Figure 1.
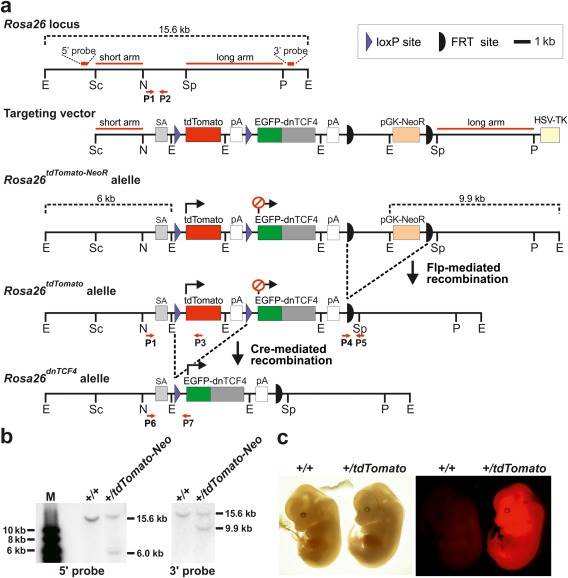
Generation of mice with inducible expression of N‐terminally truncated TCF4 protein. (a) The targeting strategy used for homologous recombination in ES cells. The targeting vector included the 5' “short” and 3' “long” Rosa26 homology arms and rabbit β‐globin splice acceptor site (SA) followed by transcription blocker [composed of tdTomato cDNA and the polyadenylation signal (pA)] flanked by two loxP sites (violet triangles). The sequence encoding dnTCF4 fused to the C‐terminus of EGFP was placed downstream of the blocker. The construct also contained the phosphoglycerate kinase promoter‐driven neomycin resistance gene (pGK‐NeoR) flanked by FRT sites (black semicircles) and the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV‐TK) gene. HSV‐TK was used for selection against clones with randomly integrated vector. Recombination of the targeting vector with the Rosa26 locus generated the Rosa26tdTomato‐NeoR allele. The Rosa26tdTomato and Rosa26dnTCF4 alleles were produced using Flp‐ or Cre‐mediated recombination, respectively. Relevant restriction enzyme sites, primers for genotyping (P1‐P7), and positions of probes used for Southern blotting are indicated. E, EcoRI; N, NheI; P, PmlI; Sc, SacII; Sp, SspI. For clarity, the sizes of the genes and DNA elements do not completely correspond to the scale indicated in the upper right corner of the scheme. (b) Southern blot analysis of ES cell genomic DNA detecting the homologous recombination at the 5' or 3' end of the Rosa26 locus. EcoRI‐digested DNA was used for both blots. M, molecular weight markers. (c) Bright field (left) and fluorescent microscopy images (right) of wt and Rosa26+/tdTomato embryos isolated at E13.5. The presence of the tdTomato allele is manifested by whole‐body red fluorescence.
