Abstract
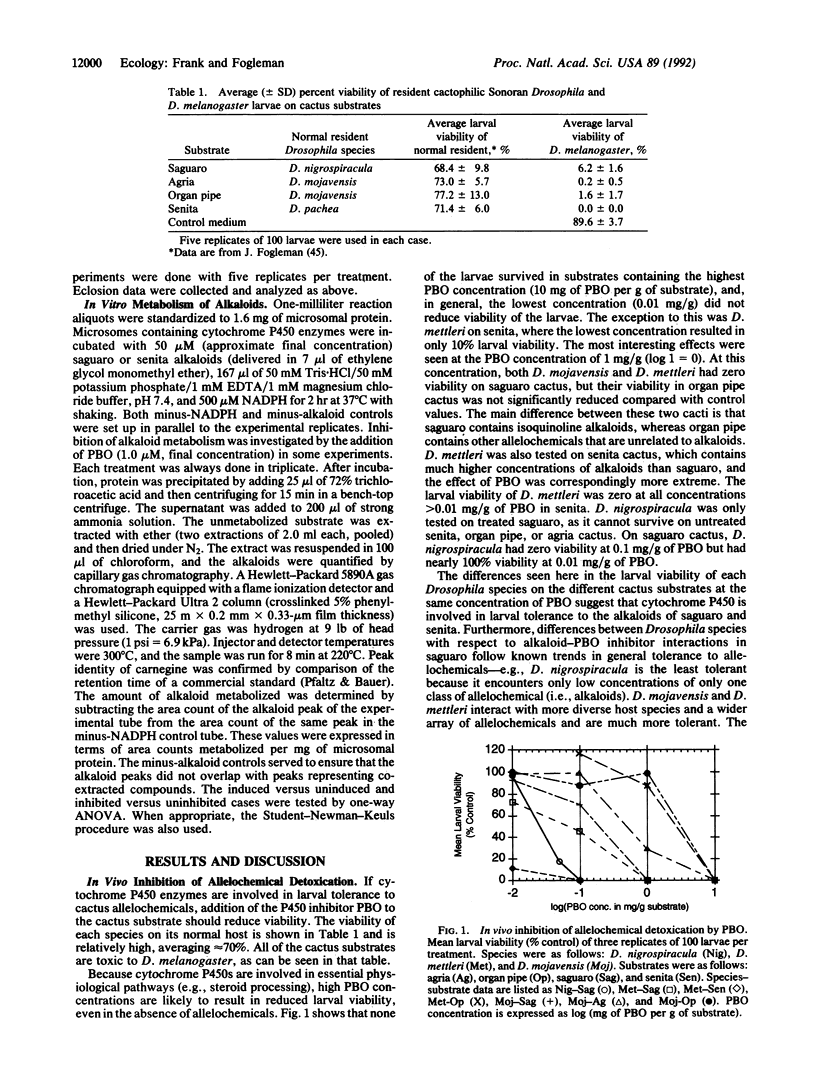
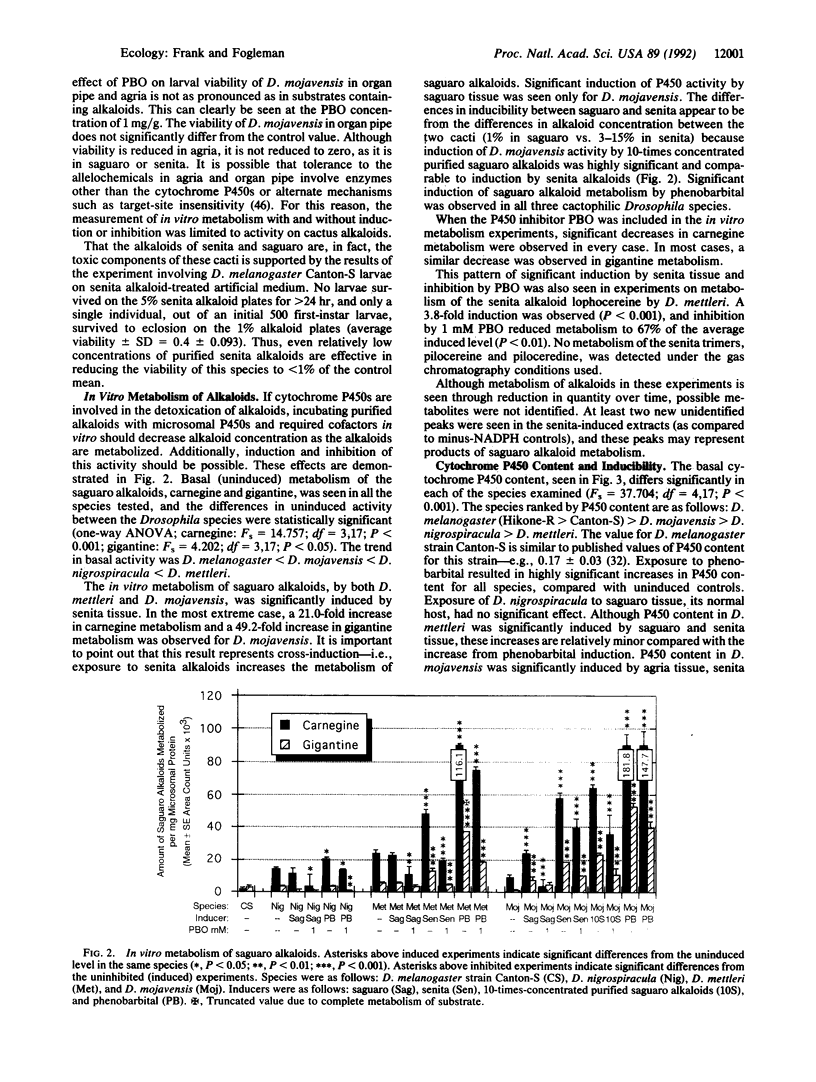
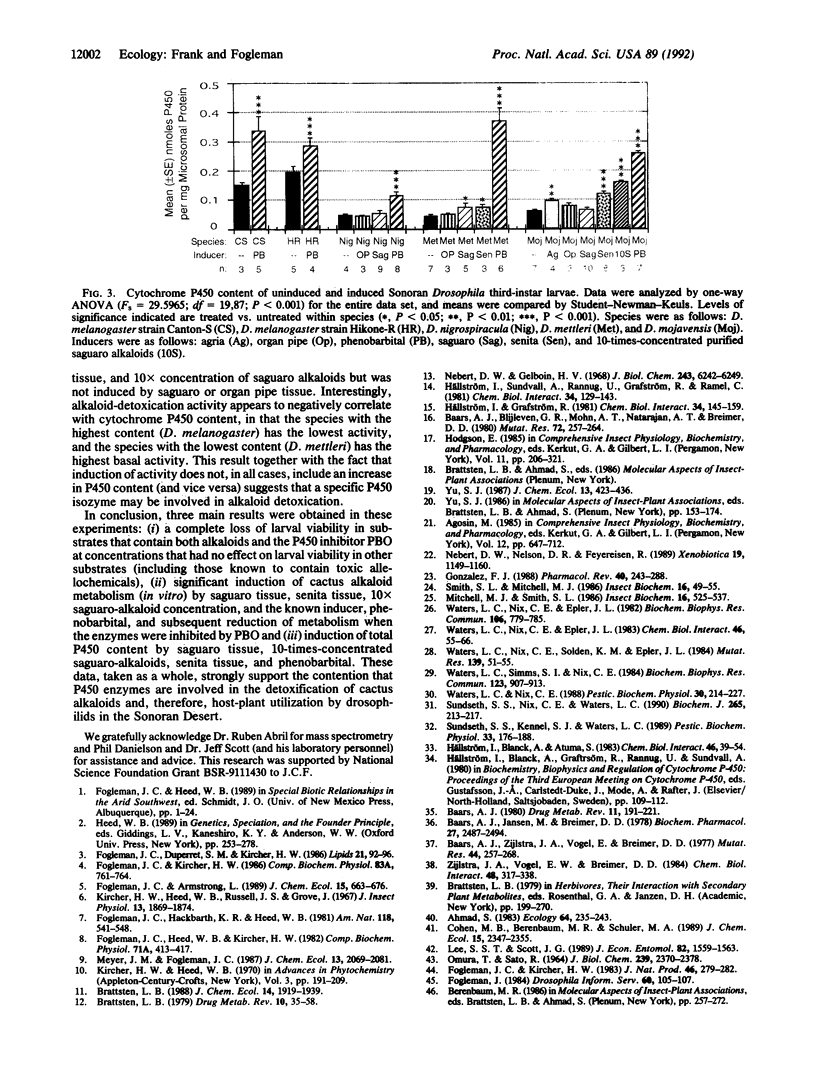
The four Drosophila species endemic to the Sonoran Desert (Drosophila mettleri, Drosophila mojavensis, Drosophila nigrospiracula, and Drosophila pachea) utilize necrotic cactus tissue or soil soaked by rot exudate as breeding substrates. Each Drosophila species uses a different cactus species as its primary host. D. pachea is limited to senita cactus by a biochemical dependency on unusual sterols available only in that cactus. For the other Drosophila species, no such chemical dependencies exist to explain the relationships with their primary host plants. Each cactus species has a different array of allelochemicals that have detrimental effects on non-resident fly species. We have hypothesized that the desert fly-cactus associations are due, in part, to differences between the fly species in their allelochemical detoxication enzymes, the cytochrome P450 system. To test whether P450s are involved in the detoxication of cactus allelochemicals, several experiments were done. (i) The effect of a specific P450 inhibitor, piperonyl butoxide, on larval survival through eclosion on each cactus substrate was investigated. (ii) In vitro metabolism of cactus alkaloids was determined for each Drosophila species. The effects of specific inducers and inhibitors were included in these experiments. (iii) The basal and induced content of cytochrome P450 in each species was determined. The results support the hypothesis that P450 enzymes are involved in host-plant utilization by these Sonoran Desert Drosophila species.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baars A. J. Biotransformation of xenobiotics in Drosophila melanogaster and its relevance for mutagenicity testing. Drug Metab Rev. 1980;11(2):191–221. doi: 10.3109/03602538008994025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baars A. J., Blijleven W. G., Mohn G. R., Natarajan A. T., Breimer D. D. Preliminary studies on the ability of Drosophila microsomal preparations to activate mutagens and carcinogens. Mutat Res. 1980 Sep;72(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baars A. J., Jansen M., Breimer D. D. The influence of phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on glutathione S-transferase activity of rat liver cytosol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(21):2487–2497. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baars A. J., Zijlstra J. A., Vogel E., Breimer D. D. The occurrence of cytochrome P-450 and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in Drosophila melanogaster microsomes, and the importance of this metabolizing capacity for the screening of carcinogenic and mutagenic properties of foreign compounds. Mutat Res. 1977 Aug;44(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(77)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brattsten L. B. Ecological significance of mixed-function oxidations. Drug Metab Rev. 1979;10(1):35–58. doi: 10.3109/03602537908993900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällström I., Sundvall A., Rannug U., Grafström R., Ramel C. The metabolism of drugs and carcinogens in isolated subcellular fractions of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Activation of vinyl chloride, 2-aminoanthracene and benzo[a]pyrene as measured by mutagenic effects in Salmonella typhimurium. Chem Biol Interact. 1981 Mar 1;34(2):129–143. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(81)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällstöm I., Blanck A., Atuma S. Comparison of cytochrome P-450-dependent metabolism in different developmental stages of Drosophila melanogaster. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Aug 15;46(1):39–54. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. S., Scott J. G. An improved method for preparation, stabilization, and storage of house fly (Diptera: Muscidae) microsomes. J Econ Entomol. 1989 Dec;82(6):1559–1563. doi: 10.1093/jee/82.6.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V. Substrate-inducible microsomal aryl hydroxylase in mammalian cell culture. I. Assay and properties of induced enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6242–6249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Feyereisen R. Evolution of the cytochrome P450 genes. Xenobiotica. 1989 Oct;19(10):1149–1160. doi: 10.3109/00498258909043167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundseth S. S., Nix C. E., Waters L. C. Isolation of insecticide resistance-related forms of cytochrome P-450 from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):213–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2650213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Nix C. E., Epler J. L. Dimethylnitrosamine demethylase activity in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):779–785. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91778-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Nix C. E., Epler J. L. Studies on the relationship between dimethylnitrosamine-demethylase activity and dimethylnitrosamine-dependent mutagenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Aug 15;46(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Nix C. E., Solden K. M., Epler J. L. Effects of genotype and age on mixed-function oxidase activities in adult Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat Res. 1984 Feb;139(2):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(84)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Simms S. I., Nix C. E. Natural variation in the expression of cytochrome P-450 and dimethylnitrosamine demethylase in Drosophila. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):907–913. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra J. A., Vogel E. W., Breimer D. D. Strain-differences and inducibility of microsomal oxidative enzymes in Drosophila melanogaster flies. Chem Biol Interact. 1984 Mar;48(3):317–338. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(84)90143-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





