Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short single-stranded non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression, particularly during development. In this study, 345 miRNAs were identified from the English green aphid, Sitobion avenae (F.), of which 168 were conserved and 177 were S. avenae-specific. Quantitative comparison of miRNA expression levels indicated that 16 and 12 miRNAs were significantly up-regulated in winged and wingless S. avenae small RNA libraries, respectively. Differential expression of these miRNAs was confirmed by real-time quantitative RT-PCR validation. The putative transcript targets for these candidate miRNAs were predicted based on sequences from a model species Drosophila melanogaster and four aphid species Acyrthosiphon pisum, Myzus persicae, Toxoptera citricida, and Aphis gosspii. Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway analyses shed light on the potential functions of these miRNAs in the regulation of genes involved in the metabolism, development and wing polyphenism of S. avenae.
The transcription of tRNAs, rRNAs and mRNAs have long been known to function in the central dogma of synthesizing functional proteins from nucleic acid information, but a large class of initially characterized non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) may play important roles in regulating the expression of protein coding genes. Nucleic acid-protein complexes perform an array of crucial cellular functions. For example, the U1 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) functions to regulate transcription initiation1, the spliceosome guides intron splicing activities2, and the ribosome facilitates protein synthesis from mRNA templates3. This known cellular repertoire of functional RNAs has expanded. Specifically, RNA interference (RNAi) pathway involves the use of short anti-sense guide RNAs bound to the protein Argonaut within the RNA Inducing Silencing Complex (RISC) which binds the sense strand of cellular RNA thereby targeting them for degradation by the endonuclease Dicer. These short guide RNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), are derived from the degradation of dsRNAs and short hairpin RNAs by Dicer. Although entering a unified pathway, miRNAs and siRNAs carry out different functions by respectively regulating endogenous gene expression and degrading invading foreign RNAs4. The biogenesis of miRNAs occur from secondary structure elements formed by transcribed ncRNAs as well as stem-loops formed by spliced intron and gene encoding transcripts themselves, and are collectively termed primary RNAs (pri-RNAs). These pri-RNAs are cleaved into shorter 70 base hairpin precursor RNAs (pre-RNAs) within the nucleus by the ribonuclease III, Drosha, in complex with the RNA binding protein, Pasha5. Pre-RNAs are also known to be generated directly from spliced intronic RNAs called mirtrons6. Following transport into the cytoplasm, pre-RNA terminal loops are cleaved by the ribonuclease, Dicer, to form a short 21 to 22 bp miRNA product with a 2 nucleotide overhang. The degradation of the passenger strand generates a functional ssRNA guide within the RISC complex7.
The miRNA guide stand directs the RISC complex by imperfect complementary base pairing mainly to 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of target mRNAs, as well as to 5′ UTRs and exons8. Despite the relaxed complementarity allowed along the 21 to 22 bp of the guide RNA/target RNA duplex, a near perfect match is required in the “seed” region located from positions 2 to 7 of the guide miRNA is believed to be involved in target specificity9. This miRNA-mediated binding of RISC is speculated to result in post-transcriptional repression by mRNA degradation, translational repression by blocking initiation factor binding, inhibition of elongation factor progression, or causing premature termination10. In contrast, miRNAs can upregulate gene transcription by potentially reversing the effects of repressive miRNAs11. Studies have demonstrated that miRNAs regulate a large fraction of mammalian protein-coding gene12, such that miRNAs may be key mediators in a range of developmental and physiological pathways including embryonic development13, tissue differentiation and apoptosis14, cell proliferation15, and morphogenesis16.
Studies have also shown that miRNAs are regulators of pattern formation necessary for insect wing development. Specifically, the Bantam miRNA guide directs RISC for targeted degradation of mRNAs for the gene enabled, the latter of which is required for pattern formation during Drosophila melanogaster development. Bantam miRNA levels are in turn repressed in wing imaginal discs by the expression of Notch, which subsequently alleviates repression of Enabled and leads to the formation of doral-ventral polarity in developing embryos17. Within wing imaginal discs of these developing D. melanogaster embryos, the Let-7 miRNA directs the specific timing of cellular division18. Indeed, the depletion of Let-7 and miR-100 reduced wing size and generated malformed vein patterning in the German cockroach, Blattella germanica19. Analogously, the loss-of -function miR-9a mutant leads to wing malformations due to dysregulation of the number of neuronal precursor cells during Drosophila development20. Surridge and colleagues21 also described the specific expression of miR-193 and miR-2788 between 24 and 72 hours post-pupation in the postman butterfly, Heliconius melpomene, and suggested their potential role in wing development. The two insulin receptors, InR1 and InR2, were suggested to regulate the development of alternative wing morphs in the migratory brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens22. In the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, comparisons of miRNA abundance among parthenogenetic females producing parthenogenetic females (virginoparae), parthenogenetic females producing sexual individuals (sexuparae), and sexual females only (oviparae), showed a phase-specific expression of miRNAs16.
The grain aphid, Sitobion avenae (F.), is a destructive pest of wheat crops that is distributed worldwide. Adults show two different morphological variants, winged and wingless that exists among clonal genetically-identical individuals produced from parthenogenic females. This polyphenism is observed in response to the environment, and results in isogenic offspring in the subsequent generation showing difference in wing development23. In this study, high-throughput sequencing was performed on short RNA libraries constructed from winged and wingless adults, from which we aim to detect and quantify the levels of these putative miRNAs in the S. avenae, as well as identify potential regulatory effect by target transcripts involved in wing development in S. avenae. These findings suggest that a specific set of miRNAs are potentially involved in regulating genes that direct wing development and provide resources for future hypothesis-driven research.
Results
RNA isolation, small RNA library construction and Illumina sequencing
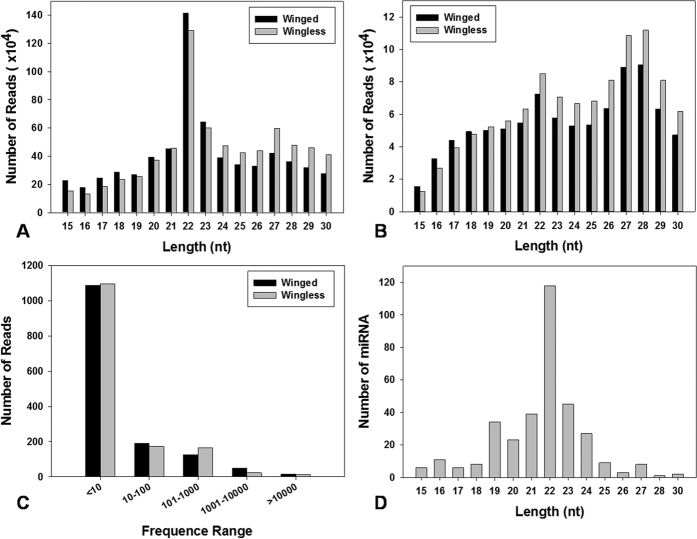
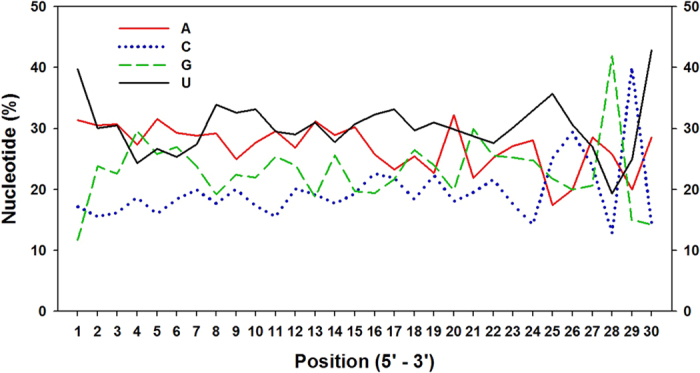
A total of 13,760,466 and 15,594,991 raw reads were obtained from winged and wingless sRNA libraries, respectively. The lengths of S. avenae sRNAs ranged from 10 nt to 30 nt, with 22 nt size comprising 21.63% and 18.58% of the total reads from winged and wingless libraries, respectively (Fig. 1A). After filtering out adapter and low quality sequences, and removal of rRNAs, tRNAs, snRNAs and snoRNAs, and repeat regions, 887,980 (49.95% of total) and 1,033,351 (50.02%) unique reads, respectively, remained from winged and wingless libraries (Table 1). In both libraries, the length distribution of unique filtered reads showed a bimodal distribution (Fig. 1B), wherein the peak at 22 nt constituted 8% of the total reads. A second size class was observed at the 27–28 nt size range (20%) which likely might represent S. avenae piRNA-like sRNAs. Furthermore, a small number of sRNAs had more than a thousand reads, whereas the majority had fewer than ten copies in the library (Fig. 1C). Sitobion avenae sRNAs exhibited a strong bias for the nucleotide U at 5′ (39.73%) and 3′ ends (42.86%), and a paucity of G at 5′ end (11.7%; Fig. 2).
Figure 1. Characterization of small RNA sequences from S. avenae deep sequencing.
Length distribution of raw reads (A) and mappable reads (B), distribution of frequencies on read counts (C) and number distribution of small miRNAs (D).
Table 1. Distribution of miRNA reads from winged and wingless S. avenae.
| Parameter | Winged | % | Wingless | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw reads | 13,760,466 | 100 | 15,594,991 | 100 |
| 3ADT and length filter | 769,767 | 43.3 | 911,013 | 44.1 |
| Short reads | 12,324 | 0.69 | 14,883 | 0.72 |
| Rfam | 104,957 | 5.9 | 104,038 | 5.04 |
| Repeats | 6,097 | 0.34 | 5,139 | 0.25 |
| rRNA | 42,852 | 0.31 | 46,219 | 0.3 |
| tRNA | 29,186 | 0.21 | 28,230 | 0.18 |
| snoRNA | 6,613 | 0.05 | 5,584 | 0.04 |
| snRNA | 7,070 | 0.05 | 6,371 | 0.04 |
| Other Rfam RNA | 19,236 | 0.14 | 17,634 | 0.11 |
| Mappable reads | 887,980 | 49.95 | 1,033,351 | 50.02 |
3ADT: reads removed due to 3ADT not found and length with <15 nt and >30 nt were removed.
Short reads: >=2N, >=7A, >=8C, >=6G, >=7T, >=10Dimer, >=6Trimer, or >=5Tetramer (N is undetermined nucleotide).
Rfam: Collection of many common non-coding RNA families except micro RNA.
Repeats: Prototypic sequences representing repetitive DNA from different eukaryotic species.
Mappable reads: reads that were passed through a series of the digital filters from the raw reads.
Figure 2. Nucleotide bias of predicated S. avenae miRNAs.
Sequence analysis and miRNA predication
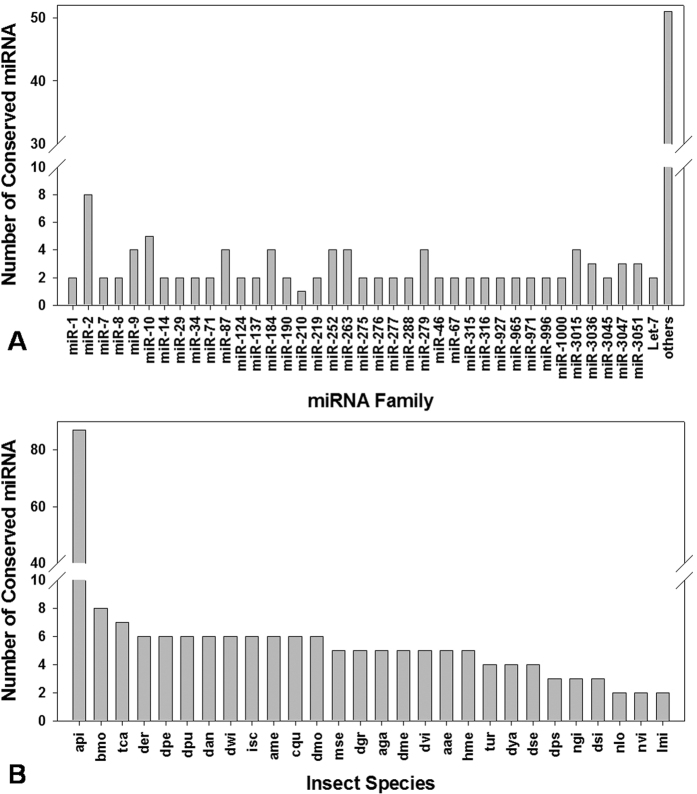
Based on the read length distribution, 22 nt-long miRNAs represented ~34% of the total miRNA species within sRNA libraries (Fig. 1D). Queries of these putative S. avenae miRNA reads against the A. pisum genomes and all insect miRNAs in miRBase resulted in the identification of 168 conserved sequences (Table S1). Additionally, the query of filtered S. avenae reads to the collection of mature miRNAs in the miRBase database identified 39 conserved miRNA sequence families (Fig. 3A). The miR-2 family was predicted to contain the most family members (n = 8), followed by miR-10 (n = 5), and miR-87, -184, -252, -263, -279, -9, -3015 (n = 4). These conserved miRNAs were shared across insects, with the majority being shared with known miRNAs from A. pisum, and a lesser extent towards putative orthologs from other insects (Fig. 3B). These results suggest that the seed region of mature miRNA sequences (base positions 2 to 8 from the 5′ end) are highly conserved across insects, whereas the 3′ tail and central nucleotide positions tend to be more divergent. For example, Let-7 and miR-7, comparatively, shares identical seed sequences across all insects (Fig. S1; Fig. S2).
Figure 3. Characterization of conserved S. avenae miRNAs.
(A) Number of identified conserved miRNAs in each miRNA family; (B) conservation profile of identified miRNAs in insect species. api: Acyrthosiphon pisum; bmo: Bombyx mori; tca: Tribolium castaneum; der: Drosophila erecta; dpe: Drosophila persimilis; dan: Drosophila ananassae; dwi: Drosophila will; isc: Ixodes scapularis; ame: Apis mellifera; cqu: Culex quinquefasciatus; dmo: Drosophila mojavensis; mse: Manduca sexta; dgr: Drosophila grimshawi; aga: Anopheles gambiae; dme: Drosophila melanogaster; dvi: Drosophila virilis; aae: Aedes aegypti; hme: Heliconius Melpomene; tur: Tetranychus urticae; dya: Drosophila yakuba; dse: Drosophila sechellia; ngi: Nasonia giraulti; dsi: Drosophila simulans; nlo: Nasonia longicornis; nvi: Nasonia vitripennis; lmi: Locusta migratoria.
A total of 177 potentially novel miRNAs were also identified and given the prefix ‘PC’ (predicted candidate) in the nomenclature we adopted (Table S2). These putatively S. avenae specific miRNAs were mapped to the A. pisum genome sequences in spite of having no detectable homology to any known insect pre-miRNAs in miRBase. Results from Mfold predicted that all S. avenae miRNAs precursor sequences form stem-loop hairpin secondary structures (≤18 kcal/mole24), and a subset of these predicted structures are shown (Fig. S3).
Differential miRNA expression between winged and wingless morphs
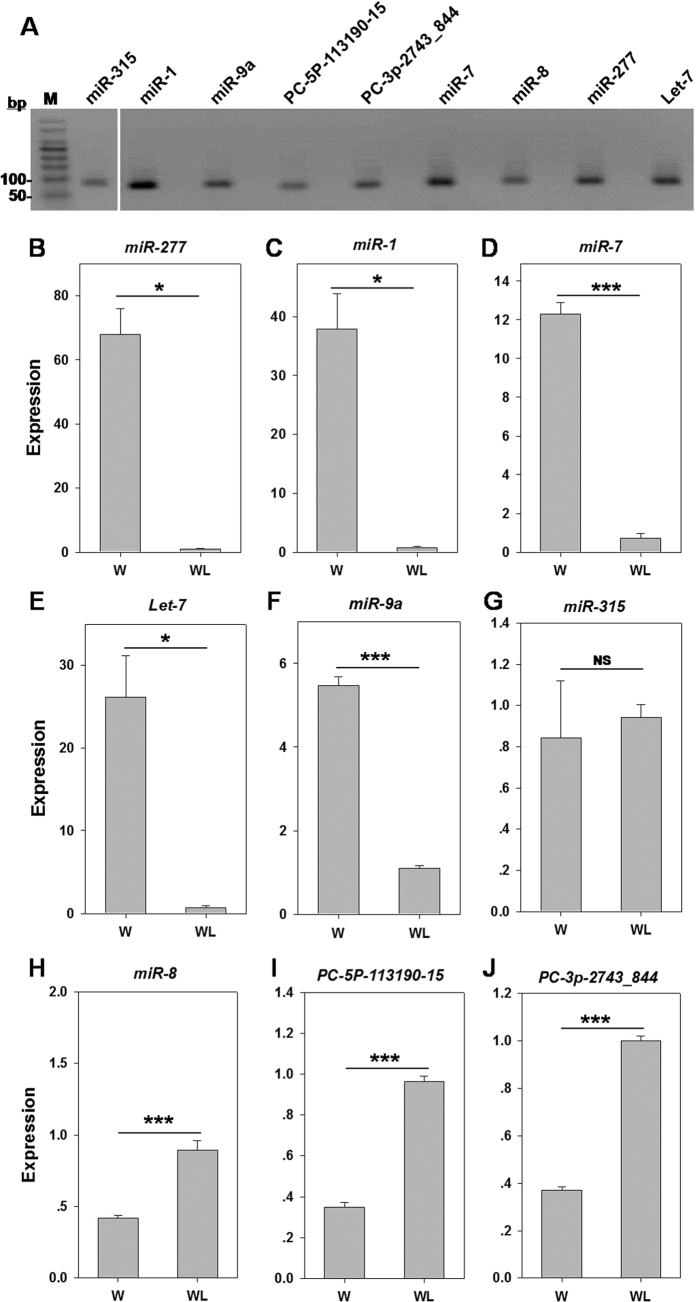
Based on normalized differences in Illumina read counts, 28 out of 345 S. avenae miRNAs (8.5%) showed significant differences in their expression level between winged and wingless morphs, including 12 up-regulated and 16 down-regulated miRNAs (Table 2). The RT-PCR amplified products for seven conserved miRNAs (Let-7, miR-1, miR-7, miR-277, miR-8, miR-9a and miR-315) and two novel miRNAs (PC-5p-113190_15 and PC-3p-2743_844) showed a single band in the expected size (60–100 bp) (Fig. 4A and S4). Subsequent analysis of real-time RT-qPCR results confirmed that the expression of five miRNAs were significantly lower in wingless compared to winged S. avenae. The highest RT-qPCR Log2 fold-changes were observed in miR-277 and miR-1 that respectively showed reductions amongst wingless adults of 73.2- (Fig. 4B) and 47.5-fold (Fig. 4C). Similarly, the expression of miR-7, Let-7, and miR-9a were 17.1-, 36.5-, 4.9- fold lower in wingless adults, respectively (Fig. 4D–F). In contrast, miR-8, PC-5p-113190_15, and PC-3p-2743_844 were up-regulated in wingless adults (Fig. 4H–J). All the above comparisons were significant (P ≤0.036), only miR-315 showed no significant difference between the two morphs (t = −0.60, P = 0.58) (Fig. 4G). Overall, RT-qPCR results were consistent with RNA-seq analyses, except miR-9a. Although the fold changes of their expression level were different, the trend was, for the most miRNAs, the same.
Table 2. The different expression of miRNAs in S.avenae small RNA libraries.
| miR_Name | Norm. Reads |
P-value | FC (WL/W) | Log2 (FC) | WL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WL | W | |||||
| PC-3p-94006_17 | 1 | 21 | 6.66E − 05 | 21.00 | −4.39 | down |
| sav-mir-100-p3 | 1 | 11 | 7.31E − 03 | 11.00 | −3.46 | down |
| PC-3p-420630_4 | 1 | 9 | 1.91E − 02 | 9.00 | −3.17 | down |
| sav-miR-277# | 2863 | 24006 | 0.00E + 00 | 8.38 | −3.07 | down |
| PC-5p-113190_15# | 19 | 3 | 2.15E − 04 | 6.33 | 2.66 | up |
| sav-miR-996 | 3 | 13 | 2.37E − 02 | 4.33 | −2.12 | down |
| sav-miR-100 | 3107 | 11992 | 0.00E + 00 | 3.86 | −1.95 | down |
| sav-let-7# | 1895 | 6399 | 0.00E + 00 | 3.38 | −1.76 | down |
| PC-3p-131984_11 | 22 | 8 | 3.83E − 03 | 2.75 | 1.46 | up |
| PC-3p-40838_47 | 9 | 21 | 4.80E − 02 | 2.47 | −1.30 | down |
| sav-miR-1# | 337 | 802 | 5.91E − 32 | 2.38 | −1.25 | down |
| sav-mir-3031-p5 | 35 | 16 | 1.95E − 03 | 2.19 | 1.13 | up |
| sav-mir-3020-p3 | 17 | 8 | 3.52E − 02 | 2.13 | 1.09 | up |
| PC-3p-66379_27 | 32 | 16 | 6.28E − 03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | up |
| sav-miR-278 | 1097 | 2118 | 2.06E − 48 | 1.93 | −0.95 | down |
| sav-miR-3030 | 26 | 14 | 2.24E − 02 | 1.86 | 0.89 | up |
| sav-miR-210 | 141 | 253 | 8.49E − 06 | 1.79 | −0.84 | down |
| PC-3p-80125_21 | 22 | 13 | 4.82E − 02 | 1.76 | 0.82 | up |
| PC-3p-2743_844# | 622 | 357 | 3.05E − 25 | 1.74 | 0.80 | up |
| sav-mir-3033-p5 | 33 | 57 | 4.99E − 02 | 1.73 | −0.79 | down |
| sav-miR-92a | 362 | 622 | 1.48E − 10 | 1.72 | −0.78 | down |
| sav-mir-92a-1-p5 | 39 | 66 | 4.34E − 02 | 1.69 | −0.76 | down |
| sav-mir-316-p3 | 205 | 123 | 1.78E − 08 | 1.67 | 0.74 | up |
| sav-miR-3041 | 85 | 54 | 8.15E − 04 | 1.57 | 0.65 | up |
| sav-miR-124 | 1541 | 2398 | 4.47E − 23 | 1.56 | −0.64 | down |
| sav-miR-2765 | 545 | 351 | 9.94E − 17 | 1.55 | 0.63 | up |
| sav-miR-92b | 3549 | 5381 | 6.21E − 43 | 1.52 | −0.60 | down |
| sav-miR-3016 | 159 | 105 | 1.61E − 05 | 1.51 | 0.60 | up |
| sav-miR-315# | 2717 | 1857 | 1.06E − 63 | 1.46 | 0.55 | up* |
| sav-miR-9a# | 1177 | 1084 | 1.31E − 06 | 1.09 | 0.12 | up* |
| sav-miR-8# | 15752 | 14611 | 1.58E − 66 | 1.08 | 0.11 | up* |
| sav-miR-7# | 3489 | 3284 | 7.08E − 14 | 1.06 | 0.09 | up* |
W and WL respectively for winged and wingless morphs; FC = Fold-change; *The expression of these miRNAs showed no significance difference between winged and wingless S.avenae; #RT- qPCR validation.
Figure 4. RT-qPCR validation of miRNAs potentially involved in S. avenae wing development.
(A) cDNAs from the winged S. avenae were used for template. Lane 1: 100 bp ladder marker; Lane 2: miR-315; Lane 4: miR-1; Lane 6: miR-9a; Lane 8: PC-5p-113190_15; Lane 10: PC-3p-2743_844; Lane 12: miR-7; Lane 14: miR-8; Lane 16: miR-277; Lane 18: Let-7. The other uneven lanes were negative controls for each target miRNA. The relative miRNA expression, including miR-277 (B), miR-1 (C), miR-7 (D), Let-7 (E), miR-9a (F), miR-315 (G), miR-8 (H), PC-5p-113190_15 (I), and PC-3p-2743_844 (J) at two wing morph was normalized to the wingless adult. W: winged adult; WL: wingless adult. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Full-length gel is presented in Supplementary Figure S4.
MicroRNA target prediction
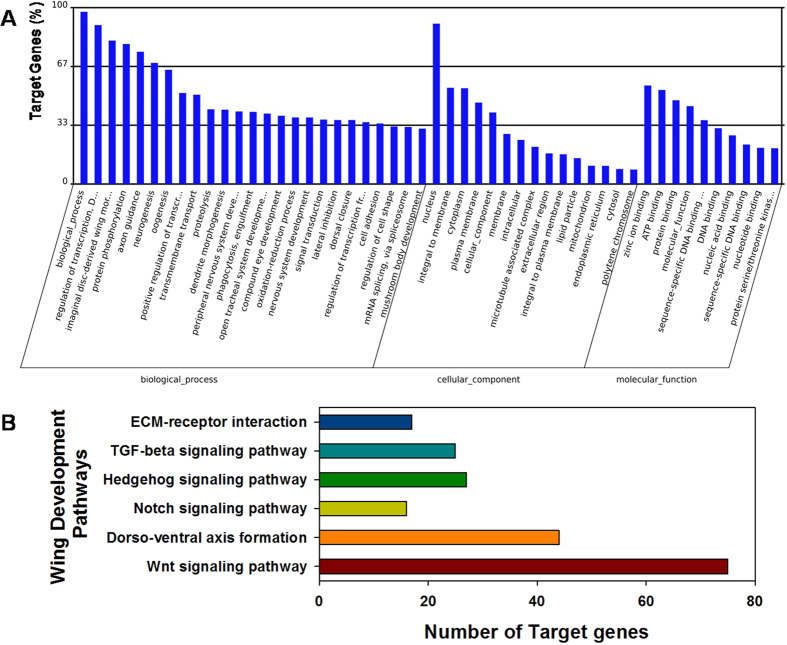
Using the 28 differentially expressed S. avenae miRNA sequences, Target Scan predicted 17,253 putative targets for these miRNAs within the UTRs of transcripts from the model insect D. melanogaster and aphid species A. pisum, M. persicae, T. citricida and A. gosspii (Table S3). This was performed due to the lack of transcript and genome sequence data for S. avenae. Functional annotation of these putative target genes by GO enrichment predicted potential involvement in various biological processes, cellular components and molecular functions, including development processes (Table S4). A total of 50 GO terms were identified for predicted miRNA target genes based on GO level 2 (Fig. 5A), including genes involved in wing development processes (e.g. GO: 0035311: wing cell fate specification with 2 targets; GO: 0007472: wing disc morphogenesis with 18 targets; GO: 0007476: imaginal disc-derived wing morphogenesis with 334 target genes).
Figure 5. Histogram presentation of GO annoation and KEGG pathway for identified miRNAs in S. avenae.
(A) Gene Ontology classification based on level two. The results are summarized in three main categories: biological process, cellular component and molecular function. The y-axis indicates the number of genes and its proportion in a category; (B) number of target genes joining wing development by KEGG analysis.
KEGG enrichment analysis predicted that genes within 124 metabolic pathways may be affected by miRNA targeting (regulation). These pathways include genes in Wnt (n = 75), Notch (n = 16), Hedgehog (n = 27), and TGF-beta signaling pathways (n = 25), and gene products involved in extra cellular matrix (ECM)-receptor interaction (n = 17) and dorso-ventral axis formation (n = 44; Fig. 5B). This transcript target prediction to orthologs from related insects indicated that S. avenae miRNAs which show significant differential expression between winged and wingless morphs may bind and facilitate the post-transcriptional regulation of various biological pathways, including wing development (Table S5).
Discussion
Ever since their initial characterization, research into the cellular roles of miRNAs has led to their description as crucial factors in the regulation of transcript abundance and therefore gene expression. MiRNAs are described among a diverse set of organisms including vertebrates, plants, arthropods and viruses (ftp://mirbase.org/pub/mirbase/CURRENT). Moreover, processes in insect development and metamorphosis are regulated by miRNAs through either degradation of target mRNA or inhibition of translation14,19,20,25. For example, the product of Decapentaplegic (Dpp) is excreted from D. melanogaster embryonic cells and forms a gradient that is required for proper pattern formation during development, and furthermore regulates the expression of other pattern formation genes26. Cell differentiation of the wing is directed by signals from receptors for both Dpp and epidermal growth factor (EGF), which in turn requires a gradient of vein (vn) and wingless (wg) gene products that respectively are directed by EGF and Wnt ligands27. The expression of these diffusible ligands, as well transcription factors that coordinate gene expression are crucial for the direction of wing formation in D. melanogaster28. Analogously, miRNAs have also been implicated in modulating gene expression during wing development29, and includes the roles of miR-730, miR-iab-431, and miR-2a32 (Table 3).
Table 3. miRNAs associated with wing development in insects.
| miRNA | Role or target genes | Insects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-9a | dLMO, senseless, affecting wing tissue and the ectopic apoptosis | Drosophila | 20 |
| miR-12, -283 | Cos-2, fu, smo, affecting Hg signaling pathway | 25 | |
| miR-8 | Dll, se, involving Wnt signaling | 60 | |
| Let-7 | Abrupt, stimulating cell proliferation and preventing apoptosis | 18 | |
| miR-315 | activating wingless signaling | 47 | |
| miR-7 | Regulating Notch signal | 61 | |
| miR-iab-4-5p | Ultrabithorax, Wing/halter sepcification | 31 | |
| miR-iab-8-5p | Ultrabithorax, abdominal A, Wing/halter sepcification | 62 | |
| bantam | Hid, enaled, mei-p26, suppression imaginal discs | 63 | |
| miR-252-5p, miR-982-5p | Dis3, suppressing wing development | 29 | |
| miR-263, -184 | affecting lepidopteron wing scale cell patterning | Butterfly | 21 |
| miR-193, -2788 | predicting their specific functions in butterfly wing | 21 | |
| miR-2768 | Cubitus interruptus, involving wing primordia patterning | 64 | |
| miR-1 | Probably relating muscle development | Locust | 40 |
| miR-125 | Predicting to regulate two phase of locust | 40 | |
| Let-7, miR-100, -125 | Affecting wing morphogenesis | Cockroach | 19 |
In the current study, we obtained 12.0 million reads from sRNA libraries wherein the length distribution of mature miRNAs in two S. avenae morphs showed a bimodal distribution of unique reads, 22 nt and 27–28 nt. The 22nt reads were shown to represent miRNAs as was found previously33, and is consistent with the size common for miRNAs resulting from Dicer digestion as well as analogous for the length distribution observed in D. melanogaster34, A. pisum16and Spodoptera litura35. The shorter sequences may be endo-siRNAs, and the longer may be piRNAs which interact with PIWI proteins and repress the expression of selfish genetic elements such as transposons36. These results show that miRNA genes have length diversity, which depends strongly on the asymmetric structural motifs present in precursor hairpins37.
The miRNA sequence composition at 5′ ends showed a strong preference for U against G at the first position33. Analogously U was the most and C the least frequently observed among miRNA sequences from S. avenae, at both 5′ and 3′ end (accounts for 39.73% and 42.86%, respectively; Fig. 2), which is similarly observed among other organisms16,35. In our analysis, we also predicted that A and U are the most common at positions 2, 3, and 5–8, the latter which corresponds to the “seed sequences” that are known to play a critical role in mature miRNAs targeting of mRNAs for translational inhibition or mRNA cleavage38. This base composition may likely play a role in the binding properties of miRNAs to their target mRNAs33.
In total, we obtained 168 conserved and 177 S. avenae-specific miRNAs in silico using A. pisum genome as a reference for comparison. The frequency of short nucleotide reads generally are highly representative of relative abundance and were used to estimate the expression level of miRNAs39,40. Highly expressed miRNAs would be likely to have a large number of sequenced reads. Some of the miRNAs identified in this study had more than thousand reads, while we found that frequencies of many miRNAs were extremely low in our library (<10 reads), which was consistent with previous conclusions suggesting that these miRNAs might be express at low levels in the specific cell types or in limited physiological processes41. Our data shows that MiR-276 was the most highly expressed miRNA in both morphs, wherein it represented 473,103 reads in the winged adults and 369,649 reads in the wingless adults. To date, miR-276 has been identified in over 34 organisms and may have a critical role in development among various organisms, but the function of this miRNA in insects remains unknown40. The 42 out of 168 conserved miRNAs were highly abundant (>1000 reads), while the number of reads for 2 of the 177 novel miRNAs were more rare (<1000 reads). Differences in miRNA abundance may be related to the different roles that miRNAs may play in insect development, as was suggested in A. pisum where increased expression of a miRNA was proposed to indicate a possible role in the temporal or spatial repression of specific target mRNAs16. The conserved S. avenae miRNAs were placed into 39 miRNA families, with each miRNA family potentially having different regulatory functions37, or influencing the expression of genes involved in different morphs40. Different members in a given miRNA family varied on the estimated number of reads, suggesting that individual miRNA family members could regulate target genes coordinately and shared common functional relationships42. A total of 12 up-regulated and 16 down regulated miRNAs were predicted by the IDEG6 program, indicating that these miRNAs may be involved in diverse functions in the two wing morphs.
Mature insect miRNA sequences are highly conserved among different species. Most of the homologous miRNAs share the same “seed region”, the 5′ region which is important for mRNA target recognition in almost all the insects38. For example, miR-7 and let-7 were high conserved at the 5′ end of the mature sequence in comparison to other insects. Notably, the variation was found at the tail or the middle position, especially for last three nucleotides, which was in line with Wheeler’s observations43.
Deep sequencing, in conjunction with RT-qPCR validation, provides an effective means for the identification of miRNAs, as demonstrated in B. mori33, Locuta migratoria40, and A. pisum16, as well as in the current study. Specifically, Legeai et al.16 reported that 17 miRNAs from A. pisum shows significant differences in their steady-state levels between two morphs, in which Let-7 and miR-100 with similar expression patterns were up-regulated and miR-2a was down-regulated between oviparae and the two other parthenogenetic morphs (virginoparae and sexuparae). This study analogously shows that Let-7 and miR-100 are significantly down-regulated among wingless S. avenae (Table 2, Fig. 4E), suggesting that Let-7 and miR-100 may be import in the differentiation of aphid morphotypes. Other miRNAs have been shown to affect lifespan by post-transcriptional silencing of mRNAs, where loss of Let-7 in mutant Drosophila have a reduced lifespan and show degrees of neurodegeneration44. Additionally, expression of miR-277 shortens Drosophila lifespan and is synthetically lethal with reduced insulin signaling45. This study shows that miR-277 and Let-7 are significantly down-regulated among wingless S. avenae (Table 2, Fig. 4B,E), which may be related to the generally observed increased lifespan of winged compared to wingless S. avenae. This increased lifespan in aphids could potentially be related to time requires involved in long distance migrations. Interestingly, miR-9a was also highly expressed in winged S. avenae which has been reported to control the generation of sensory organs in Drosophila adult wing imaginal discs46, but any potential effect any differences in sensory organ development or function within winged aphids remains unknown. Orthologs of the differentially regulated S. avenae miR-1 and miR-315 were previously associated with flight behaviors. Specifically, miR-1 is a muscle-specific miRNA that in conjunction with miR-315 is differentially regulated in gregarious compared to solitary locusts, and although their functions remain uncertain, Wei et al.40 hypothesized these miRNAs may affect thorax muscle and the wing functions.
Many studies analyze the function of miRNA during insect wing development19,20,21, wherein miR-315 is known to be a potent activator of Wingless signaling in Drosophila47. Evidence indicate that the loss of miR-7 function results in a reduction of wing size and produces smaller wing cells compared to wild types30, and decreases in miR-277-3p levels were associated with the reduced size of mutant imaginal discs48. Moreover, miR-8 influences cell survival and epithelial organization in Drosophila wings49 and the miR-9a prevents apoptosis during Drosophila wing development. Orthologs of D. melanogaster genes involved in wing development are annotated in A. pisum genome50, of which some are differentially regulated between winged and wingless green peach aphids, M. persicae51.
Based on GO enrichment and KEGG analyses, the putative orthologous targets of differentially expressed S. avenae miRNAs may be involved in wing cell fate (2 gene targets), wing disc morphogenesis (18 targets), imaginal disc-derived wing morphogenesis (334 targets), and several additional pathways (Wnt signaling pathway, dorso-ventral axis formation, Notch signaling pathway, Hedgehog signaling pathway, TGF-beta signaling pathway and ECM-receptor interaction; Fig. 5). Since pathway analysis suggests that putative transcript targets of 28 differentially expressed miRNAs may be associated with wing development, it is enticing to hypothesis that these miRNAs could potentially participate in S. avenae wing development. Generating genomic tools, such as development of transcriptome or full genome resources, are required for future investigations of S. avenae miRNA roles in key developmental, cellular or behavioral processes.
Regardless, the predicted differences in the abundance of 28 miRNAs between S.avenae winged and wingless morphs could potentially be involved in the observed wing polyphenism. Caution should be taken with regards to the interpretation of these results from cross-species analysis since we were likely limited to the discovery of targets for conserved miRNAs. Granted, many miRNAs are highly conserved across evolutionary boundaries52, suggesting that the mRNA targets of these highly conserved miRNAs may also be retained across species. In contrast, many taxon-specific miRNAs exist53, including 177 S. avenae specific miRNAs, suggesting that the likelihood of accurate prediction of putative targets for such miRNAs may be diminished as evolutionary distance with model species increase. Undoubtedly, additional future research is required to identify the targets of S. avenae miRNA and unravel their effects on morphotype development. Insulin/insulin-like growth factors, part of an evolutionarily conserved signaling pathway that modulates wing dimorphism in N. lugens22, might be one of these targets. These efforts may also reveal new insight into the interactions between different aphid miRNAs and duplicates of the RISC components dicer and argonaute found amongst the Aphidae, including S. avenae54, where these paralogs of the RISC complex are differentially regulated between wing morphs.
Materials and Methods
Aphid colony maintenance
Sitobion avenae adults were collected from wheat fields in Langfang, Hebei Province, China (39°30′42′′N, 16°36′7′′E) in 2012, and maintained on 15 cm wheat seedlings at 20 °C, 60% RH, and L:D 16:8 h photoperiod in an RXZ-380B environmental cabinet (Nb-Jn Instrument Factory, Ningbo, China). A separate isogenic aphid colony was generated from a single wingless adult female, and the resulting clonal full-sibling S. avenae adults were separated into winged and wingless groups. Individuals were dissected under a stereomicroscope (Nikon SMZ1500, Japan) to remove abdomens to avoid pseudo embryos, and the remaining tissues were immediately transferred into 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes floating on liquid nitrogen. Pooled samples of winged and wingless S. avenae were stored at −80 °C.
RNA isolation, small RNA library construction and Illumina sequencing
Total RNAs were isolated from pooled winged and wingless S. avenae samples using Trizol reagent (Ambion, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The resulting total RNA quantity was estimated on a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (ND-2000, USA), and by densitometry following denaturing agarose gel analysis. RNA integrity was further assessed using the Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent, CA, USA). Total RNA of each sample was size-fractionated on 15% TBE polyacrylaminde gel. Small RNA (sRNA) populations of 15–50 nt were extracted, purified, and ligated to 3′ chimeric oligonucleotide adapters (5′-TGG AAT TCT CGG GTG CCA AGG -3′) and 5′ (5′-GTT CAG AGT TCT ACA GTC CGA CGA TC -3′) using T4 RNA ligase (Illumina, USA). Ligation reaction products were used as template for synthesize of single-stranded cDNA with SuperScript II Reverse Transcriptase (Illumina, USA), and subsequently PCR amplified using Illumina’s primer set for 15 cycles. Amplified cDNA products were gel purified and sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) at LC Sciences (Houston, TX, USA) using the LC Bio service (Hangzhou, China).
Bioinformatics analysis and miRNA prediction
Proprietary software, ACGT101-miR, was used to analyze Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencing data generated from S. avenae winged and wingless small RNA libraries at LC Science (Houston, TX, USA). In brief, raw reads were filtered to remove the adaptor sequences and contaminated reads (including trim 3′ adapter), and then for reads <15 nt and low-quality reads with Phred quality score (Illumina 1.8+) <20. The remaining high quality reads were initially mapped to RepBase (http://www.girinst.org/repbase/) to identify putative transposon-derived miRNAs, then mapped to the ncRNA database (including rRNAs, tRNAs, snRNAs, and snoRNAs) from Rfam (http://rfam.janelia.org) using a BLASTN algorithm, and eventually mapped reads removed before further analysis. The remaining filtered reads were aligned against pre-miRNA and mature miRNA sequences deposited in the miRBase v. 20 (http://www.mirbase.org/ftp.shtml)55 using a Bowtie software56 with a single basepair mismatch allowed. The consensus alignments (pre-miRNA) were used as queries against the genome assembly of A. pisum (http://www.aphidbase.com/aphidbase/downloads) using a BLAST algorithm. Unique sequences that mapped to both insect pre-miRNAs in miRBase and to A. pisum genome were termed ‘conserved’ mature miRNA, whereas pre-miRNAs that mapped to insect entries in miRBase but not to A. pisum genome, or vice versa, were called “semi-conserved”. Lastly, unique sequences un-mapped to insect pre-miRNAs and A. pisum genome were considered as potential novel miRNAs specific for S. avenae. The potential hairpins formed by the flanking sequences of all putative S. avenae miRNA were predicted by secondary structure analysis with Mfold using the default parameters (http://mfold.rna.albany.edu/?q=mfold/RNA-Folding-Form)57. Criteria for miRNA annotation and secondary structure formation are listed in Table S6.
Differential miRNA expression between winged and wingless morphs
Differences in miRNA expression were estimated using the abundance of reads from non-normalized winged and wingless S. avenae libraries as a proxy. The read counts of raw data output from ACGT101-miR were imported into the program IDEG658 using a web portal, http://telethon.bio.unipd.it/bioinfo/IDEG6_form/. In silico normalization of miRNA counts between libraries was carried out based on the total number of reads across libraries. The significance of any difference in read count was assessed by Bonferroni corrected Chi-squared 2 × 2 test with a P-value ≤0.05 and the fold-change ≥1.5.
Nine microRNAs differentially expressed between winged and wingless S. avenae were validated by quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). Total RNA was extracted, respectively, from 50 mg of winged and wingless S. avenae adults as described above. Resultant RNA (1.0 μg) of each sample was reverse transcribed to synthesize the first strand cDNA using miScript II RT Kit (Qiagen, Germany) following manufacturer’s instructions. The miScript II RT Kit procedure attaches a universal primer at the 3′ end of cDNAs, in which a universal primer anneal size in located and used in conjunction with miRNA-specific primers for selective PCR amplification. Primers specific for S. avenae miRNAs were designed using Primer Premier 5.0 software (Premier Biosoft International, Palo Alto, CA, USA; Table 4) and synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). The PCR amplification cycles included an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 5 min, 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s and 72 °C for 30 s, and a final extension step of 10 min at 72 °C. PCR products were analyzed on 2% agarose gels, stained with ethidium bromide, and visualized using the Imaging G6 System (DHS Life Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). All PCR products were cloned and Sanger sequenced to confirm the primer specificity for the respective sRNAs.
Table 4. Primers used for RT-qPCR analysis.
| Name | miRNA name | Primers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-315 | TTTTGATTGTTGCTCAGAAAGCC |
| 2 | miR-1 | GGAATGTAAAGAAGTATGGAG |
| 3 | miR-9a | TCTTTGGTTATCTAGCTGTAT |
| 4 | PC-5p-113190_15 | TTGGATGCCTATGTGG |
| 5 | PC-3p-2743_844 | ACAGCAAAGTGAAAGAGACTGA |
| 6 | miR-7 | TGGAAGACTAGTGATTTTGTTGTT |
| 7 | miR-8 | TAATACTGTCAGGTAATGATGTC |
| 8 | miR-277 | TAAATGCACTATCTGGTACGACA |
| 9 | Let-7 | TGAGGTAGTTGGTTGTATAGT |
| References | U6 | CGCAAGGATGACACGCAA |
Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was conducted using the miScript SYBR® Green PCR Kit (Qiagen, Germany) following manufacturer’s instructions (Table 4). The S.avenae microRNA U6 was used as an endogenous small RNA reference. RT-qPCR was performed on an Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System under the following conditions: 95 °C for 15 min for template denaturation and 40 cycles of 94 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 30 s and 70 °C for 34 s followed by the melting curve. Three biological replicates and three technical replications were carried out. Relative miRNA expression was calculated from cycle threshold (CT) data averaged across technical replicates by the comparative threshold (2−ΔΔCT) method59, and normalized across samples and replicates within samples using the microRNA U6. The significance of any differential expression of each candidate miRNAs between winged and wingless adults were assessed using a two sample t-test in SAS statistical software 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA), with thresholds set at a P < 0.05.
miRNA target prediction
The putative mRNAs targeted by differentially-expressed S. avenae miRNAs were predicted against all S. avenae nucleotide sequences downloaded from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene). Additionally, targets were predicted based on orthologous insect sequences from D. melanogaster (FlyBase; http://flybase.org/), A. pisum (AphidBase; http://www.aphidbase.com), and expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from Myzus persicae, Toxoptera citricida and Aphis gosspii (AphidBase). All fasta-formatted sequence datasets were used to create separate local databases. For the latter EST datasets, open reading frames (ORFs) were predicted using the getorf program in the EMBOSS package. ORFs were extracted using a custom PERL script and then used as quires against the NCBI nr protein database to obtain the potential CDS annotations and UTR regions. All databases were queried with the putative S. avenae miRNAs suing the program Target Scan with the default parameters (http://www.targetscan.org/). All identified putative target genes were used to search the Gene Ontology (GO) database and within Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses, with threshold set at a corrected P-value ≤ 0.001.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Li, X. et al. Comparative profiling of microRNAs in the winged and wingless English grain aphid, Sitobion avenae (F.) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Sci. Rep. 6, 35668; doi: 10.1038/srep35668 (2016).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to anonymous reviewers and editor for their constructive criticisms. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Award number: 31301659), National “Twelfth Five-Year” Plan for Science & Technology Support Development Program of China (Award number: 2012BAD19B04), China Agriculture Research System (Award number: CARS-3). The information reported in this paper (No. 16-08-098) is part of a project of the Kentucky Agricultural Experiment Station and is published with the approval of the Director. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Author Contributions Conceived and designed the experiments X.L. Performed the experiments: X.L. and F.Z. Analyzed the data: X.L., F.Z., B.C. and X.Z. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: X.L., Y.Z. and D.C. Wrote the paper: X.L., F.Z., B.C. and X.Z. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- Kwek K. Y. et al. U1 snRNA associates with TFIIH and regulates transcriptional initiation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 800–805 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. The spliceosome: the most complex macromolecular machine in the cell? BioEssays 25, 1147–1149 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. & Moore P. B. RNA, the first macromolecular catalyst: the ribosome is a ribozyme. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 411–418 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer E. J. Assembly and function of RNA silencing complexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 127–138 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 425, 415–419 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynt A. S., Greimann J. C., Chung W. J., Lima C. D. & Lai E. C. MicroRNA biogenesis via splicing and exosome-mediated trimming in Drosophila. Mol. cell. 38, 900–907 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matranga C., Tomari Y., Shin C., Bartel D. P. & Zamore P. D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 123, 607–620 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark A. et al. Systematic discovery and characterization of fly microRNAs using 12 Drosophila genomes. Genome. Res. 17, 1865–1879 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. Composition of seed sequence is a major determinant of microRNA targeting patterns. Bioinformatics 15, 1377–1383 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He L. & Hannon G. J. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 522–531 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan S., Tong Y. C. & Steitz J. A. Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 318, 1931–1934 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol J., Loedige I. & Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nature Rev. 11, 597–610 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh N. et al. MicroRNA function is globally suppressed in mouse oocytes and early embryos. Curr. Biol. 20, 271–277 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu C. et al. The muscle-specific microRNAs miR-1 and miR-133 produce opposing effects on apoptosis by targeting HSP60, HSP70 and caspase-9 in cardiomyocytes. J. Cell. Sci. 120, 3045–3052 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J. et al. Deep sequencing of chicken microRNAs. BMC genomics 9, 185 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legeai F. et al. Bioinformatic prediction, deep sequencing of microRNAs and expression analysis during phenotypic plasticity in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. BMC Genomics 11, 281 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becam I., Rafel N., Hong X., Cohen S. M. & Milán M. Notch-mediated repression of bantam miRNA contributes to boundary formation in the Drosophila wing. Development 138, 3781–3789 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caygill E. E. & Johnston L. A. Temporal regulation of metamorphic processes in Drosophila by the let-7 and miR-125 heterochronic microRNAs. Curr. Biol. 18, 943–950 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio M. & Belles X. Subtle roles of microRNAs let-7, miR-100 and miR-125 on wing morphogenesis in hemimetabolan metamorphosis. J. Insect Physiol. 59, 1089–1094 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bejarano F., Smibert P. & Lai E. C. miR-9a prevents apoptosis during wing development by repressing Drosophila LIM-only. Dev. Biol. 338, 63–73 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surridge A. K. et al. Characterization and expression of microRNAs in developing wings of the neotropical butterfly Heliconius melpomene. BMC Genomics 12, 62 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. J. et al. Two insulin receptors determine alternative wing morphs in planthoppers. Nature 519, 464–467 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson J. A. Aphid wing dimorphisms: linking environmental and genetic control of trait variation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 365, 605–616 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F. et al. Identification and developmental profiling of conserved and novel microRNAs in Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 42, 381–395 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friggi-Grelin F., Lavenant-Staccini L. & Therond P. Control of antagonistic components of the hedgehog signaling pathway by microRNAs in Drosophila. Genetics. 179, 429–439 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T. & Gibson M. C. Decapentaplegic and growth control in the developing Drosophila wing. Nature 527, 375–378 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baena-López L. A. & García-Bellido A. Genetic requirements of vestigial in the regulation of Drosophila wing development. Development 130, 197–208 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schertel C. et al. A large-scale, in vivo transcription factor screen defines bivalent chromatin as a key property of regulatory factors mediating Drosophila wing development. Genome Res. 25, 514–523 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler B. P. et al. The 3′-5′ exoribonuclease Dis3 regulates the expression of specific microRNAs in Drosophila wing imaginal discs. RNA Biol. 12, 728–741 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio R., Simoes, Da Silva C. J. & Busturia A. MicroRNA miR-7 contributes to the control of Drosophila wing growth. Dev. Dyn. 244, 21–30 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronshaugen M., Biemar F., Piel J., Levine M. & Lai E. C. The Drosophila microRNA iab-4 causes a dominant homeotic transformation of halters to wings. Genes Dev. 19, 2947–2952 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulga T. A. et al. A transgenic resource for conditional competitive inhibition of conserved Drosophila microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 6, 7279 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. et al. Insect-specific microRNA involved in the development of the silkworm Bombyx mori. PLoS One. 4, e4677 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Tomancak P., Williams R. W. & Rubin G. M. Computational identification of Drosophila microRNA genes. Genome Biol. 4, R42 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge X. et al. Identification of MicroRNAs in Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera litura based on deep sequencing and homology analysis. Int. J. Bio. Sci. 9, 1–15 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig J. V., Tomari Y. & Förstemann K. piRNAs-the ancient hunters of genome invaders. Genes Dev. 21, 1707–1713 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starega-Roslan J., Koscianska E., Kozlowski P. & Krzyzosiak W. J. The role of the precursor structure in the biogenesis of microRNA. Cell.Mol.Life. Sci. 68, 2859–2871 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennecke J., Stark A., Russell R. B. & Cohen S. M. Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol. 3, e85 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf P. et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. 129, 1401–1414 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y. et al. Characterization and comparative profiling of the small RNA transcriptomes in two phases of locust. Genome Biol. 10, R6 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. et al. Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis. BMC genomics 10, 407 (2009b). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskerville S. & Bartel D. P. Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 11, 241–247 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler B. M. et al. The deep evolution of metazoan microRNAs. Evo. Dev. 11, 50–68 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawla G., Deosthale P., Childress S., Wu Y. C. & Sokol N. S. A let-7-to-miR-125 microRNA switch regulates neuronal integrity and lifespan in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 12, e1006247 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esslinger S. M. et al. Drosophila miR-277 controls branched-chain amino acid catabolism and affects lifespan. RNA Biol. 10, 1042–1056 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Wang F., Lee J. A. & Gao F. B. MicroRNA-9a ensures the precise specification of sensory organ precursors in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 20, 2793–2805 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S. J., Hagen J. W., Okamura K., Perrimon N. & Lai E. C. Functional screening identifies miR-315 as a potent activator of wingless signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 18151–18156 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. I. et al. The 5′-3′ exoribonuclease Pacman (Xrn1) regulates expression of the heat shock protein Hsp67Bc and the microRNA miR-277-3p in Drosophila wing imaginal discs. RNA Biol. 10, 1345–1355 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin K. et al. miR-8 modulates cytoskeletal regulators to influence cell survival and epithelial organization in Drosophila wings. Dev Biol. 412, 83–98 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson J. A., Ishikawa A. & Miura T. Wing development genes of the pea aphid and differential gene expression between winged and unwinged morphs. Insect Mol. Biol. 19, 63–73 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghanim M. A microarray approach identified ANT, OS-D and takeout-like genes differentially related in alate and apterous morphs of the green peach aphid Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Insect. Biochen. Molecu. Biol. 36, 857–868 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X. M. et al. The silkworm (Bombyx mori) microRNAs and their expressions in multiple developmental stages. PLoS One 3, e2997 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. B. et al. Computational and transcriptional evidence for microRNAs in the honey bee genome. Genome Biol. 8, R97 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Rivas B. et al. Evolutionary study of duplications of the miRNA machinery in aphids associated with striking rate acceleration and changes in expression profiles. BMC Evol. Biol. 12, 1 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozomara A. & Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 68–73 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmead B. & Salzberg S. L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Mathews D. H. & Turner D. H. Algorithms and Thermodynamics for RNA Secondary Structure Prediction: A Practical Guide. RNA Biochem. Biotechnol. 70, 11–43 (1999). [Google Scholar]
- Romualdi C., Bortoluzzi S., D’Alessi F. & Danieli G. A. IDEG6: a web tool for detection of differentially expressed genes in multiple tag sampling experiments. Physiol. Genomics 12, 159–162 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J. & Schmittgen T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402–408 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell J. A., Gerin I., MacDougald O. A. & Cadigan K. M. The microRNA miR-8 is a conserved negative regulator of Wnt signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. 105, 15417–15422 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark A., Brennecke J., Russell R. B. & Cohen S. M. Identification of Drosophila microRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 1, e60 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler D. M. et al. Functionally distinct regulatory RNAs generated by bidirectional transcription and processing of microRNA loci. Genes Dev. 22, 26–36 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipfner D. R., Weigmann K. & Cohen S. M. The bantam gene regulates Drosophila growth. Genetics 161, 1527–1537 (2002). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quah S., Hui J. H. & Holland P. W. A burst of miRNA innovation in the early evolution of butterflies and moths. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32, 1161–1174 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.