Abstract
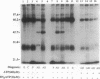
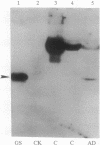
In this report, 8- and 2-azidoadenosine 5'-[gamma-32P]triphosphate were used to examine cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples for the presence of an ATP binding protein unique to individuals with Alzheimer disease (AD). A 42-kDa ATP binding protein was found in the CSF of AD patients that is not observed in CSF from normal patients or other neurological controls. The photolabeling is saturated with 30 microM 2-azidoadenosine 5'-[gamma-32P]triphosphate. Photoinsertion can be totally prevented by the addition of 25 microM ATP. Photoinsertion of 2-azidoadenosine 5'-triphosphate into the protein is only weakly protected by other nucleotides such as ADP and GTP, indicating that this is a specific ATP binding protein. A total of 83 CSF samples were examined in a blind manner. The 42-kDa protein was detected in 38 of 39 AD CSF samples and in only 1 of 44 control samples. This protein was identified as glutamine synthetase [GS; glutamate-ammonia ligase; L-glutamate:ammonia ligase (ADP-forming), EC 6.3.1.2] based on similar nucleotide binding properties, comigration on two-dimensional gels, reaction with a polyclonal anti-GS antibody, and the presence of significant GS enzyme activity in AD CSF. In brain, GS plays a key role in elimination of free ammonia and also converts the neurotransmitter and excitotoxic amino acid glutamate to glutamine, which is not neurotoxic. The involvement of GS, if any, in the onset of AD is unknown. However, the presence of GS in the CSF of terminal AD patients suggests that this enzyme may be a useful diagnostic marker and that further study is warranted to determine any possible role for glutamate metabolism in the pathology of AD.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alom J., Galard R., Catalan R., Castellanos J. M., Schwartz S., Tolosa E. Cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptide Y in Alzheimer's disease. Eur Neurol. 1990;30(4):207–210. doi: 10.1159/000117347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. A., Evans D. A. Alzheimer's disease. Dis Mon. 1992 Jan;38(1):1–64. doi: 10.1016/0011-5029(92)90010-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., Plum F. Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol Rev. 1987 Apr;67(2):440–519. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.2.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki J., Geahlen R., Haley B. Synthesis and use of azido photoaffinity analogs of adenine and guanine nucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:642–653. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boni U., McLachlan D. R. Controlled induction of paired helical filaments of the Alzheimer type in cultured human neurons, by glutamate and aspartate. J Neurol Sci. 1985 May;68(2-3):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouiche A., Frotscher M. Astroglial processes around identified glutamatergic synapses contain glutamine synthetase: evidence for transmitter degradation. Brain Res. 1991 Jun 28;552(2):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T. The role of glutamate in neurotransmission and in neurologic disease. Arch Neurol. 1986 Oct;43(10):1058–1063. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520100062016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartikainen P., Soininen H., Reinikainen K. J., Sirviö J., Soikkeli R., Riekkinen P. J. Neurotransmitter markers in the cerebrospinal fluid of normal subjects. Effects of aging and other confounding factors. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1991;84(1-2):103–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01249114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey C. O., Hershey L. A., Varnes A., Vibhakar S. D., Lavin P., Strain W. H. Cerebrospinal fluid trace element content in dementia: clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlations. Neurology. 1983 Oct;33(10):1350–1353. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.10.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Furukawa Y., Mashimoto S., Takahashi K., Yamada M. Vitamin B12 levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of people with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1990 Oct;82(4):327–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1990.tb01395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatoon S., Campbell S. R., Haley B. E., Slevin J. T. Aberrant guanosine triphosphate-beta-tubulin interaction in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1989 Aug;26(2):210–215. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Haley B. E. Synthesis and properties of 2-azido-NAD+. A study of interaction with glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3636–3641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Yang L. L., Cotman C. W. Beta-amyloid protein increases the vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to excitotoxic damage. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 19;533(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91355-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehéricy S., Hirsch E. C., Cervera P., Hersh L. B., Hauw J. J., Ruberg M., Agid Y. Selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the ventral striatum of patients with Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8580–8584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHELSON A. M. SYNTHESIS OF NUCLEOTIDE ANHYDRIDES BY ANION EXCHANGE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 11;91:1–13. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara E., Hirai S., Amari M., Shoji M., Yamaguchi H., Okamoto K., Ishiguro K., Harigaya Y., Wakabayashi K. Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin as a possible biochemical marker for Alzheimer-type dementia. Ann Neurol. 1990 Oct;28(4):561–567. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P. Antigenic changes similar to those seen in neurofibrillary tangles are elicited by glutamate and Ca2+ influx in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90447-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Hackenberg R., Gershman H. Regulation of glutamine synthetase in cultured 3T3-L1 cells by insulin, hydrocortisone, and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D., Martinez-Hernandez A. Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Feb 2;161(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. C., Esiri M. M., Hiorns R. W., Wilcock G. K., Powell T. P. Anatomical correlates of the distribution of the pathological changes in the neocortex in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4531–4534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penney J. B., Maragos W. F., Greenamyre J. T., Debowey D. L., Hollingsworth Z., Young A. B. Excitatory amino acid binding sites in the hippocampal region of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Apr;53(4):314–320. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.4.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry T. L., Yong V. W., Bergeron C., Hansen S., Jones K. Amino acids, glutathione, and glutathione transferase activity in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1987 Apr;21(4):331–336. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Haley B. E. Photoaffinity labeling of nucleotide binding sites with 8-azidopurine analogs: techniques and applications. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:613–633. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior R., Mönning U., Schreiter-Gasser U., Weidemann A., Blennow K., Gottfries C. G., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Quantitative changes in the amyloid beta A4 precursor protein in Alzheimer cerebrospinal fluid. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Mar 11;124(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90824-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procter A. W., Palmer A. M., Francis P. T., Lowe S. L., Neary D., Murphy E., Doshi R., Bowen D. M. Evidence of glutamatergic denervation and possible abnormal metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1988 Mar;50(3):790–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinikainen K. J., Soininen H., Riekkinen P. J. Neurotransmitter changes in Alzheimer's disease: implications to diagnostics and therapy. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Dec;27(4):576–586. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Chavan A. J., Haley B. E. Identification of peptides from the adenine binding domains of ATP and AMP in adenylate kinase: isolation of photoaffinity-labeled peptides by metal chelate chromatography. Biochemistry. 1992 May 12;31(18):4479–4487. doi: 10.1021/bi00133a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. P., Iqbal K., Bucht G., Winblad B., Wisniewski H. M., Grundke-Iqbal I. Alzheimer's disease: paired helical filament immunoreactivity in cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(1):6–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00310917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gool W. A., Bolhuis P. A. Cerebrospinal fluid markers of Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991 Oct;39(10):1025–1039. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1991.tb04052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]