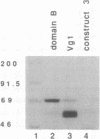
Abstract
Vg1 mRNA, a maternal message encoding a member of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily, undergoes localization to the vegetal cortex of Xenopus laevis oocytes during a narrow period of oogenesis. A 340-nucleotide sequence has been identified in Vg1 RNA that directs its vegetal localization [Mowry, K. L. & Melton, D. A. (1992) Science 255, 991-994]. To understand how cis- and trans-acting factors are involved in Vg1 mRNA localization, we have looked for specific interactions in vitro between oocyte proteins and Vg1 mRNA. S100 extracts of late-stage oocytes contain a protein-binding activity that protects specific regions of labeled Vg1 mRNA from degradation by RNase T1. The use of different regions of Vg1 RNA in competition reactions reveals two binding sites, both in the first half of the 3' untranslated region of Vg1 message. UV crosslinking predominantly labels a 69-kDa protein; saturation analysis and competitor studies indicate that this protein binds with a high affinity to the down-stream site, which corresponds to the 340-nucleotide vegetal localization sequence. Binding to this region is inhibited by another vegetally localized message, transforming growth factor beta 5 but is not inhibited by an animally localized RNA, An2. These data indicate that vegetally localized mRNAs share a binding motif that helps them achieve their intracellular distribution through specific RNA-protein interactions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H. A developmentally regulated activity that unwinds RNA duplexes. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilchik M. V., Gerhart J. C. Differentiation of the animal-vegetal axis in Xenopus laevis oocytes. I. Polarized intracellular translocation of platelets establishes the yolk gradient. Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;122(1):101–112. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnbrough C. H., Ford P. J. Identification in Xenopus laevis of a class of oocyte-specific proteins bound to messenger RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):415–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L., Banker G. A., Steward O. Selective dendritic transport of RNA in hippocampal neurons in culture. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):477–479. doi: 10.1038/330477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Dickinson L. K., Lehmann R. Oskar organizes the germ plasm and directs localization of the posterior determinant nanos. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):37–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90137-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigerio G., Burri M., Bopp D., Baumgartner S., Noll M. Structure of the segmentation gene paired and the Drosophila PRD gene set as part of a gene network. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner C. C., Tucker R. P., Matus A. Selective localization of messenger RNA for cytoskeletal protein MAP2 in dendrites. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):674–677. doi: 10.1038/336674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery W. R. Spatial distribution of messenger RNA in the cytoskeletal framework of ascidian eggs. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):482–492. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim-Ha J., Smith J. L., Macdonald P. M. oskar mRNA is localized to the posterior pole of the Drosophila oocyte. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90136-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of complexes involved in the splicing of precursors to mRNAs. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondaiah P., Sands M. J., Smith J. M., Fields A., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Melton D. A. Identification of a novel transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta 5) mRNA in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1089–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A. Improved synthesis of full-length RNA probe at reduced incubation temperatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6463–6463. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H. Intracellular localization of messenger RNAs for cytoskeletal proteins. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold E. A., Munro H. N. Cytoplasmic protein binds in vitro to a highly conserved sequence in the 5' untranslated region of ferritin heavy- and light-subunit mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2171–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald P. M. bicoid mRNA localization signal: phylogenetic conservation of function and RNA secondary structure. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):161–171. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Struhl G. cis-acting sequences responsible for anterior localization of bicoid mRNA in Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):595–598. doi: 10.1038/336595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Sharp P. A. Identification and characterization of a HeLa nuclear protein that specifically binds to the trans-activation-response (TAR) element of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Translocation of a localized maternal mRNA to the vegetal pole of Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):80–82. doi: 10.1038/328080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowry K. L., Melton D. A. Vegetal messenger RNA localization directed by a 340-nt RNA sequence element in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):991–994. doi: 10.1126/science.1546297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. T., Schiller D. L., Franke W. W. Sequence analysis of cytoplasmic mRNA-binding proteins of Xenopus oocytes identifies a family of RNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Neupert B., Kühn L. C. A specific mRNA binding factor regulates the iron-dependent stability of cytoplasmic transferrin receptor mRNA. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokrywka N. J., Stephenson E. C. Microtubules mediate the localization of bicoid RNA during Drosophila oogenesis. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):55–66. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. A., Ellisman M. H., Benzer S. Subcellular localization of transcripts in Drosophila photoreceptor neurons: chaoptic mutants have an aberrant distribution. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):806–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff J. W., Whitfield W. G., Glover D. M. Two distinct mechanisms localise cyclin B transcripts in syncytial Drosophila embryos. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1249–1261. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
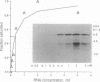
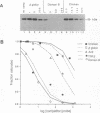
- Rebagliati M. R., Weeks D. L., Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Identification and cloning of localized maternal RNAs from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Lehmann R. Nanos is the localized posterior determinant in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90110-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Melton D. A. A maternal mRNA localized to the vegetal hemisphere in Xenopus eggs codes for a growth factor related to TGF-beta. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield W. G., González C., Sánchez-Herrero E., Glover D. M. Transcripts of one of two Drosophila cyclin genes become localized in pole cells during embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):337–340. doi: 10.1038/338337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Tafuri S., Ranjan M., Familari M. The Y-box factors: a family of nucleic acid binding proteins conserved from Escherichia coli to man. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wylie C. C., Brown D., Godsave S. F., Quarmby J., Heasman J. The cytoskeleton of Xenopus oocytes and its role in development. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Nov;89 (Suppl):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Melton D. A. Synthesis of long, capped transcripts in vitro by SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:42–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Melton D. A. The material mRNA Vg1 is correctly localized following injection into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):592–595. doi: 10.1038/336592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Sokol S., Melton D. A. A two-step model for the localization of maternal mRNA in Xenopus oocytes: involvement of microtubules and microfilaments in the translocation and anchoring of Vg1 mRNA. Development. 1990 Feb;108(2):289–298. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Mukhtar K. A., Webb A. C. An ultrastructural study of primordial germ cells, oogonia and early oocytes in Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1971 Oct;26(2):195–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]