Abstract
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the major cause of cervical cancer, a deadly threat to millions of females. The early oncogene product (E7) of the high-risk HPV16 is the primary agent associated with HPV-related cervical cancers. In order to understand how E7 contributes to the transforming activity, we investigated the structural features of the flexible N-terminal region (46 residues) of E7 by carrying out N-15 heteronuclear NMR experiments and replica exchange molecular dynamics simulations. Several NMR parameters as well as simulation ensemble structures indicate that this intrinsically disordered region of E7 contains two transient (10-20% populated) helical pre-structured motifs that overlap with important target binding moieties such as an E2F-mimic motif and a pRb-binding LXCXE segment. Presence of such target-binding motifs in HPV16 E7 provides a reasonable explanation for its promiscuous target-binding behavior associated with its transforming activity. [BMB Reports 2016; 49(8): 431-436]
Keywords: E7 oncoprotein, Human papillomavirus (HPV), Intrinsically disordered protein (IDP), Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), Pre-structured motif (PreSMo)
INTRODUCTION
Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are the primary agents causing several types of cancers including cervical cancer, one of the leading causes of female death in developing countries. Even though anti-HPV vaccines became available (1), effective pharmaceuticals are still needed for those who have already developed an infection with HPV. Approximately 200 types of HPVs are known, and many of them are classified into high- or low-risk types based on their clinical prognosis (2). HPV16 is a high-risk alpha HPV, one of the most prevalent HPVs found in cervix carcinomas. Its genome encodes for 8 proteins among which two oncoproteins, E6 and E7, are known to be essential factors for the development of cancer by debilitating p53 (by E6) and functioning as retinoblastoma (pRb) tumor suppressor (by E7), respectively (3). E7 is known to be primarily responsible for the transforming activity, and is known to interact with diverse cellular targets (4, 5). This sort of promiscuity is observed in other viral proteins, including the X protein of hepatitis B virus (6). The reason for such promiscuity is not clearly understood.
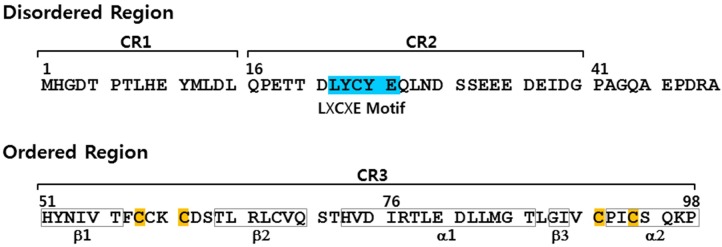
The E7 of HPV16 consists of 98 amino acid residues and is composed of three conserved regions (CRs), based on the homology with the adenovirus E1A protein (Fig. 1). Structurally, E7 has a flexible or disordered N-terminus and a well-structured C-terminal domain (7). The disordered N-terminal region contains two repeats, CR1 (residues 2-15) and CR2 (residues 16-41). The former interacts with several cellular targets such as p600, Skp2, p300, and IRF-1, and the latter with HPV E2, Rb1, FHL2, TBP, CKII, p300, HIF-1a, and p21 to name a few. The C-terminal structured domain contains CR3 (residues 54-95) which forms a zinc finger with a β1β2α1β3α2 topology (8, 9). Interestingly, E7 may form oligomers, depending upon solution conditions (10-13). Among various oligomers, the dimers are known to be the most prominent at physiological condition (11). Dimerization of E7 is believed to occur via the structured C-terminal domain (50-98) involving the α-helices of each monomer and an intermolecular antiparallel β-sheet between the β2 strand of one monomer and the β3 strand of the other (11).
Fig. 1. The primary sequence of HPV16 E7 oncoprotein is drawn with two conserved regions (CR1, CR2), L22XCXE26 motif (sky blue) that binds with the B-box of pRb, CR3 and two conserved Zn-binding motifs (C58XXC61, C91XXC94, Cys marked in yellow) within CR3. The boxes in CR3 indicate the secondary structures.
Proteins often contain short flexible linkers or disordered loops that are typically composed of less than 10-20 amino acid residues. This has been known as for decades as the phenomenon of protein disorder. A special case of protein disorder that has emerged since 1990s is intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs), which do not form a well-defined three-dimensional structure but are nonetheless functional (14). These unorthodox proteins are defined to contain at least one long (more than 40, and up to hundreds, of residues) intrinsically disordered region (IDR). An important point is that without relying on three dimensional structures, many IDPs and IDRs are responsible for specific biological functions such as transcription, translation, chaperoning, and cell cycle regulation (15), or causing diseases such as prion diseases, neurodegeneration, cancers and so on (16, 17). Several viral proteins in HIV, HBV, SARS virus, AI virus and MERS virus are IDPs (6, 18). The mechanism of how IDPs/IDRs perform biological functions or cause diseases is not well understood as yet.
Initially, IDPs/IDRs were thought to be completely unstructured with no observable secondary structures (19, 20). However, during the last two decades, useful information was obtained function from several NMR structural investigations that helps us understand how IDPs/IDRs. In contrast to the initial conjecture, these studies demonstrated that as many as three dozen IDPs/IDRs contain transient local structural elements or pre-structured motifs (PreSMos) in their target-unbound state, which mediates the binding of IDPs/IDRs with targets (15). Based upon the PreSMo concept, IDPs/IDRs can be classified into two types: the mostly unstructured (MU) type that contain PreSMos, and the completely unstructured (CU) type with absolutely no transient secondary structures that may represent true random coils. Currently, ∼80% of IDPs/IDRs are known to be the MU type. Since IDPs/IDRs cannot form a spatially disposed target-binding pocket found in globular proteins, they seem to utilize transiently-structured PreSMos that are primed for target binding in order to interact with targets (proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, metals, etc.).
One well-known characteristic of IDPs/IDRs is their promiscuity; IDPs can interact with many partners, in contrast to globular proteins. For example, the 73-residue intrinsically disordered N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD) of p53 contains three PreSMos which enable binding of p53 TAD to different targets (21-28). Since the N-terminal region of E7 is known to be disordered and interacts with many targets (4) we hypothesized that this IDR should contain at least one PreSMo. To test this hypothesis, we investigated the structural properties of the N-terminal region (residues 1-46) of HPV16 E7 oncoprotein (N-E7) by high resolution NMR spectroscopy combined with replica exchange molecular dynamics (REMD) simulation. Results indicate that N-E7 has two clear helical PreSMos and additional non-helical transient structures. Here, we discuss the ramifications of the presence of these PreSMos in terms of E7 function.
RESULTS
A fingerprint region of a 15N-1H heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) spectrum of N-E7 with assigned residues is shown in Fig. 2. The spectrum has narrow chemical-shift dispersion in both 15N and 1H dimensions, indicating that N-E7 does not form a globular structure under the non-denaturing experimental condition used (aqueous buffer at pH 6.5). Such an overall disordered nature of N-E7 is consistent with the results of the previous metal-free CD spectrum (11) and NMR experiments on N-E7 (29), and also with bioinformatics predictions (30). We achieved a full NMR resonance assignment for backbone 15N and amide protons of N-E7 by following the standard triple-resonance assignment procedure, except for 3 prolines which do not have backbone amide NH nitrogens and protons. Resonance assignment for N-E7 is summarized Table S1 (See Supplementary Information). The first two N-terminal residues of the recombinant N-E7, Met, and His originated from the N-terminal glutathione-S-transferase fusion linker. The level of achieved resonance assignment was sufficient for subsequent structural characterization of N-E7, in particular, for delineation of residues that form PreSMos.
Fig. 2. A fingerprint region in a 15N-1H HSQC spectrum of the N-terminal region of HPV16 E7 oncoprotein (N-E7) obtained at 10℃ and pH 6.5 on 90% H2O/10% D2O. The backbone 15N and amide of 43 residues out of 46 residues were assigned (3 proline residues without amide NH are not visible in this spectrum).
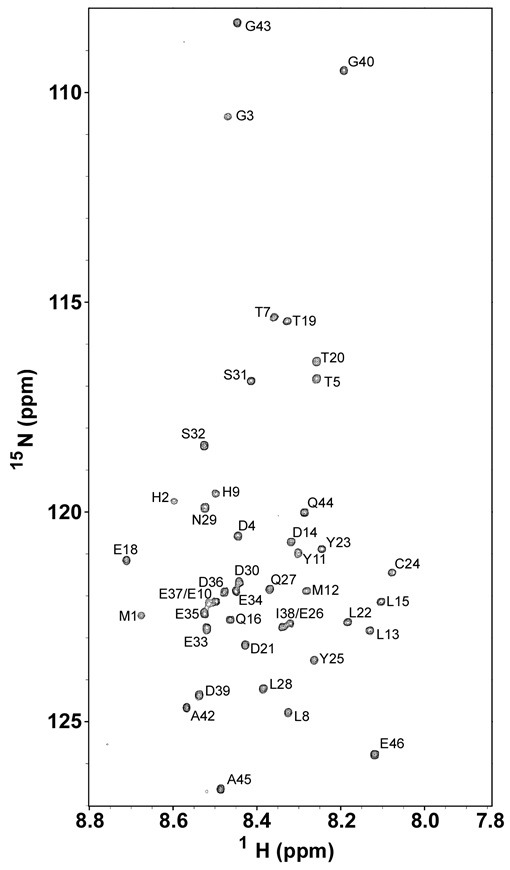
Fig. 3 shows the NMR parameters measured for N-E7. The left panel in Fig. 3 is the summary of chemical shifts and SSP (secondary structure propensity) scores. The SSP scores are obtained by combining various chemical shifts (Hα, Cα, Cβ) (31) and hence are often more informative in detecting PreSMos than individual chemical shifts. Positive SSP scores over 4 residues or more indicate the formation of a helix, whereas negative values suggest non-helical (β-type) secondary structures. Fig. 3D shows that N-E7 contains two helical PreSMos, one formed by residues 7-14 and the other by residues 20-26. The first is ∼10% pre-populated and the second ∼20%. Note that the first is an E2F mimic and the second PreSMo corresponds to the well-known Rb-binding LXCXE segment. The C-terminal portion (residues 30-46 in CR2) of N-E7 has a potential to form additional non-helical (β-type) PreSMos (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 3D). A recent prediction study on full E7 using the ANCHOR program also suggested similar helical PreSMos as potential target-binding segments (30). The location of two helical PreSMos in N-E7 is also visible by 1H–15N heteronuclear NOEs (Fig. 3E). Small positive 1H–15N heteronuclear NOEs (typically 0-0.5) are indicative of local pre-structuring (15). 1H–15N heteronuclear NOEs for stable secondary structures in globular proteins are 0.8-1.0, and large negative values indicate a highly flexible region. Small (< 5 ppb/K) backbone NH temperature coefficients (Fig. 3H) are evidence for formation of hydrogen bonds. Fig. 3H shows that helical PreSMos have 2 residues whose temperature coefficients are very small (down to 3 ppb/K), and additional 2-3 residues have values of ∼5.
Fig. 3. Left panel: deviation of (A) 1Hα, (B) 13Cα, (C) amide carbonyl chemical shifts from random coil values and (D) the SSP (secondary structure propensity) scores. In (D) positive scores indicate helical propensity while negative values suggest formation of non-helical type PreSMos. Right panel: 1H–15N heteronuclear NOEs (E), backbone 15N relaxation times, T1 (F), T2 (G), and temperature coefficients of the backbone amide hydrogens (H). The horizontal lines in (F) and (G) indicate an average value.
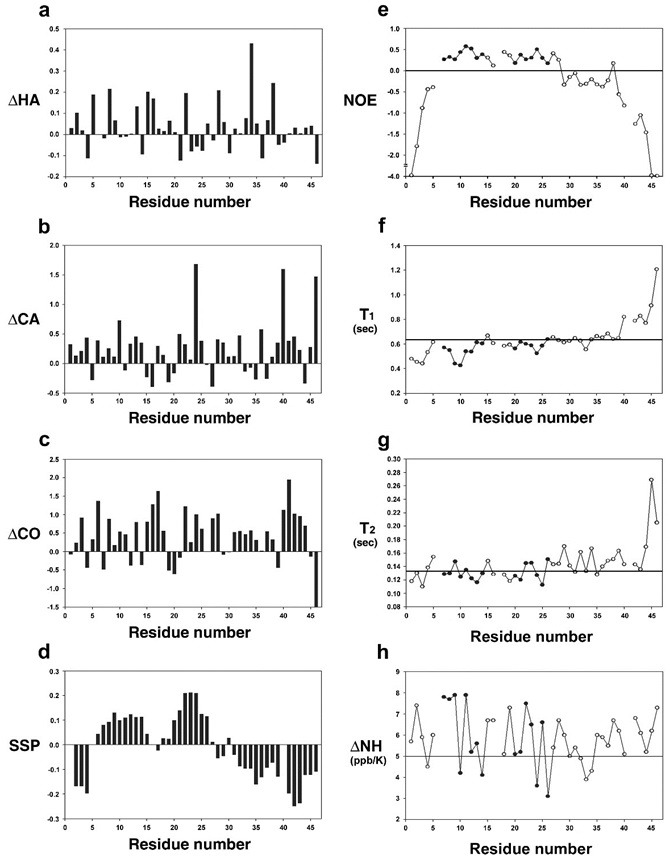
Note that the residues 33-34, potentially forming non-helical transient structures suggested by the SSP scores, also have small temperature coefficients. Presence of non-helical transient structures was noted in a previous 13C-based NMR study which used a similar-sized N-terminal fragment (residues 1-40) of E7 (29). This 13C-HMQC based NMR study concluded that two helical PreSMos were formed by residues 8-13 and 17-29, which was slightly different from our results. Also, the degree of pre-population for the two helical PreSMos was reported to be less than 5%, which is in clear contrast to what we observe. Furthermore, this study used as much as 50% of a helix-inducing solvent (trifluoroethanol, TFE) in order to enhance the visibility of helical segments. By definition, PreSMos are the transient structures detected in aqueous solution (15). Almost all NMR studies on IDPs/IDRs used N-15 isotope labeled proteins under aqueous solutions. In the early days of IDP research, some investigators employed hydrophobic solvents in order to make “expected” helices clearly visible in NMR measurements (32, 33); however, the helices observed in such a manner are not accepted as PreSMos (15). Hence, it is not clear how reliable the previous C-13 NMR results are in terms of characterizing PreSMos.
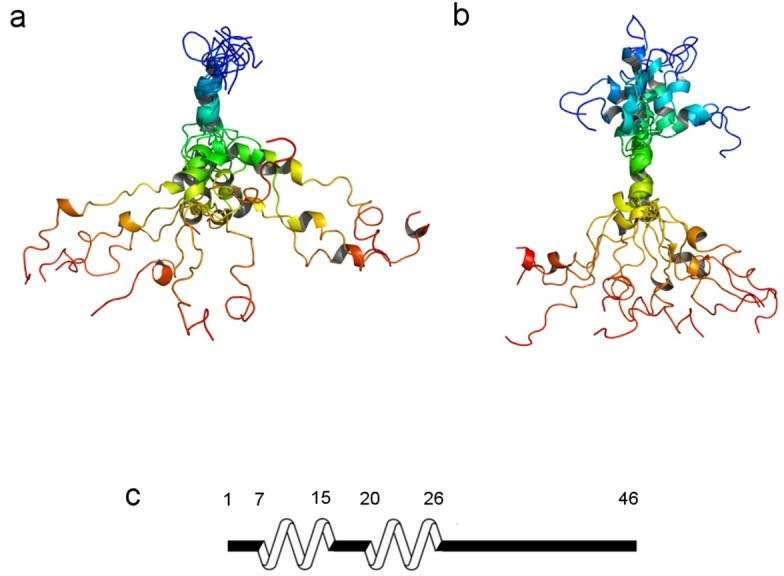
In order to augment the results of NMR measurements, we undertook REMD simulations on N-E7. After performing clustering analysis for the temperature trajectories, ensemble structures of highly-populated 10 clusters in each temperature trajectory were collected. In order to check the extent of agreement between the computed ensemble structures and the structures suggested by NMR data, the Hα chemical shifts calculated from the ensemble structures by Shift-X program (34) were compared with the experimentally measured NMR chemical shifts. Using this consistency check procedure, we obtained the structural ensembles of N-E7 that showed a high Pearson’s correlation (PC) with experimental results (PC coefficient > 0.65). The final ensemble structures of N-E7 possess two helical PreSMos; one is pre-populated at ∼15% and is formed by residues 3-15 which covers the most part of CR1, and the other is formed by residues 17-30 and is ∼10% pre-populated and encompasses the N-terminal half of CR2. Thus, the two calculated helical PreSMos by REMD are slightly longer than the ones detected by NMR, i.e., one with residues 7-14 and the other with 20-26. Combining NMR and REMD results we conclude that two helical PreSMos in N-E7 are formed by the residues 7-14 and by 20-26, which are common denominators suggested by both techniques. Fig. 4 shows two ensemble structures of N-E7. The left panel is an ensemble superimposed along the first helical PreSMo (residues 7-14), whereas the left panel displays an ensemble superimposed along the second helical PreSMo (residues 20-26). The residues 7-14 and 20-26 in the REMD ensembles are pre-populated at the level of ∼20% and ∼11%, respectively.
Fig. 4. Two REMD ensembles of N-E7. The left (A) is generated by aligning the residues 7-14 that form the first helical PreSMo. The right (B) is an ensemble generated by superimposing the second helical PreSMo. All ensemble structures showed a high correlation with the SSP scores from NMR experiments (PCC > 0.65, See Materials and Methods Section). Shown at the bottom (C) is a schematic diagram showing the location of two helical PreSMos suggested by both NMR and REMD simulations. The structures are color-coded from the N- to the C-terminus (blue→green→yellow→brown).
DISCUSSION
Currently, the high resolution heteronuclear multidimensional NMR spectroscopy is the best tool providing the exact location of PreSMos in IDPs/IDRs. The PreSMos are transient secondary structures detected by NMR in aqueous solutions, without using secondary structure-inducing hydrophobic solvents such as TFE. They are increasingly being acknowledged as the putative target-binding active sites in IDPs/IDRs (35, 36). Presence of PreSMos in IDPs is accepted well in recent years, especially after it was succinctly demonstrated by our laboratory three years ago that PreSMos are present in 3 dozens of MU type IDPs/IDRs (16). However, their existence in the target-free states of IDPs/IDRs was mostly ignored in the 1990s when the concept of IDPs was barely being conceived, and experimental techniques used for characterization of IDPs/IDRs, e.g., CD spectropolarimetry, gel electrophoresis, did not provide detailed per-residue structural information on IDPs/IDRs. Some early NMR reports failed to acknowledge the existence of PreSMos due to the fleeting or transient nature of PreSMos, misleading the IDP field (19, 20, 32). In fact, none of the PreSMos discovered so far are 100% pre-populated. An average pre-population of PreSMos is ∼30% (± 10). Recently, Flexible-Meccano calculations in combination with NMR parameters are possible, and show explicit distribution of different conformer populations within a structural ensemble of IDPs/IDRs (37). In using NMR parameters to characterize PreSMos, it is important to combine several parameters before a conclusion is drawn on the existence of PreSMos since employing one parameter often fails to unambiguously point to the presence of a PreSMo due to their transient nature. In some MU type IDPs/IDRs such as 4EBP1, p53TAD, and HIV-1 Nef, the existence of PreSMos is very clearly recognized. In other cases, detecting PreSMos in synucleins and preS1 of hepatitis B virus was not so straightforward (15). The N-E7 seems to belong to a latter type.
Due to its structural flexibility, it has not been straightforward to obtain the detailed structural picture of the N-terminal disordered region of E7. Attempts to understand the role of the disordered N-terminal region of E7 were made by bioinformatics analyses using various independent disorder prediction programs; it suggested that the N-terminal region of HPV16 E7 was not entirely disordered (30). In consistent with such prediction results, our investigation, together with the previous CD and NMR studies, show that the N-terminal half of E7, either N-E7 (this study) or the 40-residue N-terminal fragment (29), is disordered and contains two helical PreSMos that mediate binding of N-E7 with partners; the first PreSMo is an E2F-mimic motif and the second encompasses the LXCXE motif allowing the binding of E7 with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein, pRB (38). We conclude that the N-terminal half of E7 displays promiscuity using its multiple PreSMos. The full E7 oncoprotein is therefore a hybrid type IDP resembling a prion protein, where an N-terminal disordered region coexists with a C-terminal globular domain. An abnormal behavior in the electrophoretic behavior of E7 was noticed in an earlier study and was explained in terms of general charge effects (11). With the knowledge that the full-length E7 is a hybrid type IDP, we propose that the abnormal electrophoretic behavior of E7 should be ascribed to its disordered N-terminus since IDPs are known to behave atypically in gel electrophoresis or in gel permeation chromatography eluting at a position corresponding to a larger protein (39).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Detailed experimental and computational procedures are described in Supplementary Information.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Korea-Hungary Joint Lab Program from National Research Council of Science and Technology (NST) (NTC2251422) of Korea (to KH), and by National Research Foundation (NRF, RBM4421112) (to KH). The computing resources were supported by the strategic support program of Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI, KSC-2012-C3-052).
References
- 1.Frazer I. Vaccines for papillomavirus infection. Virus Res. (2002);89:271–274. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1702(02)00195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Roman A, Munger K. The papillomavirus E7 proteins. Virology. (2013);445:138–168. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Meyers J, Munger K. Cancer associated human papillomaviruses. Curr Opin Virol. (2012);2:459–466. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chemes LB, Glavina J, Faivovich J, de Prat-Gay G, Sanchez IE. Evolution of linear motifs within the papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. J Mol Biol. (2012);422:336–346. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.05.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Munger K, Basile JR, Duensing S, et al. Biological activities and molecular targets of the human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. Oncogene. (2001);20:7888–7898. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee SH, Cha EJ, Lim JE, et al. Structural characterization of an intrinsically unfolded mini-HBX protein from hepatitis B virus. Mol Cells. (2012);34:165–169. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-0060-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Garcia-Alai MM, Alonso LG, de Prat-Gay G. The N-terminal module of HPV16 E7 is an intrinsically disordered domain that confers conformational and recognition plasticity to the oncoprotein. Biochemistry. (2007);46:10405–10412. doi: 10.1021/bi7007917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liu X, Clements A, Zhao K, Marmorstein R. Structure of the human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein and its mechanism for inactivation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. J Biol Chem. (2005);281:578–586. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508455200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ohlenschlager O, Seiboth T, Zengerling H, et al. Solution structure of the partially folded high-risk human papilloma virus 45 oncoprotein E7. Oncogene. (2006);25:5953–5959. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Todorovic B, Massimi P, Hung K, Shaw GS, Banks L, Mymryk JS. Systematic analysis of the amino acid residues of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 conserved region 3 involved in dimerization and transformation. J Virol. (2011);85:10048–10057. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00643-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Alonso LG, García-Alai MM, Nadra AD, et al. High-risk (HPV16) human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein is highly stable and extended, with conformational transitions that could explain its multiple cellular binding partners. Biochemistry. (2002);41:10510–10518. doi: 10.1021/bi025579n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Clements A, Johnston K, Mazzarelli JM, Ricciardi RP, Marmorstein R. Oligomerization properties of the viral oncoproteins adenovirus E1A and human papillomavirus E7 and their complexes with the retinoblastoma protein. Biochemistry. (2000);39:16033–16045. doi: 10.1021/bi002111g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alonso LG, García-Alai MM, Smal C, et al. The HPV16 E7 viral oncoprotein self-assembles into defined spherical oligomers. Biochemistry. (2004);43:3310–3317. doi: 10.1021/bi036037o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dunker AK, Babu MM, Barbar E, et al. What’s in a name? Why these proteins are intrinsically disordered. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. (2013);1:e24157. doi: 10.4161/idp.24157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee S-H, Kim D-H, Han JJ, et al. Understanding pre-structured motifs (PreSMos) in intrinsically unfolded proteins. Curr Protein Pept Sci. (2012);13:34–54. doi: 10.2174/138920312799277974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Uversky VN, Oldfield CJ, Dunker AK. Intrinsically disordered proteins in human diseases: Introducing the D2 concept. Ann Rev Biophys. (2008);37:215–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.125924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.James TL, Liu H, Ulyanov NB, et al. Solution structure of a 142-residue recombinant prion protein corresponding to the infectious fragment of the scrapie isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1997);94:10086–10091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xue B, Blocquel D, Habchi J, et al. Structural disorder in viral proteins. Chem Rev. (2014);114:6880–6911. doi: 10.1021/cr4005692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Radhakrishnan I, Pérez-Alvarado GC, Parker D, Dyson HJ, Montminy MR, Wright PE. Solution structure of the KIX domain of CBP bound to the transactivation domain of CREB: A model for activator:coactivator interactions. Cell. (1997);91:741–752. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80463-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fletcher CM, Wagner G. The interaction of eIF4E with 4E-BP1 is an induced fit to a completely disordered protein. Protein Sci. (1998);7:1639–1642. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560070720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.De Guzman RN, Wojciak JM, Martinez-Yamout MA, Dyson HJ, Wright PE. CBP/p300 TAZ1 domain forms a structured scaffold for ligand binding. Biochemistry. (2005);44:490–497. doi: 10.1021/bi048161t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Di Lello P, Jenkins LMM, Jones TN, et al. Structure of the Tfb1/p53 complex: Insights into the interaction between the p62/Tfb1 subunit of TFIIH and the activation domain of p53. Mol Cell. 2006;22:731–740. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rowell JP, Simpson KL, Stott K, Watson M, Thomas JO. HMGB1-facilitated p53 DNA binding occurs via HMG-Box/p53 transactivation domain interaction, regulated by the acidic tail. Structure. (2012);20:2014–2024. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ha J-H, Shin J-S, Yoon M-K, et al. Dual-site interactions of p53 protein transactivation domain with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins reveal a highly convergent mechanism of divergent p53 pathways. J Biol Chem. (2013);288:7387–7398. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee CW, Martinez-Yamout MA, Dyson HJ, Wright PE. Structure of the p53 transactivation domain in complex with the nuclear coactivator binding domain of CBP. Biochemistry. (2010);49:9964–9971. doi: 10.1021/bi1012996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bochkareva E, Kaustov L, Ayed A, et al. Single-stranded DNA mimicry in the p53 transactivation domain interaction with replication protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2005);102:15412–15417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504614102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee H, Mok KH, Muhandiram R, et al. Local structural elements in the mostly unstructured transcriptional activation domain of human p53. J Biol Chem. (2000);275:29426–29432. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003107200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chi S-W, Lee S-H, Kim D-H, et al. Structural details on mdm2-p53 interaction. J Biol Chem. (2005);280:38795–38802. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508578200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Noval MG, Gallo M, Perrone S, Salvay AG, Chemes LB, de Prat-Gay G. Conformational dissection of a viral intrinsically disordered domain involved in cellular transformation. PLoS One. (2013);8:e72760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nicolau-Junior N, Giuliatti S. Modeling and molecular dynamics of the intrinsically disordered e7 proteins from high- and low-risk types of human papillomavirus. J Mol Model. (2013);19:4025–4037. doi: 10.1007/s00894-013-1915-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marsh JA, Singh VK, Jia Z, Forman-Kay JD. Sensitivity of secondary structure propensities to sequence differences between α- and γ-synuclein: Implications for fibrillation. Protein Sci. (2006);15:2795–2804. doi: 10.1110/ps.062465306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.O’Hare P, Williams G. Structural studies of the acidic transactivation domain of the Vmw65 protein of herpes simplex virus using 1H NMR. Biochemistry. (1992);31:4150–4156. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dahlman-Wright K, Baumann H, McEwan IJ, et al. Structural characterization of a minimal functional transactivation domain from the human glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1995);92:1699–1703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Neal S, Nip AM, Zhang H, Wishart DS. Rapid and accurate calculation of protein 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shifts. J Biomol NMR. (2003);26:215–240. doi: 10.1023/A:1023812930288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim D-H, Lee C, Cho Y-J, et al. A pre-structured helix in the intrinsically disordered 4EBP1. Mol BioSyst. (2015);11:366–369. doi: 10.1039/C4MB00532E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Borcherds W, Theillet F-X, Katzer A, et al. Disorder and residual helicity alter p53-Mdm2 binding affinity and signaling in cells. Nat Chem Biol. (2014);10:1000–1002. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schneider R, Huang JR, Yao M, et al. Towards a robust description of intrinsic protein disorder using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Mol Biosyst. (2012);8:58–68. doi: 10.1039/C1MB05291H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Iesmantavicius V, Dogan J, Jemth P, Teilum K, Kjaergaard M. Helical propensity in an intrinsically disordered protein accelerates ligand binding. Angew Chem Int Ed. (2014);53:1548–1551. doi: 10.1002/anie.201307712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Csizmók V, Szőllősi E, Friedrich P, Tompa P. A novel two-dimensional electrophoresis technique for the identification of intrinsically unstructured proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2006);5:265–273. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M500181-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]