Abstract
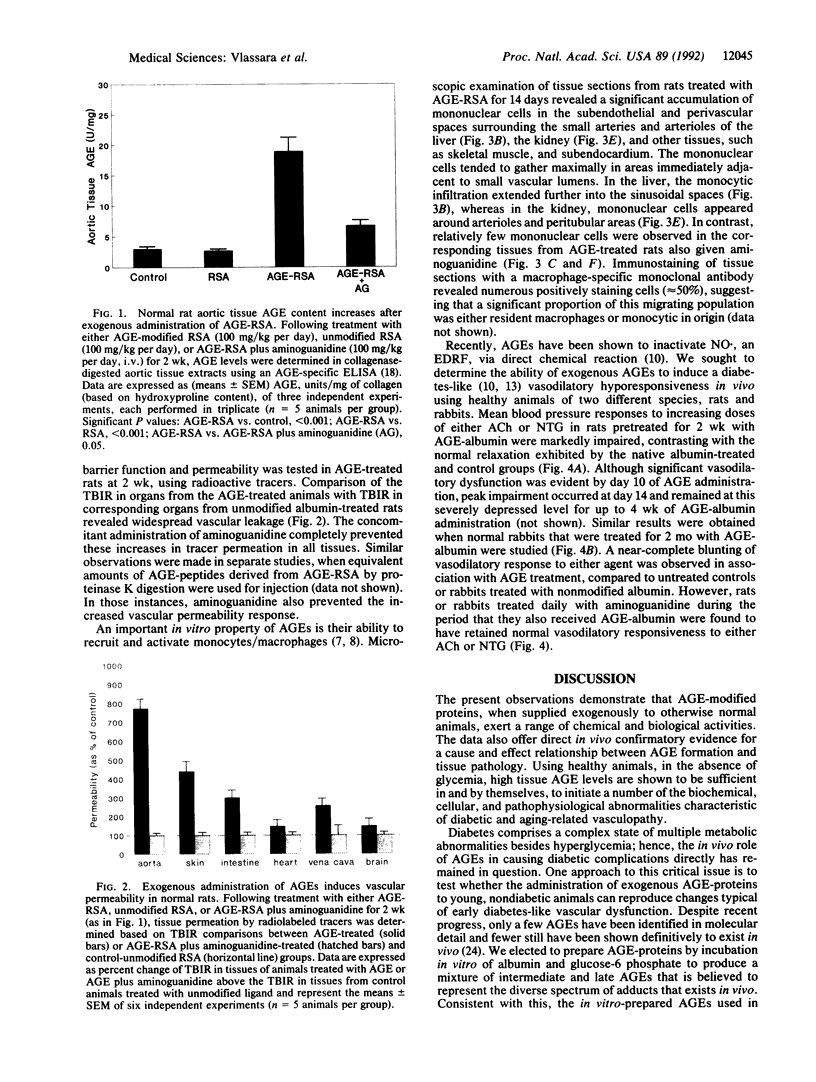
Advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs) have been implicated in many of the complications of diabetes and normal aging. Markedly elevated vascular tissue and circulating AGEs were linked recently to the accelerated vasculopathy of end-stage diabetic renal disease. To determine the pathogenic role of AGEs in vivo, AGE-modified albumin was administered to healthy nondiabetic rats and rabbits alone or in combination with the AGE-crosslink inhibitor aminoguanidine. Within 2-4 weeks of AGE treatment, the AGE content of aortic tissue samples rose to six times the amount found in controls (P < 0.001). Cotreatment with aminoguanidine limited tissue AGE accumulation to levels two times that of control. AGE administration was associated with a significant increase in vascular permeability, as assessed by 125I label tracer methods. This alteration was absent in animals that received aminoguanidine in addition to AGE. Significant mononuclear cell migratory activity was observed in subendothelial and periarteriolar spaces in various tissues from AGE-treated rats compared to normal cellularity noted in tissues from animals treated with aminoguanidine. Blood pressure studies of AGE-treated rats and rabbits revealed markedly defective vasodilatory responses to acetylcholine and nitroglycerin compared to controls (P < 0.001), consistent with marked NO. inactivation; aminoguanidine treatment significantly prevented this defect. These in vivo data demonstrate directly that AGEs, independent of metabolic or genetic factors, can induce complex vascular alterations resembling those seen in diabetes or aging. AGE administration represents an animal model system for the study of diabetic and aging complications as well as for assessing the efficacy of newly emerging therapies aimed at inhibiting advanced glycosylation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barger A. C., Beeuwkes R., 3rd, Lainey L. L., Silverman K. J. Hypothesis: vasa vasorum and neovascularization of human coronary arteries. A possible role in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):175–177. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1315–1321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Pongor S., Cerami A. Covalent attachment of soluble proteins by nonenzymatically glycosylated collagen. Role in the in situ formation of immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1739–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Vlassara H., Kooney A., Ulrich P., Cerami A. Aminoguanidine prevents diabetes-induced arterial wall protein cross-linking. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1629–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.3487117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Advanced glycosylation products quench nitric oxide and mediate defective endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in experimental diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):432–438. doi: 10.1172/JCI115014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong A. S., Van Kessel-van Vark M., Raap A. K. Sensitivity of various visualization methods for peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase activity in immunoenzyme histochemistry. Histochem J. 1985 Oct;17(10):1119–1130. doi: 10.1007/BF01002537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Vlassara H., Kirstein M., Yamada Y., Striker G. E., Striker L. J. Receptor-specific increase in extracellular matrix production in mouse mesangial cells by advanced glycosylation end products is mediated via platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2873–2877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito C., Gerlach H., Brett J., Stern D., Vlassara H. Endothelial receptor-mediated binding of glucose-modified albumin is associated with increased monolayer permeability and modulation of cell surface coagulant properties. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1387–1407. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes H. P., Martin S., Federlin K., Geisen K., Brownlee M. Aminoguanidine treatment inhibits the development of experimental diabetic retinopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11555–11558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Schmelzer J. D., Poduslo J. F., Curran G. L., Nickander K. K., Low P. A. Aminoguanidine effects on nerve blood flow, vascular permeability, electrophysiology, and oxygen free radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6107–6111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilzer P., Chang K., Marvel J., Rowold E., Jaudes P., Ullensvang S., Kilo C., Williamson J. R. Albumin permeation of new vessels is increased in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1985 Apr;34(4):333–336. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein M., Aston C., Hintz R., Vlassara H. Receptor-specific induction of insulin-like growth factor I in human monocytes by advanced glycosylation end product-modified proteins. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):439–446. doi: 10.1172/JCI115879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein M., Brett J., Radoff S., Ogawa S., Stern D., Vlassara H. Advanced protein glycosylation induces transendothelial human monocyte chemotaxis and secretion of platelet-derived growth factor: role in vascular disease of diabetes and aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9010–9014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita Z., Radoff S., Rayfield E. J., Yang Z., Skolnik E., Delaney V., Friedman E. A., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in patients with diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 19;325(12):836–842. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109193251202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita Z., Vlassara H., Cerami A., Bucala R. Immunochemical detection of advanced glycosylation end products in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5133–5138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meraji S., Jayakody L., Senaratne M. P., Thomson A. B., Kappagoda T. Endothelium-dependent relaxation in aorta of BB rat. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):978–981. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata S., Monnier V. Immunohistochemical detection of advanced glycosylation end products in diabetic tissues using monoclonal antibody to pyrraline. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1102–1112. doi: 10.1172/JCI115690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnier V. M., Kohn R. R., Cerami A. Accelerated age-related browning of human collagen in diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):583–587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Palinski W., Ylä-Herttuala S., Butler S., Witztum J. L. Distribution of oxidation specific lipid-protein adducts and apolipoprotein B in atherosclerotic lesions of varying severity from WHHL rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):336–349. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H., Brownlee M., Manogue K. R., Dinarello C. A., Pasagian A. Cachectin/TNF and IL-1 induced by glucose-modified proteins: role in normal tissue remodeling. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1546–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.3259727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Chang K., Tilton R. G., Prater C., Jeffrey J. R., Weigel C., Sherman W. R., Eades D. M., Kilo C. Increased vascular permeability in spontaneously diabetic BB/W rats and in rats with mild versus severe streptozocin-induced diabetes. Prevention by aldose reductase inhibitors and castration. Diabetes. 1987 Jul;36(7):813–821. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.7.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Makita Z., Horii Y., Brunelle S., Cerami A., Sehajpal P., Suthanthiran M., Vlassara H. Two novel rat liver membrane proteins that bind advanced glycosylation endproducts: relationship to macrophage receptor for glucose-modified proteins. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):515–524. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





