Abstract
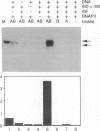
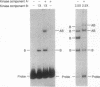
The carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II contains a tandemly repeated heptapeptide sequence. Previous work has shown that this sequence is phosphorylated at multiple sites by a template-associated protein kinase, in a reaction that is closely associated with the initiation of RNA synthesis. We have purified this kinase to apparent homogeneity from human (HeLa) cells. The purified kinase phosphorylates native RNA polymerase II only in the presence of DNA and the general transcription factors TFIID (TBP), TFIIB, and TFIIF. Two kinase components are required for full activity: a catalytic component and a DNA-binding regulatory component. The regulatory component has been identified as Ku autoantigen, based on the molecular weights of its component polypeptides, its DNA-binding properties, and its reactivity with anti-Ku monoclonal antibodies. The Ku autoantigen recruits the catalytic component of the kinase to the template. Ku autoantigen has been previously proposed to interact with DNA by a characteristic bind-and-slide mechanism. This mode of interaction may provide a mechanism for targeting the kinase to the transcription complex and other DNA-bound substrates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Ingles C. J. Mutations in RNA polymerase II enhance or suppress mutations in GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2794–2798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Wong J. K., Fitzpatrick V. D., Moyle M., Ingles C. J. The C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Drosophila melanogaster, and mammals: a conserved structure with an essential function. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):321–329. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias J. A., Dynan W. S. Promoter-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II using immobilized enzyme complexes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3223–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias J. A., Peterson S. R., Dynan W. S. Promoter-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by a template-bound kinase. Association with transcriptional initiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8055–8061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei M. S., Halden N. F., Cullen C. R., Corden J. L. Genetic analysis of the repetitive carboxyl-terminal domain of the largest subunit of mouse RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):330–339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Dahmus M. E. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T., Vancurová I., Sun I., Lou W., DeLeon S. A DNA-activated protein kinase from HeLa cell nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6460–6471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase by the murine homologue of the cell-cycle control protein cdc2. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):679–684. doi: 10.1038/339679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor has an associated DNA-dependent ATPase (dATPase) activity strongly stimulated by the TATA region of promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7356–7360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Garrett K. P., Hanley J. P., Conaway J. W. Mechanism of promoter selection by RNA polymerase II: mammalian transcription factors alpha and beta gamma promote entry of polymerase into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6205–6209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Gileadi O., Li Y., Kornberg R. D. CTD kinase associated with yeast RNA polymerase II initiation factor b. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1223–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90298-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Kostrub C. F., Li J., Chavez D. P., Wang B. Q., Fang S. M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F. A cDNA encoding RAP74, a general initiation factor for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):464–467. doi: 10.1038/355464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Killeen M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F., Reinberg D. The small subunit of transcription factor IIF recruits RNA polymerase II into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9999–10003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gileadi O., Feaver W. J., Kornberg R. D. Cloning of a subunit of yeast RNA polymerase II transcription factor b and CTD kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1389–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.1445600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith A. J., Blier P. R., Mimori T., Hardin J. A. Ku polypeptides synthesized in vitro assemble into complexes which recognize ends of double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle T. J. A protein kinase from wheat germ that phosphorylates the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. Plant Cell. 1989 Aug;1(8):827–836. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.8.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson S. I., Knuth M. W., Burgess R. R. The human U1 snRNA promoter correctly initiates transcription in vitro and is activated by PSE1. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2048–2060. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Cloning of a human gene encoding the general transcription initiation factor IIB. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):689–695. doi: 10.1038/352689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuth M. W., Gunderson S. I., Thompson N. E., Strasheim L. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and characterization of proximal sequence element-binding protein 1, a transcription activating protein related to Ku and TREF that binds the proximal sequence element of the human U1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17911–17920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase IIA occurs subsequent to interaction with the promoter and before the initiation of transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13165–13173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. Transcription-dependent structural changes in the C-terminal domain of mammalian RNA polymerase subunit IIa/o. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6693–6698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Greenleaf A. L. A protein kinase that phosphorylates the C-terminal repeat domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Greenleaf A. L. CTD kinase large subunit is encoded by CTK1, a gene required for normal growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene Expr. 1991 May;1(2):149–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees-Miller S. P., Chen Y. R., Anderson C. W. Human cells contain a DNA-activated protein kinase that phosphorylates simian virus 40 T antigen, mouse p53, and the human Ku autoantigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6472–6481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. M., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain contributes to the response to multiple acidic activators in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2431–2440. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado E., Ha I., Cortes P., Weis L., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: role of transcription factors IIA, IID, and IIB during formation of a transcription-competent complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6335–6347. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Akizuki M., Yamagata H., Inada S., Yoshida S., Homma M. Characterization of a high molecular weight acidic nuclear protein recognized by autoantibodies in sera from patients with polymyositis-scleroderma overlap. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):611–620. doi: 10.1172/JCI110295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hardin J. A. Mechanism of interaction between Ku protein and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10375–10379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Characterization of the DNA-binding protein antigen Ku recognized by autoantibodies from patients with rheumatic disorders. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2274–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Ohosone Y., Hama N., Suwa A., Akizuki M., Homma M., Griffith A. J., Hardin J. A. Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding the 80-kDa subunit protein of the human autoantigen Ku (p70/p80) recognized by autoantibodies from patients with scleroderma-polymyositis overlap syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M. L., Young R. A. Intragenic and extragenic suppressors of mutations in the heptapeptide repeat domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):715–724. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paillard S., Strauss F. Analysis of the mechanism of interaction of simian Ku protein with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5619–5624. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. The transition of RNA polymerase II from initiation to elongation is associated with phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain of subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19621–19629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson S. R., Dvir A., Anderson C. W., Dynan W. S. DNA binding provides a signal for phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II heptapeptide repeats. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):426–438. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Sthoeger Z. M. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the p70 (Ku) lupus autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5047–5052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H. Use of monoclonal antibodies for the characterization of novel DNA-binding proteins recognized by human autoimmune sera. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):18–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. R., Miskimins W. K., Ruddle F. H. Nuclear proteins TREF1 and TREF2 bind to the transcriptional control element of the transferrin receptor gene and appear to be associated as a heterodimer. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):151–164. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Chao D., Lopes J., Hirsch J. P., Henry S., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II C-terminal repeat influences response to transcriptional enhancer signals. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):491–494. doi: 10.1038/347491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. A carboxyl-terminal-domain kinase associated with RNA polymerase II transcription factor delta from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Maupin M. K. 5,6-Dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole inhibits a HeLa protein kinase that phosphorylates an RNA polymerase II-derived peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):508–515. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Steinberg T. H., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro transcription by monoclonal antibodies prepared against wheat germ RNA polymerase II that react with the heptapeptide repeat of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11511–11520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A. I., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Anderson C. W. Double-stranded DNA induces the phosphorylation of several proteins including the 90 000 mol. wt. heat-shock protein in animal cell extracts. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):139–145. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaneva M., Wen J., Ayala A., Cook R. cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of the 86-kDa subunit of the Ku antigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13407–13411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehring W. A., Lee J. M., Weeks J. R., Jokerst R. S., Greenleaf A. L. The C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II largest subunit is essential in vivo but is not required for accurate transcription initiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Corden J. L. Identification of phosphorylation sites in the repetitive carboxyl-terminal domain of the mouse RNA polymerase II largest subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2290–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Corden J. L. Phosphorylation causes a conformational change in the carboxyl-terminal domain of the mouse RNA polymerase II largest subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2297–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W. W., Yaneva M. On the mechanisms of Ku protein binding to DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):574–579. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80847-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., Bergsma W. G., Arnberg A. C., van der Vliet P. C. HeLa nuclear protein recognizing DNA termini and translocating on DNA forming a regular DNA-multimeric protein complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]