p=0.31; cohort: F(1,23)=0.65, p=0.43) intake. Nor did TCS altered preference of (C) alcohol-only (interaction: F(1,23)=0.34, p=0.57; drug: F(1,23)=3.71, p=0.07; cohort: F(1,23)=0.7, p=0.41) or (D) alcohol-quinine (interaction: F(1,23)=0.06, p=0.81; drug: F(1,23)=0.06, p=0.81; cohort: F(1,23)=2.37, p=0.14). Data are shown as mean±SEM.