Figure 3.
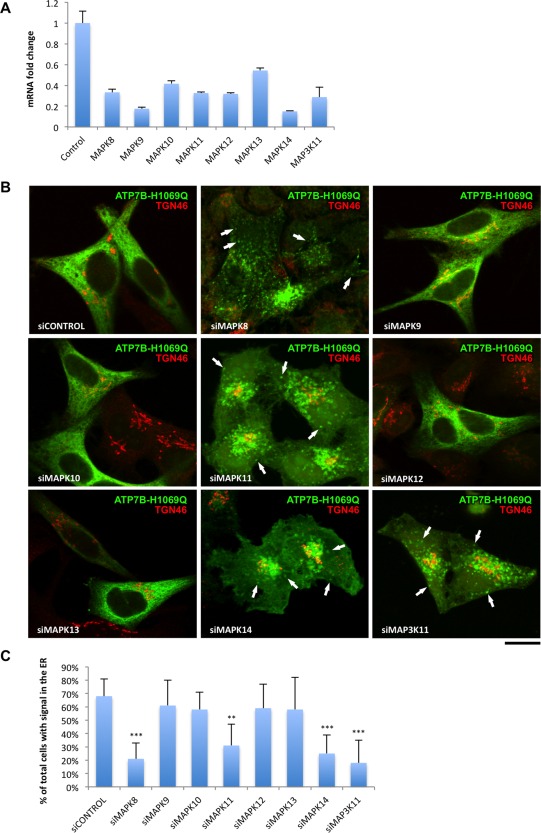
Silencing of several p38 and JNK isoforms corrects localization and trafficking of the ATP7BH1069Q mutant. (A) HeLa cells were incubated with small interfering RNA, which targets specific genes (indicated in graph) belonging to the p38 and JNK pathways. The efficiency of silencing for each gene was evaluated by quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction and expressed as fold‐change (average ± standard deviation, n = 3 experiments) after normalization to messenger RNA levels of the same gene in control cells (treated with scramble small interfering RNA). (B) HeLa cells were silenced for different p38 and JNK isoforms as in (A), then infected with Ad‐ATP7BH1069Q‐GFP and incubated for 2 hours with 100 μM CuSO4. Fixed cells were then labeled for TGN46 and visualized under a confocal microscope. Silencing of MAPK8, MAPK11, MAPK14, or MAP3K11 showed the rescue of ATP7BH1069Q from the ER and its movement to the post‐Golgi vesicles (arrows) and PM. (C) Cells were treated as in (B). The percentage of cells (average ± standard deviation, n = 10 fields) with ATP7BH1069Q signal in the ER was calculated. RNA interference of MAPK8, MAPK11, MAPK14, and MAP3K11 reduced the percentage of cells exhibiting ATP7BH1069Q in the ER. Scale bar = 4.7 μm (B). Abbreviations: mRNA, messenger RNA; si, small interfering.
